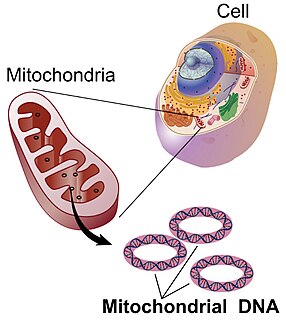
Mitochondrial DNA is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants and algae, also in plastids such as chloroplasts.

Dianchi Lake, also known as Lake Dian and Kunming Lake, is a large lake located on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau close to Kunming, Yunnan, China. Its nickname is the "Sparkling Pearl Embedded in a Highland" and it was the model for the Kunming Lake in the Summer Palace in Beijing. Its name is the source of Yunnan's Chinese abbreviation 滇.

The crocodile icefish or white-blooded fish comprise a family (Channichthyidae) of notothenioid fish found in the Southern Ocean around Antarctica. They are the only known vertebrates to lack hemoglobin in their blood as adults. Icefish populations are known to reside in the Atlantic and Indian sectors of the Southern Ocean, as well as the continental shelf waters surrounding Antarctica. Water temperatures in these regions remain relatively stable, generally ranging from −1.8 to 2 °C. One icefish, Champsocephalus esox, is distributed north of the Antarctic Polar Frontal Zone. At least 16 species of crocodile icefish are currently recognized, although eight additional species have been proposed for the icefish genus Channichthys.
Salangidae, the icefishes or noodlefishes, are a family of small osmeriform fish, related to the smelts. They are found in Eastern Asia, ranging from the Russian Far East in the north to Vietnam in the south, with the highest species richness in China. Some species are widespread and common, but others have relatively small ranges and are threatened. Depending on species, they inhabit coastal marine, brackish or fresh water habitats, and some are anadromous, only visiting fresh water to spawn.
The ariakehimeshirauo, Neosalanx reganius, is a species of icefish in the family Salangidae endemic to Japan. It is only known from Midori and Chikugo Rivers in Kyushu. Its maximum total length is 63 mm (2.5 in), and has a lifespan of about one year. It seems to be relatively rare in its limited habitat, and is classified as an endangered species by IUCN.

Fuxian Lake stretches out through Chengjiang, Jiangchuan and Huaning Counties in Yunnan Province, spanning an area of 212 square kilometers. The lake is ranked third-largest in Yunnan, after Dian Lake and Erhai Lake. Also the deepest lake in Yunnan, it is 155 meters deep at its greatest depth. It is also the third-deepest fresh water lake in China, after Tianchi and Kanas Lake.
Neosalanx tangkahkeii, the Chinese icefish or short-snout icefish, is a species of icefish endemic to fresh and brackish waters in China. Despite its common name it is not the only icefish in China; the majority of the species in this family are found in the country.
The Kanglang fish is a species of cyprinid fish. It is a pelagic species endemic to Fuxian Lake in Yunnan, southern China. However, the species may now be in the process of extinction because of the introduced noodlefish Neosalanx taihuensis, with which it is competing for food.
Schizothorax prenanti, also known as Ya-fish, is a species of ray-finned fish in the genus Schizothorax from the middle and upper parts of the Yangtze basin in China. It is also known as Yayu, as it is native to the city of Ya'an, Sichuan.

Cyprinus rubrofuscus, the Amur carp, is a species of cyprinid fish, and is the wild form of the well-known koi. It is widespread in the fresh waters of eastern Asia, native to China, Vietnam and Laos from the Amur to Red River basins, and has also been introduced outside its native range. It is known for its muddy flavor and boniness, hence, it is not commonly eaten by locals except when stewed.

Solute carrier family 52, member 3, formerly known as chromosome 20 open reading frame 54 and riboflavin transporter 2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC52A3 gene.

Aphia minuta, the transparent goby, is a species of the goby native to the northeastern Atlantic Ocean where it can be found from Trondheim, Norway to Morocco. It is also found in the Mediterranean, Black Sea and the Sea of Azov. It is a pelagic species, inhabiting inshore waters and estuaries. It can be found at depths of from the surface to 97 metres (318 ft), though it is usually found at 5 to 80 metres, over sandy and muddy bottoms and also in eelgrass beds. This species can reach a length of 7.9 centimetres (3.1 in) TL. It is an important species to local commercial fisheries. It is currently the only known member of its genus.
Hemisalanx brachyrostralis is a species of icefish endemic to the Yangtze basin, China. It is the only known species in the genus Hemisalanx, after Hemisalanx prognathus was moved to genus Salanx. In a study of the five freshwater icefish species in the Yangtze, it was a relatively low-density species, being much less frequent than Neosalanx taihuensis and N. oligodontis, but more than Protosalanx hyalocranius and N. tangkahkeii. H. brachyrostralis reaches up to 13.6 cm (5.4 in) in total length.
Protosalanx is a small genus of icefishes that are native to China, Korea and Vietnam where they primarily inhabit coastal waters and nearby fresh waters. They are commercially fished and used for aquaculture in China, where also introduced to some inland waters like Lake Dianchi. In addition to being eaten locally in Asia, they are exported to southern Europe as a replacement of the more expensive transparent goby, a Mediterranean species used in the local cuisine. This replacement is often done openly, but sometimes it is done fraudulently.

The blackfin icefish, also known as the Scotia Sea icefish, is a species of crocodile icefish belonging to the family Channichthyidae. The blackfin icefish belongs to Notothenioidei, a suborder of fishes that accounts for 90% of the fish fauna on the Antarctic continental shelf. Icefishes, also called white-blooded fishes, are a unique family in that they are the only known vertebrates to lack haemoglobin, making their blood oxygen carrying capacity just 10% that of other teleosts. Icefishes have translucent blood and creamy white gills.

Channichthys is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. They are native to the Southern Ocean.

Chionodraco is a genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. They are found in the Southern Ocean.

Jonah's icefish is a benthopelagic species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. It is the only member of the monotypic genus Neopagetopsis. It is found in the Southern Ocean at depths of from 20 to 900 metres. It has a circum-Antarctic distribution on the continental slope and continental shelf, with the northernmost records from the South Shetland and the South Orkney Islands.

Cipangopaludina cathayensis is a species of large, freshwater snail with an operculum and a gill, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Viviparidae, the river snails.
Cryodraco antarcticus, the long-fingered icefish, is a demersal species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Channichthyidae, the crocodile icefishes. It occurs only in deep waters of the Southern Ocean.











