
Nymphaea is a genus of hardy and tender aquatic plants in the family Nymphaeaceae. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution. Many species are cultivated as ornamental plants, and many cultivars have been bred. Some taxa occur as introduced species where they are not native, and some are weeds. Plants of the genus are known commonly as water lilies, or waterlilies in the United Kingdom. The genus name is from the Greek νυμφαία, nymphaia and the Latin nymphaea, which means "water lily" and were inspired by the nymphs of Greek and Latin mythology.

Nymphaea glandulifera is a species of waterlily native to tropical America.

Nymphaea prolifera is a species of waterlily naturally found from Mexico to Brazil and northeastern Argentina. Additionally, it has been reported to occur in Uruguay.

Nymphaea gardneriana is a species of waterlily native to Cuba and tropical South America.

Nymphaea potamophila is a species of waterlily native to the region spanning from Venezuela to northern Brazil. Additionally, it has been reported to occur in Colombia.
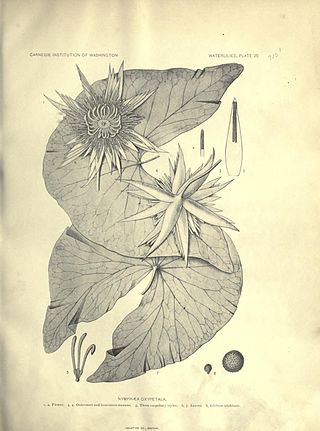
Nymphaea oxypetala is a species of waterlily native to Bolivia, Brazil, Cuba, Ecuador, Paraguay, and Venezuela. It is a remarkable species with excessively acuminate and acute sepals and petals.

Nymphaea rudgeana is a species of waterlily native to the region spanning from Mexico to tropical South America.
Nymphaea tenuinervia is a species of waterlily native to Colombia, Guyana and Brazil.

Nymphaea jamesoniana is a species of waterlily native to the USA, Mexico, and tropical South America.
Nymphaea belophylla is a species of waterlily native to Bolivia, Brazil and Venezuela.

Nymphaea amazonum is a species of water lily native to the region spanning from Mexico to tropical South America. It has been introduced to Bangladesh.

Nymphaea caatingae is a species of waterlily endemic to Northeast Brazil.

Nymphaea lasiophylla is a species of waterlily native to East Brazil. It has also been introduced to the Venezuelan Antilles.
Nymphaea pedersenii is a species of waterlily native to Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, and Uruguay.
Nymphaea lingulata is a species of waterlily native to Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay.
Nymphaea novogranatensis is a species of waterlily native to Colombia, Mexico, and Venezuela.

Nymphaea gracilis is a species of waterlily endemic to Mexico. It is the only species of its genus which is endemic to Mexico.

Nymphaea loriana is a species of waterlily endemic to Manitoba, and Saskatchewan, Canada.

Nymphaea rubra is a species of waterlily native to the region spanning from Sri Lanka and northeastern India to western and central Malesia. Additionally, it has been introduced to regions such as Southeast China, Cuba, Guyana, Hungary, and Suriname.

Nymphaea subg. Hydrocallis is a subgenus of the genus Nymphaea.













