
Tutchone is an Athabaskan language spoken by the Northern and Southern Tutchone First Nations in central and southern regions of Yukon Territory, Canada. Tutchone belongs to the Northern Athabaskan linguistic subfamily and has two primary varieties, Southern and Northern. Although they are sometimes considered separate languages, Northern and Southern Tutchone speakers are generally able to understand each other in conversation, albeit with moderate difficulty.

Athabaskan is a large family of Indigenous languages of North America, located in western North America in three areal language groups: Northern, Pacific Coast and Southern. Kari and Potter (2010:10) place the total territory of the 53 Athabaskan languages at 4,022,000 square kilometres (1,553,000 sq mi).

The Tagish or Tagish Khwáan are a First Nations people of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group that lived around Tagish Lake and Marsh Lake, in Yukon of Canada. The Tagish intermarried heavily with Tlingit from the coast and the Tagish language became extinct in 2008. Today Tagish people live mainly in Carcross or Whitehorse and are members of the Carcross/Tagish First Nation or the Kwanlin Dün First Nation.

The Kwanlin Dün First Nation (KDFN) or Kwänlin Dän kwächʼǟn is located in and around Whitehorse in Yukon, Canada.
The First Nation of Na-Cho Nyäk Dun is a First Nation band government in Yukon, Canada. Its main population centre is in Mayo, Yukon, but many of its members live across Canada and the United States. Members of the First Nation of Na-Cho Nyak Dun claim Gwich'in ancestry, located in north, and Dene ancestry, located in the east, along with their Northern Tutchone ancestry. The Na-cho Nyak Dun are the northernmost representatives of the Northern Tutchone language and culture.
The Little Salmon/Carmacks First Nation is a First Nation in the central Yukon Territory in Canada. Its original population centre was Little Salmon, Yukon, but most of its citizens live in Carmacks, Yukon. The language originally spoken by the Little Salmon/Carmacks First Nation people was Northern Tutchone. They call themselves Tagé Cho Hudän.

The Selkirk First Nation (Hucha Hudan people) is a First Nation self-government in the Canadian territory, Yukon. Its original population centre was the trading post of Fort Selkirk, Yukon along the Yukon River, but most of its citizens now live in Pelly Crossing, Yukon where the Klondike Highway crosses the Pelly River. The language originally spoken by the Selkirk people was Northern Tutchone. There is a great effort to preserve the language and culture, as can be seen by the popularity of the Selkirk "Keeper of the Songs", Jerry Alfred.
The Vuntut Gwitchin First Nation (VGFN) is a First Nation in the northern Yukon in Canada. Its main population centre is Old Crow. The language originally spoken by the people is Gwichʼin.
The White River First Nation (WRFN) is a First Nation of Upper Tanana, Northern Tutchone, and Southern Tutchone peoples in the western Yukon Territory in Canada. Its main population centre is Beaver Creek, Yukon.
The Yukon Land Claims refer to the process of negotiating and settling Indigenous land claim agreements in Yukon, Canada between First Nations and the federal government. Based on historic occupancy and use, the First Nations claim basic rights to all the lands.

The Southern Tutchone are a First Nations people of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group living mainly in the southern Yukon in Canada. The Southern Tutchone language, traditionally spoken by the Southern Tutchone people, is a variety of the Tutchone language, part of the Athabaskan language family. Some linguists suggest that Northern and Southern Tutchone are distinct and separate languages.

Mayo is a village in Yukon, Canada, along the Silver Trail and the Stewart River. It had a population of 200 in 2016. The Yukon Bureau of Statistics estimated a population of 496 in 2019. It is also the home of the First Nation of Na-Cho Nyak Dun, whose primary speak the northern variety of the Tutchone language. Na-Cho Nyäk Dun translates into "big river people."
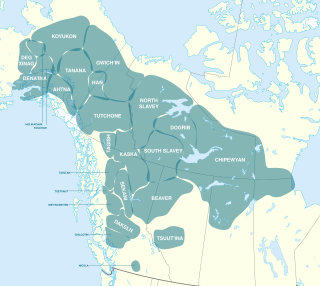
Northern Athabaskan is a geographic sub-grouping of the Athabaskan language family spoken by indigenous peoples in the northern part of North America, particularly in Alaska, Yukon, and the Northwest Territories. The Northern Athabaskan languages consist of 31 languages that can be divided into seven geographic subgroups.

Fort Selkirk is a former trading post on the Yukon River at the confluence of the Pelly River in Canada's Yukon. For many years it was home to the Selkirk First Nation.

The Hän, Han or Hwëch'in / Han Hwech’in are a First Nations people of Canada and an Alaska Native Athabaskan people of the United States; they are part of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group. Their traditional lands centered on a heavily forested area around the Upper Yukon River, Klondike River (Tr'on'Dëk), Bonanza Creek and Sixtymile River and straddling what is now the Alaska-Yukon Territory border. In later times, the Han population became centered in Dawson City, Yukon and Eagle, Alaska.

The history of the Yukon covers the period from the arrival of Paleo-Indians through the Beringia land bridge approximately 20,000 years ago. In the 18th century, Russian explorers began to trade with the First Nations people along the Alaskan coast, and later established trade networks extending into Yukon. By the 19th century, traders from the Hudson's Bay Company were also active in the region. The region was administered as a part of the North-Western Territory until 1870, when the United Kingdom transferred the territory to Canada and it became the North-West Territories.

Mayo-Tatchun is an electoral district which returns an MLA to the Legislative Assembly of the Yukon Territory in Canada. It is an amalgamation of the former Mayo and Tatchun electoral districts.

Louise Profeit-LeBlanc is an Aboriginal storyteller, cultural educator artist, writer, choreographer, and film script writer from the Northern Tutchone Nation, Athabaskan language spoken in northeastern Yukon in Canada. She was raised in Mayo.

The Indigenous peoples of Yukon are ethnic groups who, prior to European contact, occupied the former countries now collectively known as Yukon. While most First Nations in the Canadian territory are a part of the wider Dene Nation, there are Tlingit and Métis nations that blend into the wider spectrum of indigeneity across Canada. Traditionally hunter-gatherers, indigenous peoples and their associated nations retain close connections to the land, the rivers and the seasons of their respective countries or homelands. Their histories are recorded and passed down the generations through oral traditions. European contact and invasion brought many changes to the native cultures of Yukon including land loss and non-traditional governance and education. However, indigenous people in Yukon continue to foster their connections with the land in seasonal wage labour such as fishing and trapping. Today, indigenous groups aim to maintain and develop indigenous languages, traditional or culturally-appropriate forms of education, cultures, spiritualities and indigenous rights.
Tatchun was an electoral district which returned an MLA to the Legislative Assembly of the Yukon Territory in Canada. It was created in 1978 out of the ridings of Klondike and Pelly River. It was abolished in 1992 when it was amalgamated with the riding of Mayo to form the riding of Mayo-Tatchun.













