
The cusk-eel family, Ophidiidae, is a group of marine boney fishes in the order Ophidiiformes. The scientific name is from the Greek ophis meaning "snake", and refers to their eel-like appearance. True eels, however, diverged from other ray-finned fish during the Jurassic, while cusk-eels are part of the Percomorpha clade, along with tuna, perch, seahorses, and others. Unlike true eels of the order Anguilliformes, cusk-eels have ventral fins that are developed into a forked barbel-like organ below the mouth. In the true eels by contrast, the ventral fins are never well-developed and usually missing entirely.
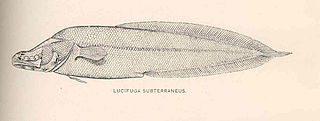
Lucifuga is a genus of viviparous brotulas. Most of the species are native to caves and sinkholes in Cuba and the Bahamas; L. inopinata from deep water off the Galápagos Islands is the only exception. The four species rated by the IUCN are all considered vulnerable. The largest species in the genus reaches about 15 cm (5.9 in) in length.

Saccogaster is a genus of viviparous brotulas. They are found in the western Atlantic and Indo-Pacific.
Bellottia is a genus of viviparous brotulas which is found in the subtropical waters of the North Atlantic, the Mediterranean Sea and the Indo-Pacific.

Hephthocara is a small genus of Indo-Pacific viviparous brotula.
Eurypleuron is a genus of pearlfishes, with these currently recognized species:
Pyramodon is a genus of pearlfishes, with these currently recognized species:
Dicrolene is a genus of cusk-eels.
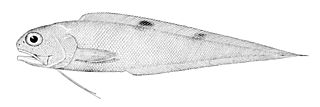
Neobythites is a genus of cusk-eels.

Ophidion is a genus of cusk-eels.
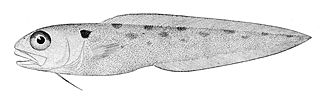
Otophidium is a genus of cusk-eels, part of the subfamily Ophidiinae in the family Ophidiidae. They are found in the western Atlantic and eastern Pacific.
Parophidion is a genus of cusk-eels found in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
Porogadus is a genus of cusk-eels.
The banded cusk-eel is a species of cusk-eel found along the southeast coast of South America from southern Brazil to northern Argentina. It occurs at depths of from 40 to 150 metres and is of minor importance in commercial fisheries. This species grows to a length of 31 centimetres (12 in) TL. It is the only known member of its genus. The generic name honours the American ichthyologist Edward C. Raney (1909-1984) of Cornell University who introduced the describer Charles R. Robins to ichthyology.

Sirembo is a genus of cusk-eels of the subfamily Neobythitinae, family Ophidiidae, which are found in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. The species in this genus have a rather robust body with the dorsal fin originating over vertebrae 1–5. The head and bod are completely covered in scales, they have large eyes which are almost equal in diameter to the length of snout, the pelvic fins have two rays which are joined together within an area of tough skin, They have a short spine on the operculum which does not extend to the posterior edge of the head. Their coloration is variable but almost all species have black spots or eyespots on the dorsal fin, sometimes both, while the middle part of the anal fin frequently has a black band. The body and/or head are marked with diagonal or horizontal dark stripes or horizontal rows of quite large dusky spots.

The band cusk-eel is a fish species in the family Ophidiidae. Widespread in the Western Atlantic from North Carolina, United States, and northern Gulf of Mexico to southeastern Brazil. Absent from The Bahamas. Marine reef-associated tropical demersal fish, up to 30 cm (12 in) long.
Brotulotaenia brevicauda is a benthopelagic marine fish species in the family Ophidiidae. This totally black fish is usually found in the Atlantic Ocean but it has also been reported in the Indian. B. brevicauda lives in deep water and grows up to 32 cm in length. It is also occasionally known as the Short-tail cusk-eel.

Ophidiinae is a subfamily of the cusk eel family Ophidiidae. The species in the subfamily are characterised by having their pelvic fins situated far forward on the body and supported by an forward orientated extension of the pelvic girdle, they lack barbels on the mouth and chin and they are covered in small cycloid scales arranged in horizontal or diagonal rows. Some species have a modified swim bladder and the anterior vertebrae which enables them to generate sounds. and some of these modifications are sexually dimorphic and make the fish capable of generating sound. They have two rays in each ventral fin and the caudal fin has 9 rays. Most species are benthic and occur on the continental shelf.
Echiodon neotes is a fish species described by Markle and Olney, 1990. Echiodon neotes is part of the genus Echiodon and the subfamily Carapinae.
Onuxodon fowleri is a species of pearlfish first described by Smith, 1955. Onuxodon fowleri is part of the genus Onuxodon and the subfamily Carapinae. No subspecies are listed in the Catalog of Life.











