Related Research Articles

The Australian Democrats is a centrist political party in Australia. Founded in 1977 from a merger of the Australia Party and the New Liberal Movement, both of which were descended from Liberal Party dissenting splinter groups, it was Australia's largest minor party from its formation in 1977 through to 2004 and frequently held the balance of power in the Senate during that time.

The House of Representatives is the lower house of the bicameral Parliament of Australia, the upper house being the Senate. Its composition and powers are set down in Chapter I of the Constitution of Australia.

Pauline Lee Hanson is an Australian politician who is the founder and leader of One Nation, a right-wing populist political party. Hanson has represented Queensland in the Australian Senate since the 2016 Federal Election.

Pauline Hanson's One Nation, also known as One Nation or One Nation Party, is a right-wing populist political party in Australia. It is led by Pauline Hanson.
David Ernest Oldfield is an Australian former politician who co-founded and was national director of the Pauline Hanson's One Nation party.
The electoral system of Australia comprises the laws and processes used for the election of members of the Australian Parliament and is governed primarily by the Commonwealth Electoral Act 1918. The system presently has a number of distinctive features including compulsory enrolment; compulsory voting; majority-preferential instant-runoff voting in single-member seats to elect the lower house, the House of Representatives; and the use of the single transferable vote proportional representation system to elect the upper house, the Senate.
Electoral systems of the Australian states and territories are broadly similar to the electoral system used in federal elections in Australia.
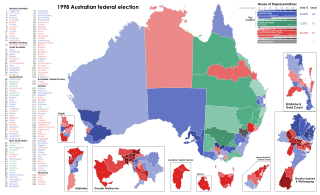
The 1998 Australian federal election was held to determine the members of the 39th Parliament of Australia. It was held on 3 October 1998. All 148 seats of the House of Representatives and 40 seats of the 76-seat Senate were up for election. The incumbent centre-right Liberal/National Coalition government led by Prime Minister John Howard of the Liberal Party and coalition partner Tim Fischer of the National Party defeated the centre-left Australian Labor Party opposition led by Opposition Leader Kim Beazley, despite losing the nationwide popular and two-party preferred vote. However, the Australian Labor Party gained seats from the previous election.

The 2004 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 9 October 2004. All 150 seats in the House of Representatives and 40 seats in the 76-member Senate were up for election. The incumbent Liberal Party of Australia led by Prime Minister of Australia John Howard and coalition partner the National Party of Australia led by John Anderson defeated the opposition Australian Labor Party led by Mark Latham.

The Family First Party was a conservative political party in Australia which existed from 2002 to 2017. It was founded in South Australia where it enjoyed its greatest electoral support. Since the demise of the Australian Conservatives into which it merged, it has been refounded in that state as the Family First Party (2021), where it contested the state election in 2022, but failed to win a seat.

The Libertarian Party, formerly known as the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP), is an Australian political party founded in Canberra in 2001. The party espouses smaller government and supports policies that are based on classical liberal, libertarian principles, such as lower taxes, opposing restrictions on civil liberties, decentralisation, uranium mining, and the relaxation of smoking laws.

The 1987 Australian federal election was held in Australia on 11 July 1987, following the granting of a double dissolution on 5 June by the Governor-General Sir Ninian Stephen. Consequently, all 148 seats in the House of Representatives as well as all 76 seats in the Senate were up for election. The incumbent Australian Labor Party, led by Prime Minister Bob Hawke, defeated the opposition Liberal Party of Australia, led by John Howard and the National Party of Australia led by Ian Sinclair. This was the first, and to date only, time the Labor Party won a third consecutive election.

The Commonwealth Electoral Act 1918 is an Act of the Australian Parliament which continues to be the core legislation governing the conduct of elections in Australia, having been amended on numerous occasions since 1918. The Act was introduced by the Nationalist Party of Billy Hughes, the main purpose of which was to replace first-past-the-post voting with instant-runoff voting for the House of Representatives and the Senate. The Labor Party opposed the introduction of preferential voting. The Act has been amended on several occasions since.

The Non-Custodial Parents Party was a minor political party in Australia registered between 1999 and 2020. It supported less government control of many aspects of daily family life, focusing on reform of family law and child support.

The Rise Up Australia Party (RUAP) was a far-right political party in Australia. The party's policy platform was focused on nationalist and Christian conservative issues, such as opposing Islamic immigration and religious freedom for Australian Muslims and opposition to same-sex marriage in Australia. The party was launched in 2011 and was led by Pentecostal minister Danny Nalliah until its dissolution in June 2019. Its slogan was "Keep Australia Australian". Nalliah is the president of Catch the Fire Ministries.

The United Australia Party (UAP), formerly known as Clive Palmer's United Australia Party and the Palmer United Party (PUP), is an Australian political party formed by mining magnate Clive Palmer in April 2013. The party was deregistered by the Australian Electoral Commission in 2017, revived and re-registered in 2018, and voluntarily deregistered in 2022. The party fielded candidates in all 150 House of Representatives seats at the 2013 federal election. Palmer, the party's leader, was elected to the Division of Fairfax and it reached a peak of three senators following the rerun of the Western Australian senate election in 2014. When the party was revived under its original name in 2018, it was represented by ex-One Nation senator Brian Burston in the federal parliament.
The history of the Australian Labor Party has its origins in the Labour parties founded in the 1890s in the Australian colonies prior to federation. Labor tradition ascribes the founding of Queensland Labour to a meeting of striking pastoral workers under a ghost gum tree in Barcaldine, Queensland in 1891. The Balmain, New South Wales branch of the party claims to be the oldest in Australia. Labour as a parliamentary party dates from 1891 in New South Wales and South Australia, 1893 in Queensland, and later in the other colonies.

The Arts Party is an Australian political party inspired by the importance of the arts and creative action. The party was voluntarily deregistered with the Australian Electoral Commission on 25 June 2019, but remains registered for local elections with the New South Wales Electoral Commission.

The Western Australia Party (WAP) was a regional political party active in Western Australia.
The Australian Sex Party was an Australian political party founded in 2009 in response to concerns over the purported increasing influence of religion in Australian politics. The party was born out of an adult-industry lobby group, the Eros Association. Its leader, Fiona Patten, was formerly the association's CEO.
References
- 1 2 "No Goods and Services Tax Party". Deregistered political parties. Australian Electoral Commission. 5 January 2011. Retrieved 15 June 2022.
- ↑ Simms, Marian; Warhurst, John (2000). Howard's Agenda: The 1998 Australian Election. Univ. of Queensland Press. ISBN 978-0-7022-3163-6.
- ↑ Green, Antony. "Stephen asks why there are fewer 'oddball' candidates in recent elections". Australia Votes 2004. Retrieved 14 June 2022.
- ↑ "Double dissolution is an empty threat". The Age . 25 June 2002. Retrieved 15 June 2022.
- ↑ "Deregistration of Political Parties". Australian Electoral Commission. 22 December 2006. Archived from the original on 9 June 2007.
- ↑ Electoral and Referendum Amendment (Electoral Integrity and Other Measures) Act 2006 (Cth)