
Selenocysteine is the 21st proteinogenic amino acid. Selenoproteins contain selenocysteine residues. Selenocysteine is an analogue of the more common cysteine with selenium in place of the sulfur.

Pyrrolysine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins in some methanogenic archaea and bacteria; it is not present in humans. It contains an α-amino group, a carboxylic acid group. Its pyrroline side-chain is similar to that of lysine in being basic and positively charged at neutral pH.

Proteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are incorporated biosynthetically into proteins during translation. The word "proteinogenic" means "protein creating". Throughout known life, there are 22 genetically encoded (proteinogenic) amino acids, 20 in the standard genetic code and an additional 2 that can be incorporated by special translation mechanisms.

A transferase is any one of a class of enzymes that catalyse the transfer of specific functional groups from one molecule to another. They are involved in hundreds of different biochemical pathways throughout biology, and are integral to some of life's most important processes.
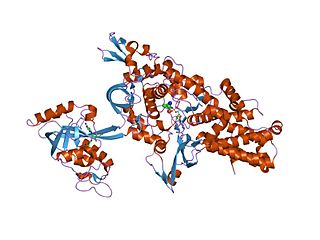
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its precursor to one of all its compatible cognate tRNAs to form an aminoacyl-tRNA. In humans, the 20 different types of aa-tRNA are made by the 20 different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid of the genetic code.

In enzymology, a L-seryl-tRNASec selenium transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an asparaginyl-tRNA synthase (glutamine-hydrolysing) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glutaminyl-tRNA synthase (glutamine-hydrolysing) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
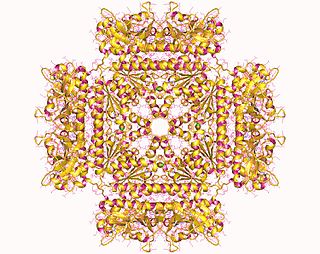
In molecular biology, the protein domain SAICAR synthase is an enzyme which catalyses a reaction to create SAICAR. In enzymology, this enzyme is also known as phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthase. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a selenide, water dikinase (EC 2.7.9.3) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Selenide, water dikinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SEPHS1 gene.

SARS and cytoplasmic seryl-tRNA synthetase are a human gene and its encoded enzyme product, respectively. SARS belongs to the class II amino-acyl tRNA family and is found in all humans; its encoded enzyme, seryl-tRNA synthetase, is involved in protein translation and is related to several bacterial and yeast counterparts.

O-phosphoseryl-tRNA(Sec) selenium transferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SEPSECS gene.

Seryl-tRNA synthetase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SARS2 gene.

Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 3 (GPAT-3) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AGPAT9 gene. GPAT-3 is also known as:
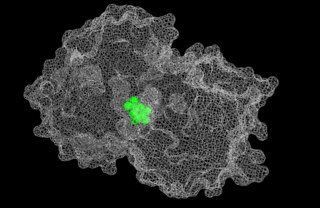
5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase is an enzyme produced by plants and microorganisms. EPSPS catalyzes the chemical reaction:
Radical SAM is a designation for a superfamily of enzymes that use a [4Fe-4S]+ cluster to reductively cleave S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) to generate a radical, usually a 5′-deoxyadenosyl radical (5'-dAdo), as a critical intermediate. These enzymes utilize this radical intermediate to perform diverse transformations, often to functionalize unactivated C-H bonds. Radical SAM enzymes are involved in cofactor biosynthesis, enzyme activation, peptide modification, post-transcriptional and post-translational modifications, metalloprotein cluster formation, tRNA modification, lipid metabolism, biosynthesis of antibiotics and natural products etc. The vast majority of known radical SAM enzymes belong to the radical SAM superfamily, and have a cysteine-rich motif that matches or resembles CxxxCxxC. rSAMs comprise the largest superfamily of metal-containing enzymes.
O-phospho-L-seryl-tRNA:Cys-tRNA synthase is an enzyme with systematic name O-phospho-L-seryl-tRNACys:hydrogen sulfide 2-aminopropanoate transferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
O-phosphoseryl-tRNASec kinase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:L-seryl-tRNASec O-phosphotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
O-phospho-L-serine—tRNA ligase is an enzyme with systematic name O-phospho-L-serine:tRNACys ligase (AMP-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:












