The Lower Paleolithic era on the Korean Peninsula and in Manchuria began roughly half a million years ago. The earliest known Korean pottery dates to around 8000 BC and the Neolithic period began thereafter, followed by the Bronze Age by 2000 BC, and the Iron Age around 700 BC. The Paleolithic people are likely not the direct ancestors of the present Korean people, but their direct ancestors are thought to be the Neolithic People of about 2000 BC.

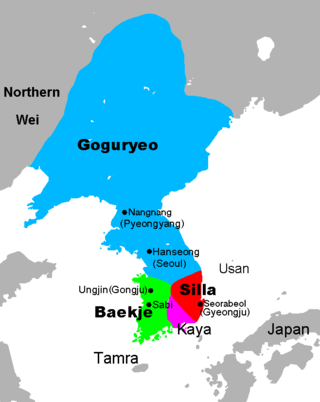
Goguryeo also later known as Goryeo, was a Korean kingdom which was located on the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of modern-day Northeast China (Manchuria). At its peak of power, Goguryeo encompassed most of the Korean Peninsula and large parts of Manchuria, along with parts of eastern Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and modern-day Russia.
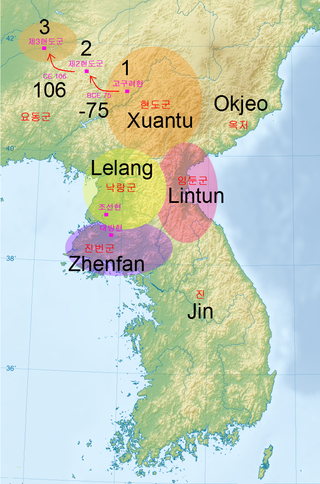
The Lelang Commandery was a commandery of the Han dynasty established after it had conquered Wiman Joseon in 108 BC and lasted until Goguryeo conquered it in 313. The Lelang Commandery extended the rule of the Four Commanderies of Han as far south as the Han River in present-day South Korea. South Korean scholars have described its administrative areas as being limited to the Pyongan and Hwanghae regions, whose southern bounds lie roughly 75 miles north of the Han River.

Baekje or Paekche was a Korean kingdom located in southwestern Korea from 18 BCE to 660 CE. It was one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea, together with Goguryeo and Silla. While the three kingdoms were in separate existence, Baekje had the highest population of approximately 3,800,000 people, which was much larger than that of Silla and similar to that of Goguryeo.

The Three Kingdoms of Korea or Samhan competed for hegemony over the Korean Peninsula during the ancient period of Korean history. During the Three Kingdoms period (Korean: 삼국시대), many states and statelets consolidated until, after Buyeo was annexed in 494 and Gaya was annexed in 562, only three remained on the Korean Peninsula: Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla. The "Korean Three Kingdoms" contributed to what would become Korea; and the Goguryeo, Baekje and Silla peoples became the Korean people.

Gojoseon, contemporary name Joseon, was the first kingdom on the Korean Peninsula. According to Korean mythology, the kingdom was established by the legendary king Dangun. Gojoseon possessed the most advanced culture in the Korean Peninsula at the time and was an important marker in the progression towards the more centralized states of later periods. The addition of Go, meaning "ancient", is used in historiography to distinguish the kingdom from the Joseon dynasty, founded in 1392 CE.

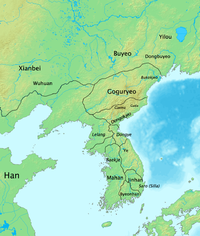
Buyeo, also rendered as Puyŏ or Fuyu, was an ancient kingdom that was centered in northern Manchuria in modern-day northeast China. It had ties to the Yemaek people, who are considered to be the ancestors of modern Koreans. Buyeo is considered a major predecessor of the Korean kingdoms of Goguryeo and Baekje.
The Goguryeo language, or Koguryoan, was the language of the ancient kingdom of Goguryeo, one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea. Early Chinese histories state that the language was similar to those of Buyeo, Okjeo and Ye. Lee Ki-Moon grouped these four as the Puyŏ languages. The histories also stated that these languages were different from those of the Yilou and Mohe. All of these languages are unattested except for Goguryeo, for which evidence is limited and controversial.

Ye or Dongye, which means the Eastern Ye, was a Korean chiefdom which occupied portions of the northeastern Korean peninsula from roughly 3rd-century BC to around early 5th-century AD. It bordered Goguryeo and Okjeo to the north, Jinhan to the south, and China's Lelang Commandery to the west. Today, this territory consists of the provinces of South Hamgyŏng and Kangwon in North Korea, and Gangwon in South Korea.

Samhan, or Three Han, is the collective name of the Byeonhan, Jinhan, and Mahan confederacies that emerged in the first century BC during the Proto–Three Kingdoms of Korea, or Samhan, period. Located in the central and southern regions of the Korean Peninsula, the Samhan confederacies eventually merged and developed into the Baekje, Gaya, and Silla kingdoms. The name "Samhan" also refers to the Three Kingdoms of Korea.
Chumo, posthumously Chumo the Saint, was the founding monarch of the kingdom of Goguryeo, and was worshipped as a god-king by the people of Goguryeo and Goryeo. Chumo, originally Buyeo slang for an excellent archer, later became his name. He was commonly recorded as Jumong by various Chinese sources, including history books written by Northern Qi and Tang. This name became dominant in future writings including the Samguk sagi and the Samguk yusa. Chumo's title was changed to Dongmyeong the Saint, literally translating to the Brilliant Saintly King of the East, at some point in time prior to the compilation of the Samguk sagi (1145). His other names include Chumong, Jungmo, Nakamu, or Tomo. In the Samguk sagi, he was recorded as Jumong with the surname Go, and was also known as Junghae or Sanghae.

