The Canada–United States Free Trade Agreement (CUSFTA), official name as the Free Trade Agreement between Canada and the United States of America, was a bilateral trade agreement reached by negotiators for Canada and the United States on October 4, 1987, and signed by the leaders of both countries on January 2, 1988. The agreement phased out a wide range of trade restrictions in stages, over a ten-year period, and resulted in a substantial increase in cross-border trade as an improvement to the last replaced trade deal. With the addition of Mexico in 1994, CUSFTA was superseded by the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA).

Duncan Lee Hunter is an American politician. He was a Republican member of the House of Representatives from California's 52nd, 45th and 42nd districts from 1981 to 2009.

The Dominican Republic–Central America–United States Free Trade Agreement is a free trade agreement. Originally, the agreement encompassed the United States and the Central American countries of Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua, and was called CAFTA. In 2004, the Dominican Republic joined the negotiations, and the agreement was renamed CAFTA-DR.
The Australia – United States Free Trade Agreement (AUSFTA) is a preferential trade agreement between Australia and the United States modelled on the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). The AUSFTA was signed on 18 May 2004 and came into effect on 1 January 2005.

The main event by far shaping the foreign policy of the United States during the presidency of George W. Bush (2001–2009) was the 9/11 terrorist attacks against the United States on September 11, 2001, and the subsequent war on terror. There was massive domestic and international support for destroying the attackers. With UN approval, US and NATO forces quickly invaded the attackers' base in Afghanistan and drove them out and the Taliban government that harbored them. It was the start of a 20-year quagmire that finally ended in failure with the withdrawal of United States troops from Afghanistan.
The US-Morocco Free Trade Agreement is a bilateral trade agreement between the United States and Morocco. The agreement was signed on June 15, 2004, followed by U.S. President George W. Bush's signing of the USMFTA Implementation Act on August 17, 2004. The United States House of Representatives ratified the pact on July 22, 2004 by a 323–99 vote. The United States Senate passed the bill by unanimous consent on July 21, 2004. The Morocco FTA came into effect on January 1, 2006.
The United States–Peru Trade Promotion Agreement is a bilateral free trade agreement, whose objectives are eliminating obstacles to trade, consolidating access to goods and services and fostering private investment in and between the United States and Peru. Besides commercial issues, it incorporates economic, institutional, intellectual property, labor and environmental policies, among others. The agreement was signed on April 12, 2006; ratified by the Peruvian Congress on June 28, 2006; by the U.S. House of Representatives on November 2, 2007, and by the U.S. Senate on December 4, 2007. The Agreement was implemented on February 1, 2009.
The United States–Jordan Free Trade Agreement is the first free trade agreement (FTA) between the United States and an Arab country. It is Jordan's second free trade agreement, after the 1997 Greater Arab Free Trade Agreement. The agreement, which grants duty-free status to nearly all Jordanian exports to the United States, was signed on 24 October 2000 and went into force on 17 December 2001. Rules of origin require that goods be composed of a minimum of 35 percent Jordanian content to be eligible for duty-free entry.

The United States–Bahrain Free Trade Agreement (USBFTA) is a free trade agreement (FTA) between the United States and Bahrain, signed on September 14, 2004. It was ratified by the United States House of Representatives on December 7, 2005, by 327–95, with 10 not voting.

