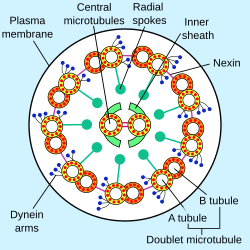
Nexin is a proteinous inter-doublet linkage that prevents microtubules in the outer layer of axonemes from moving with respect to one another; otherwise, vesicular transport proteins such as dynein would dissolve the whole structure. [1]

Nexin is a proteinous inter-doublet linkage that prevents microtubules in the outer layer of axonemes from moving with respect to one another; otherwise, vesicular transport proteins such as dynein would dissolve the whole structure. [1]