
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula R−C(=O)−NR′R″, where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, such as in the amino acids asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a derivative of a carboxylic acid with the hydroxyl group replaced by an amine group ; or, equivalently, an acyl (alkanoyl) group joined to an amine group.
Demethylation is the chemical process resulting in the removal of a methyl group (CH3) from a molecule. A common way of demethylation is the replacement of a methyl group by a hydrogen atom, resulting in a net loss of one carbon and two hydrogen atoms.

A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting an electron pair from a Lewis base to form a Lewis adduct. A Lewis base, then, is any species that has a filled orbital containing an electron pair which is not involved in bonding but may form a dative bond with a Lewis acid to form a Lewis adduct. For example, NH3 is a Lewis base, because it can donate its lone pair of electrons. Trimethylborane () is a Lewis acid as it is capable of accepting a lone pair. In a Lewis adduct, the Lewis acid and base share an electron pair furnished by the Lewis base, forming a dative bond. In the context of a specific chemical reaction between NH3 and Me3B, a lone pair from NH3 will form a dative bond with the empty orbital of Me3B to form an adduct NH3•BMe3. The terminology refers to the contributions of Gilbert N. Lewis.
In organic chemistry, a carbanion is an anion in which carbon is negatively charged.
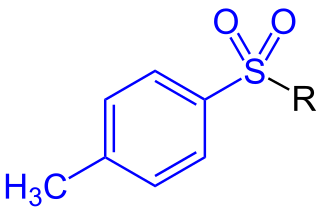
In organic chemistry, a toluenesulfonyl group (tosyl group, abbreviated Ts or Tos) is a univalent functional group with the chemical formula −SO2−C6H4−CH3. It consists of a tolyl group, −C6H4−CH3, joined to a sulfonyl group, −SO2−, with the open valence on sulfur. This group is usually derived from the compound tosyl chloride, CH3C6H4SO2Cl (abbreviated TsCl), which forms esters and amides of toluenesulfonic acid, CH3C6H4SO2OH (abbreviated TsOH). The para orientation illustrated (p-toluenesulfonyl) is most common, and by convention tosyl without a prefix refers to the p-toluenesulfonyl group.

In organic chemistry, an imine is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond. The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bonds. Imines are common in synthetic and naturally occurring compounds and they participate in many reactions.
In chemistry, a superacid (according to the original definition) is an acid with an acidity greater than that of 100% pure sulfuric acid (H2SO4), which has a Hammett acidity function (H0) of −12. According to the modern definition, a superacid is a medium in which the chemical potential of the proton is higher than in pure sulfuric acid. Commercially available superacids include trifluoromethanesulfonic acid (CF3SO3H), also known as triflic acid, and fluorosulfuric acid (HSO3F), both of which are about a thousand times stronger (i.e. have more negative H0 values) than sulfuric acid. Most strong superacids are prepared by the combination of a strong Lewis acid and a strong Brønsted acid. A strong superacid of this kind is fluoroantimonic acid. Another group of superacids, the carborane acid group, contains some of the strongest known acids. Finally, when treated with anhydrous acid, zeolites (microporous aluminosilicate minerals) will contain superacidic sites within their pores. These materials are used on massive scale by the petrochemical industry in the upgrading of hydrocarbons to make fuels.

Trimethylaluminium is one of the simplest examples of an organoaluminium compound. Despite its name it has the formula Al2(CH3)6 (abbreviated as Al2Me6 or TMA), as it exists as a dimer. This colorless liquid is pyrophoric. It is an industrially important compound, closely related to triethylaluminium.
An isocyanide is an organic compound with the functional group –N+≡C−. It is the isomer of the related nitrile (–C≡N), hence the prefix is isocyano. The organic fragment is connected to the isocyanide group through the nitrogen atom, not via the carbon. They are used as building blocks for the synthesis of other compounds.

Meldrum's acid or 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-4,6-dione is an organic compound with formula C6H8O4. Its molecule has a heterocyclic core with four carbon and two oxygen atoms; the formula can also be written as [−O−(C 2)−O−(C=O)−(CH2)−(C=O)−].