The United States–Singapore Free Trade Agreement was signed 6 May 2003 and ratified by the US House of Representatives on 24 July 2003 by a vote of 272-155. The US Senate ratified the bill on 31 July 2003 by a vote of 66-32. President George W. Bush signed into law the United States-Singapore Free Trade Agreement Implementation Act on 3 September 2003. The trade pact was implemented by both countries on 1 January 2004.
The United States–Israel States Free Trade Agreement (FTA) is a trade pact between the State of Israel and the United States of America established in 1985 to lower trade barriers in some goods. The agreement reduces rates of duty, and in some case eliminates all duties, on merchandise exported from Israel to the United States. The agreement also covers merchandise exported from the Gaza Strip and the West Bank.
The United States-Colombia Trade Promotion Agreement (CTPA) is a bilateral free trade agreement between the United States and Colombia. Sometimes called the Colombia Free Trade Agreement, it was signed on November 22, 2006, by Deputy U.S. Trade Representative John Veroneau and Colombian Minister of Trade, Industry, and Tourism Jorge Humberto Botero. CTPA is a comprehensive agreement that will eliminate tariffs and other barriers to trade in goods and services between the United States and Colombia, including government procurement, investment, telecommunications, electronics commerce, intellectual property rights, and labor and environmental protection The United States Congress. Colombia's Congress approved the agreement and a protocol of amendment in 2007. Colombia's Constitutional Court completed its review in July 2008, and concluded that the Agreement conforms to Colombia's Constitution. President Obama tasked the Office of the U.S. Trade Representative with seeking a path to address outstanding issues surrounding the Colombia FTA. The United States Congress then took on the agreement and passed it on October 12, 2011. The agreement went into effect on May 15, 2012.
The fast track authority for brokering trade agreements is the authority of the President of the United States to negotiate international agreements in an expedited manner and with limited congressional oversight. Renamed the trade promotion authority (TPA) in 2002, the TPA is an impermanent power granted by Congress to the President. It remained in effect from 1975 to 1994, pursuant to the Trade Act of 1974 and from 2002 to 2007 pursuant to the Trade Act of 2002. Although it technically expired in July 2007, it remained in effect for agreements that were already under negotiation until their passage in 2011. In June 2015, a third renewal passed Congress and was signed into law by President Barack Obama.

The United States–Korea Free Trade Agreement, also known as KORUS FTA, is a trade agreement between the United States and South Korea. Negotiations were announced on February 2, 2006, and concluded on April 1, 2007. The treaty was first signed on June 30, 2007, with a renegotiated version signed in early December 2010.
The Decent Working Conditions and Fair Competition Act is the title of several bills that have been introduced in the United States Congress to try to "prohibit the import, export, and sale of goods made with sweatshop labor". As of February 2009, they have all died in committee and thus not become law.
The political positions of Norm Coleman have changed dramatically over his career. Originally a Democrat and an anti-war activist as a university student during the Vietnam War, Coleman has since switched parties and is now generally considered a moderate Republican.

The United States Senate career of Barack Obama began on January 3, 2005, and ended on November 16, 2008. A member of the Democratic Party from the state of Illinois, Obama previously served three terms in the Illinois Senate from 1997 to 2005. He resigned his seat in the U.S. Senate upon being elected President of the United States.
The Detainee Treatment Act of 2005 (DTA) is an Act of the United States Congress that was signed into law by President George W. Bush on December 30, 2005. Offered as an amendment to a supplemental defense spending bill, it contains provisions relating to treatment of persons in custody of the Department of Defense, and administration of detainees held in Guantanamo Bay, Cuba, including:
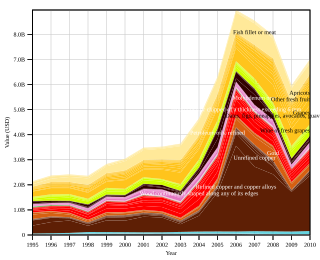
The United States-Chile Free Trade Agreement is a free trade agreement (FTA) between the United States and Chile signed on June 6, 2003. The pact came into force on January 1, 2004. On that date, tariffs on 90% of U.S. exports to Chile and 95% of Chilean exports to the United States were eliminated. The agreement also established that Chile and the U.S. will establish duty-free trade in all products within a maximum of 12 years (2016). In 2009, bilateral trade between the United States and Chile reached US$15.4 billion, a 141% increase over bilateral trade levels before the U.S.-Chile FTA took effect. In particular, U.S. exports to Chile in 2009 showed a 248% increase over pre-FTA levels.

The Agreement between the United States of America, Mexico, and Canada (USMCA) is a free trade agreement between the United States, Mexico, and Canada. It replaced the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) implemented in 1994, and is sometimes characterized as "NAFTA 2.0", or "New NAFTA", since it largely maintains or updates the provisions of its predecessor. USMCA is one of the world's largest free trade zones, with a population of more than 510 million people and an economy of $30.997 trillion in nominal GDP — nearly 30 percent of the global economy.











