Ophidiiformes is an order of ray-finned fish that includes the cusk-eels, pearlfishes, viviparous brotulas, and others. Members of this order have small heads and long slender bodies. They have either smooth scales or no scales, a long dorsal fin and an anal fin that typically runs into the caudal fin. They mostly come from the tropics and subtropics, and live in both freshwater and marine habitats, including abyssal depths. They have adopted a range of feeding methods and lifestyles, including parasitism. The majority are egg-laying, but some are viviparous.

The cusk-eel family, Ophidiidae, is a group of marine bony fishes in the Ophidiiformes order. The scientific name is from the Greek ophis meaning "snake", and refers to their eel-like appearance. True eels, however, diverged from other ray-finned fish during the Jurassic, while cusk-eels are part of the Percomorpha clade, along with tuna, perch, seahorses, and others.

Saccogaster is a genus of viviparous brotulas. They are found in the western Atlantic and Indo-Pacific.

Abyssobrotula galatheae is a species of cusk eel in the family Ophidiidae. It is the deepest-living fish known; one specimen, trawled from a depth of 8,370 m (27,460 ft) in the Puerto Rico Trench in 1970, holds the record for the deepest fish ever captured. Although generally recognized, some have suggested that the record-breaking individual might have been caught with a non-closing net and therefore perhaps caught shallower.
Bellottia is a genus of viviparous brotulas which is found in the subtropical waters of the North Atlantic, the Mediterranean Sea and the Indo-Pacific.

Bidenichthys is a genus of viviparous brotulas.
Eurypleuron is a genus of pearlfishes, with these currently recognized species:
Onuxodon is an Indo-Pacific genus of pearlfishes from the family Carapidae. The generic name is derived from the Greek onyx meaning "claw" and odon meaning "tooth", referring to the sharp fang like teeth of Onuxodon parvibrachium. Species in this genus are distributed from South Africa to Hawaii. They live commensally with molluscs. The three currently recognized species are:
Pyramodon is a genus of pearlfishes, with these currently recognized species:
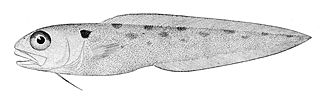
Otophidium is a genus of cusk-eels, part of the subfamily Ophidiinae in the family Ophidiidae. They are found in the western Atlantic and eastern Pacific.
Parophidion is a genus of cusk-eels found in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.

Sirembo is a genus of cusk-eels of the subfamily Neobythitinae, family Ophidiidae, which are found in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. The species in this genus have a rather robust body with the dorsal fin originating over vertebrae 1–5. The head and bod are completely covered in scales, they have large eyes which are almost equal in diameter to the length of snout, the pelvic fins have two rays which are joined together within an area of tough skin, They have a short spine on the operculum which does not extend to the posterior edge of the head. Their coloration is variable but almost all species have black spots or eyespots on the dorsal fin, sometimes both, while the middle part of the anal fin frequently has a black band. The body and/or head are marked with diagonal or horizontal dark stripes or horizontal rows of quite large dusky spots.
The faceless cusk is a genus of cusk-eel found in the Indian and Pacific Oceans at depths from 3,935 to 5,100 m. This species grows to 46.5 cm (18.3 in) in standard length.

The band cusk-eel is a fish species in the family Ophidiidae. Widespread in the Western Atlantic from North Carolina, United States, and northern Gulf of Mexico to southeastern Brazil. Absent from The Bahamas. Marine reef-associated tropical demersal fish, up to 30 cm (12 in) long.
Brotulotaenia brevicauda is a benthopelagic marine fish species in the family Ophidiidae. This totally black fish is usually found in the Atlantic Ocean but it has also been reported in the Indian. B. brevicauda lives in deep water and grows up to 32 cm in length. It is also occasionally known as the Short-tail cusk-eel.

Brotula barbata, commonly known as the goatsbeard brotula, is a species of cusk-eel in the genus Brotula. It lives in the Indo-Pacific, in depths of up to 300 meters. It is dark brown with a submarginal black band and narrow white border on the dorsal and anal fins versus greenish to orange brown with orange-bordered dorsal and anal fins, and it grows up to be around 100 centimeters. It has a carnivorous diet, and it is oviparous.

Brosmophycinae is a subfamily of the viviparous brotulas. They are divided from the subfamily Bythitinae by having the dorsal fin, caudal fin and anal fin all separate whereas they are joined in the Bythitinae. It is divided into the tribes Dinematichthyini and Brosmophycini, with the first having hardened genital claspers and the second soft genital claspers. A review in 2016 elevated the Dinematichthyini to the status of a family the Dinematichthyidae.

Brosmophycini is a tribe of viviparous brotula, one of two tribes in the subfamily Brosmophycinae. They are distinguished from the other brosmophycin tribe, the Dinematichthyini, by having a male intromittent organ which has no ossified parts, a scale-covered body and well developed gill rakers.

Bythitinae is a subfamily of viviparous brotulas, one of the two subfamilies in the family Bythitidae. This subfamily is characterised by having the dorsal, caudal and anal fins combined. They are mostly found in temperate to tropical seas, from reefs to the benthopelagic zone, but some species from the North Atlantic Ocean occur in into Arctic waters.
Bythitoidei is a suborder of the order Ophidiiformes, the cusk eels. They are distinguished from the other Ophidiform suborder, the Ophidioidei, by being largely viviparous.