Fluorene, or 9H-fluorene is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4)2CH2. It forms white crystals that exhibit a characteristic, aromatic odor similar to that of naphthalene. It has a violet fluorescence, hence its name. For commercial purposes it is obtained from coal tar. It is insoluble in water and soluble in many organic solvents. Although sometimes classified as a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, the five-membered ring has no aromatic properties. Fluorene is mildly acidic.

Fluoroantimonic acid is a mixture of hydrogen fluoride and antimony pentafluoride, containing various cations and anions. This mixture is a superacid that, in terms of corrosiveness, is trillions of times stronger than 100% sulfuric acid in terms of its protonating ability measured by Hammett function. It even protonates some hydrocarbons to afford pentacoordinate carbocations. Like its precursor hydrogen fluoride, it attacks glass, but can be stored in containers lined with PTFE (Teflon) or PFA.

Ammonia borane, also called borazane, is the chemical compound with the formula H3NBH3. The colourless or white solid is the simplest molecular boron-nitrogen-hydride compound. It has attracted attention as a source of hydrogen fuel, but is otherwise primarily of academic interest.
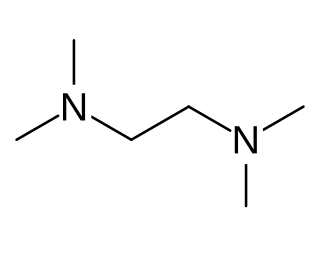
Tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA or TEMED) is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3)2NCH2CH2N(CH3)2. This species is derived from ethylenediamine by replacement of the four amine hydrogens with four methyl groups. It is a colorless liquid, although old samples often appear yellow. Its odor is similar to that of rotting fish.
The reduction of nitro compounds are chemical reactions of wide interest in organic chemistry. The conversion can be effected by many reagents. The nitro group was one of the first functional groups to be reduced. Alkyl and aryl nitro compounds behave differently. Most useful is the reduction of aryl nitro compounds.
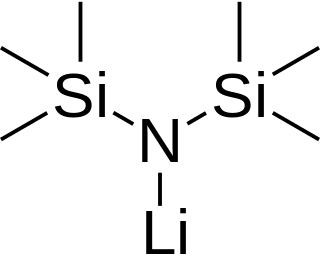
Lithium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide is a lithiated organosilicon compound with the formula LiN(Si(CH3)3)2. It is commonly abbreviated as LiHMDS or Li(HMDS) (lithium hexamethyldisilazide - a reference to its conjugate acid HMDS) and is primarily used as a strong non-nucleophilic base and as a ligand. Like many lithium reagents, it has a tendency to aggregate and will form a cyclic trimer in the absence of coordinating species.

1,2-Dimethyldiborane is an organoboron compound with the formula [(CH3)BH2]2. Structurally, it is related to diborane, but with methyl groups replacing terminal hydrides on each boron. It is the dimer of methylborane, CH3BH2, the simplest alkylborane. 1,2-Dimethyldiborane can exist in a cis- and a trans arrangement. 1,2-Dimethyldiborane is an easily condensed, colorless gas that ignites spontaneously in air.

Organotantalum chemistry is the chemistry of chemical compounds containing a carbon-to-tantalum chemical bond. A wide variety of compound have been reported, initially with cyclopentadienyl and CO ligands. Oxidation states vary from Ta(V) to Ta(-I).
The Riley oxidation is a selenium dioxide-mediated oxidation of methylene groups adjacent to carbonyls. It was first reported by Riley and co-workers in 1932. In the decade that ensued, selenium-mediated oxidation rapidly expanded in use, and in 1939, Guillemonat and co-workers disclosed the selenium dioxide-mediated oxidation of olefins at the allylic position. Today, selenium-dioxide-mediated oxidation of methylene groups to alpha ketones and at the allylic position of olefins is known as the Riley Oxidation.
A Fischer carbene is a type of transition metal carbene complex, which is an organometallic compound containing a divalent organic ligand. In a Fischer carbene, the carbene ligand is a σ-donor π-acceptor ligand. Because π-backdonation from the metal centre is generally weak, the carbene carbon is electrophilic.
















