Related Research Articles

Galla Placidia, daughter of the Roman emperor Theodosius I, was a mother, tutor, and advisor to emperor Valentinian III, and a major force in Roman politics for most of her life. She was queen consort to Ataulf, king of the Visigoths from 414 until his death in 415, briefly empress consort to Constantius III in 421, and managed the government administration as a regent during the early reign of Valentinian III, until her death.
The 450s decade ran from January 1, 450, to December 31, 459.
The 440s decade ran from January 1, 440, to December 31, 449.
Year 454 (CDLIV) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aetius and Studius. The denomination 454 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 455 (CDLV) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Valentinianus and Anthemius. The denomination 455 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Anicius Olybrius was Roman emperor from July 472 until his death later that same year; his rule as Augustus in the western Roman Empire was not recognised as legitimate by the ruling Augustus in the eastern Roman Empire, Leo I. He was in reality a puppet ruler raised to power by Ricimer, the magister militum of Germanic descent, and was mainly interested in religion, while the actual power was held by Ricimer and his nephew Gundobad.

Valentinian III was Roman emperor in the West from 425 to 455. Made emperor in childhood, his reign over the Roman Empire was one of the longest, but was dominated by powerful generals vying for power amid civil wars and the invasions of Late antiquity's Migration Period, including the campaigns of Attila the Hun.

Aetius was a Roman general and statesman of the closing period of the Western Roman Empire. He was a military commander and the most influential man in the Empire for two decades (433–454). He managed policy in regard to the attacks of barbarian federates settled throughout the West. Notably, he mustered a large Roman and allied (foederati) army in the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains, ending a devastating invasion of Gaul by Attila in 451, though the Hun and his subjugated allies still managed to invade Italy the following year, an incursion best remembered for the ruthless Sack of Aquileia and the intercession of Pope Leo I.

The Battle of the Catalaunian Plains, also called the Battle of the Campus Mauriacus, Battle of Châlons, Battle of Troyes or the Battle of Maurica, took place on June 20, 451 AD, between a coalition – led by the Roman general Flavius Aetius and by the Visigothic king Theodoric I – against the Huns and their vassals – commanded by their king Attila. It proved one of the last major military operations of the Western Roman Empire, although Germanic foederati composed the majority of the coalition army. Whether the battle was of strategic significance is disputed; historians generally agree that the Siege of Orleans was the decisive moment in the campaign and stopped the Huns' attempt to advance any further into Roman territory or establish vassals in Roman Gaul. However, the Huns successfully looted and pillaged much of Gaul and crippled the military capacity of the Romans and Visigoths. Attila died only two years later, in 453; after the Battle of Nedao in 454, the coalition of the Huns and the incorporated Germanic vassals gradually disintegrated.
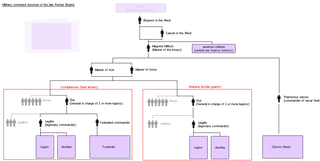
Magister militum was a top-level military command used in the later Roman Empire, dating from the reign of Constantine the Great. The term referred to the senior military officer of the empire. In Greek sources, the term is translated either as strategos or as stratelates.

Petronius Maximus was Roman emperor of the West for two and a half months in 455. A wealthy senator and a prominent aristocrat, he was instrumental in the murders of the Western Roman magister militum, Aëtius, and the Western Roman emperor, Valentinian III.

The term Western Roman Empire is used in modern historiography to refer to the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent Imperial court—and particularly during the period from 395 to 476, in which there were separate, coequal courts dividing the governance of the empire in the Western provinces from that of the Eastern provinces, with a distinct imperial succession in the separate courts. The terms Western Roman Empire and Eastern Roman Empire were coined in modern times to describe political entities that were de facto independent; contemporary Romans did not consider the Empire to have been split into two empires but viewed it as a single polity governed by two imperial courts as an administrative expediency. The Western Roman Empire collapsed in 476, and the Western imperial court in Ravenna was formally dissolved by Justinian in 554. The Eastern imperial court lasted until 1453.

Bonifatius was a Roman general and governor of the diocese of Africa. He campaigned against the Visigoths in Gaul and the Vandals in North Africa. An ally of Galla Placidia, mother and advisor of Valentinian III, Bonifacius engaged in Roman civil wars on her behalf against the generals Felix in 427-429 and Aetius in 432. Although he defeated the latter at the Battle of Rimini, Bonifacius suffered a fatal wound and was succeeded by his son-in-law Sebastianus as patricius of the Western Roman Empire.
Placidia was a daughter of Valentinian III, Roman emperor of the West from 425 to 455, and from 454/455 the wife of Olybrius, who became western Roman emperor in 472. She was one of the last imperial spouses in the Roman west, during the Fall of the Western Roman Empire during Late Antiquity.

Licinia Eudoxia was a Roman Empress, daughter of Eastern Roman Emperor Theodosius II. Her husbands included the Western Roman Emperors Valentinian III and Petronius Maximus.

Attila is a 2001 American television miniseries set during the waning days of the Western Roman Empire, in particular during the invasions of the Huns in Europe.

Attila is a 1954 Italian-French co-production, directed by Pietro Francisci and produced by Dino De Laurentiis and Carlo Ponti for Lux Film. Based on the life of Attila the Hun, it stars Anthony Quinn as Attila and Sophia Loren as Honoria, with French leading man, Henri Vidal, as the Hun's antagonist, Flavius Aetius. Irene Papas, in the second of three contract pictures for Lux Film, plays one of Attila's wives, Grune. Ettore Manni, Christian Marquand, and Claude Laydu are among the supporting cast of mostly French and Italian actors. American Scott Marlowe (1932–2001) made his screen debut in the film. Along with The Pride and the Passion and Houseboat, it was one of Loren's biggest box-office successes during the 1950s.
Heraclius was an influential eunuch of the Western Roman Emperor Valentinian III.
The history of the Later Roman Empire covers the history of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the rule of Diocletian in 284 AD and the establishment of the Tetrarchy in 293 AD by Diocletian to the death of Heraclius in 641 AD.
Thraustila was a Hun or a Goth bodyguard of Roman general Aetius, who participated in the assassination of Emperor Valentinian III, ordered by Petronius Maximus. He probably served Aetius as a bucellarius.
References
- 1 2 Hughes, Ian (2012). Aetius Attila's Nemesis. Pen & Sword Books. ISBN 9781783461349 . Retrieved 19 November 2022.
- ↑ MacDowall, Simon (2015). Catalaunian Fields AD 451 Rome's Last Great Battle. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 9781472807458 . Retrieved 19 November 2022.
- ↑ Fields, Nic (2015). Attila the Hun. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 40. ISBN 9781472808882 . Retrieved 19 November 2022.
- ↑ Given, John (2014). The Fragmentary History of Priscus: Attila, the Huns and the Roman Empire, AD 430–476. Arx Publishing. p. 128. ISBN 978-1-935228-14-1.