The Proto–Three Kingdoms period refers to the proto-historical period in the Korean Peninsula, after the fall of Gojoseon and before the maturation of Goguryeo, Baekje, and Silla into full-fledged kingdoms. It is a subdivision of what is traditionally called Korea's Three Kingdoms period and covers the first three centuries of the Common Era, corresponding to the later phase of the Korean Iron Age.

The Dongyi or Eastern Yi was a collective term for ancient peoples found in Chinese records. The definition of Dongyi varied across the ages, but in most cases referred to inhabitants of eastern China, then later, the Korean peninsula and Japanese Archipelago. Dongyi refers to different group of people in different periods. As such, the name "Yí" 夷 was something of a catch-all and was applied to different groups over time. According to the earliest Chinese record, the Zuo Zhuan, the Shang dynasty was attacked by King Wu of Zhou while attacking the Dongyi and collapsed afterward.

Jumong is an epic South Korean historical series that aired on MBC from 2006 to 2007 as the network's 45th anniversary special. Originally scheduled for 60 episodes, MBC extended it to 81 because of its popularity.

The Four Commanderies of Han were Chinese commanderies located in the north of the Korean Peninsula and part of the Liaodong Peninsula from around the end of the second century BC through the early 4th AD, for the longest lasting. The commanderies were set up to control the populace in the former Gojoseon area as far south as the Han River, with a core area at Lelang near present-day Pyongyang by Emperor Wu of the Han dynasty in early 2nd century BC after his conquest of Wiman Joseon. As such, these commanderies are seen as Chinese colonies by some scholars. Though disputed by North Korean scholars, Western sources generally describe the Lelang Commandery as existing within the Korean peninsula, and extend the rule of the four commanderies as far south as the Han River. However, South Korean scholars assumed its administrative areas to Pyongan and Hwanghae provinces.
The Goguryeo–Wei War was a series of invasions of Goguryeo from 244 to 245 launched by Cao Wei.

Xuantu Commandery was a commandery of the Chinese Han dynasty. It was one of Four Commanderies of Han, established in 107 BCE in the northern Korean Peninsula and part of the Liaodong Peninsula, after the Han dynasty conquered Wiman Joseon. Xuantu moved its capital to Liaodong in 75 BC due to native resistance and the area formerly under the Lintun Commandery was transferred to the Lelang Commandery. Xuantu was conquered by Goguryeo in 319 AD.
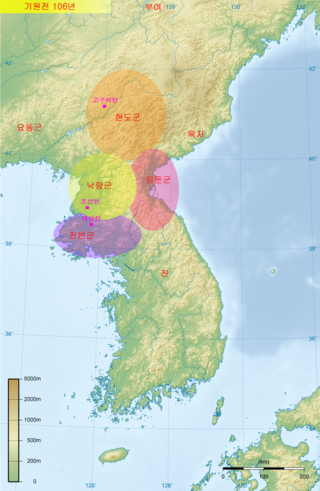
Gaogouli County was a county of the Chinese Han dynasty under the administration of Xuantu Commandery located in southern Manchuria and the northern Korean Peninsula. It was established by the Han dynasty after its conquest of Gojoseon to keep the tribes of Goguryeo in check. In 75 BC, Xuantu Commandery was forced to move its seat of power from Fort Okjeo to Gaogouli County due to Yemaek raids. From 75 BC to 12 AD, Goguryeo tribes were under administration of Gaogouli County and engaged in tributary relationship with the Han dynasty. In 12 AD, Goguryeo rebelled against the Han dynasty and established its own kingdom, and in 105 AD, began attacking the Chinese commanderies of Xuantu and Liaodong. Later, in the 4th century, the State of Goguryeo conquered Xuantu Commandery, along with the Liaodong and Lelang commanderies, ending Han rule over the Liaodong Peninsula and the Korean Peninsula.

The Puyŏ or Puyo-Koguryoic languages are four languages of northern Korea and eastern Manchuria mentioned in ancient Chinese sources. The languages of Buyeo, Goguryeo, Dongye and Okjeo were said to be similar to one another but different from the language of the Yilou to the north . Other sources suggest that the ruling class of Baekje may have spoken a Puyŏ language.
Xiangping is a historical name of Liaoyang, Liaoning province. Xiangping was first mentioned in history as the capital of the Liaodong Commandery in the state of Yan, and the eastern terminus of the Great Wall of Yan established in 284 BC. After the unification of China by the Qin dynasty, Xiangping became the political and cultural center of what is now Northeastern China. From the 4th century onward, Xiangping was successively ruled by the Former Yan and Later Yan. The city was taken by Goguryeo in AD 404 and renamed to Liaodong/Yodong (遼東) City. It saw several major battles during the Goguryeo–Sui War and Goguryeo–Tang Wars before eventually falling to the Tang dynasty.