
The sea lettuces comprise the genus Ulva, a group of edible green algae that is widely distributed along the coasts of the world's oceans. The type species within the genus Ulva is Ulva lactuca, lactuca being Latin for "lettuce". The genus also includes the species previously classified under the genus Enteromorpha, the former members of which are known under the common name green nori.

Palmaria palmata, also called dulse, dillisk or dilsk, red dulse, sea lettuce flakes, or creathnach, is a red alga (Rhodophyta) previously referred to as Rhodymenia palmata. It grows on the northern coasts of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. It is a well-known snack food. In Iceland, where it is known as söl[ˈsœːl̥], it has been an important source of dietary fiber throughout the centuries.

Alaria esculenta is an edible seaweed, also known as dabberlocks or badderlocks, or winged kelp. It is a traditional food along the coasts of the far north Atlantic Ocean. It may be eaten fresh or cooked in Greenland, Iceland, Scotland and Ireland. It is the only one of twelve species of Alaria to occur in both Ireland and in Great Britain.

Pelvetia canaliculata, the channelled wrack, is a very common brown alga (Phaeophyceae) found on the rocks of the upper shores of Europe. It is the only species remaining in the monotypic genus Pelvetia. In 1999, the other members of this genus were reclassified as Silvetia due to differences of oogonium structure and of nucleic acid sequences of the rDNA.
The history of phycology is the history of the scientific study of algae. Human interest in plants as food goes back into the origins of the species, and knowledge of algae can be traced back more than two thousand years. However, only in the last three hundred years has that knowledge evolved into a rapidly developing science.
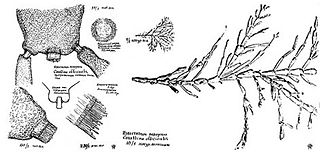
Corallina officinalis is a calcareous red seaweed which grows in the lower and mid-littoral zones on rocky shores.

Morum oniscus is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Harpidae, the harp snails.
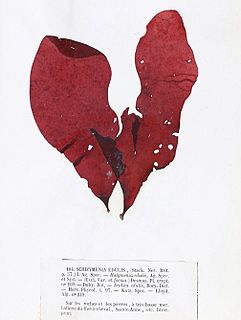
Dilsea carnosa, commonly known as the poor man's weather glass or the sea belt, is a species of red algae in the Dumontiaceae family of the order Gigartinales.

Chorda filum, commonly known as dead man's rope or sea lace among other names, is a species of brown algae in the genus Chorda. It is widespread in the temperate waters of the northern hemisphere. The species also has numerous other common names related to its physical appearance. Names include mermaid's tresses, cat's gut or sea-catgut, bootlace weed, sea-twine, and mermaid's fishing line.
Polysiphonia denudata is a small red alga, Rhodophyta, growing as tufts up to 20 cm long without a main branch axis.

Polysiphonia stricta is a small red marine alga in the Division Rhodophyta.
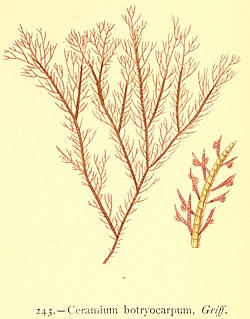
Ceramium botryocarpum is a small red marine alga in the Division Rhodophyta.
Ceramium pallidum is a small marine alga. It occurs in waters off of Europe and Africa (Morocco).

Ceramium virgatum, or the red hornweed, is a small red marine alga.

Halidrys siliquosa is a large marine brown algae.
Hypoglossum hypoglossoides, known as under tongue weed, is a small red marine alga in the family Delesseriaceae.

Phycodrys rubens is a red marine alga of up to 30 cm long.

Phyllophora crispa is a medium-sized fleshy, marine red alga. This alga forms dense mats of up to 15 cm thickness, which influence environmental factors, thus creating habitat for several associated organisms.
Phyllophora sicula, the hand leaf bearer, is a small red marine alga.

Gymnogongrus griffithsiae is a small uncommon seaweed.
















