Related Research Articles

The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part of Scythia at the time; the Huns' arrival to Europe is associated with the migration westward of an Iranian people, the Alans. By 370 AD, the Huns had arrived on the Volga, and by 430, they had established a vast, if short-lived, dominion in Europe, conquering the Goths and many other Germanic peoples living outside of Roman borders and causing many others to flee into Roman territory. The Huns, especially under their King Attila, made frequent and devastating raids into the Eastern Roman Empire. In 451, they invaded the Western Roman province of Gaul, where they fought a combined army of Romans and Visigoths at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, and in 452, they invaded Italy. After the death of Attila in 453, the Huns ceased to be a major threat to Rome and lost much of their empire following the Battle of Nedao. Descendants of the Huns, or successors with similar names, are recorded by neighboring populations to the south, east, and west as having occupied parts of Eastern Europe and Central Asia from about the 4th to 6th centuries. Variants of the Hun name are recorded in the Caucasus until the early 8th century.

The Bulgars were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomadic equestrians in the Volga-Ural region, but some researchers say that their ethnic roots can be traced to Central Asia. During their westward migration across the Eurasian steppe, the Bulgar tribes absorbed other tribal groups and cultural influences in a process of ethnogenesis, including Iranian, Finnic and Hunnic tribes. Modern genetic research on Central Asian Turkic people and ethnic groups related to the Bulgars points to an affiliation with Western Eurasian populations. The Bulgars spoke a Turkic language, i.e. Bulgar language of Oghuric branch. They preserved the military titles, organization and customs of Eurasian steppes, as well as pagan shamanism and belief in the sky deity Tangra.

Bleda was a Hunnic ruler, the brother of Attila the Hun.
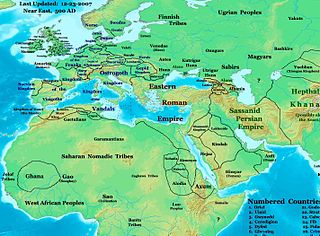
The Sabirs were nomadic people who lived in the north of the Caucasus beginning in the late-5th -7th century, on the eastern shores of the Black Sea, in the Kuban area, and possibly came from Western Siberia. They were skilled in warfare, used siege machinery, had a large army and were boat-builders. They were also referred to as Huns, a title applied to various Eurasian nomadic tribes in the Pontic-Caspian Steppe during late antiquity. Sabirs led incursions into Transcaucasia in the late-400s/early-500s, but quickly began serving as soldiers and mercenaries during the Byzantine-Sasanian Wars on both sides. Their alliance with the Byzantines laid the basis for the later Khazar-Byzantine alliance.
The Hunnic language, or Hunnish, was the language spoken by Huns in the Hunnic Empire, a heterogeneous, multi-ethnic tribal confederation which invaded Eastern and Central Europe, and ruled most of Pannonian Eastern Europe, during the 4th and 5th centuries CE. A variety of languages were spoken within the Hun Empire. A contemporary report by Priscus has that Hunnish was spoken alongside Gothic and the languages of other tribes subjugated by the Huns.
The Onoğurs or Oğurs, were Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between 5th and 7th century, and spoke the Oghuric language.
Khazar, also known as Khazaric, was a Turkic dialect group spoken by the Khazars, a group of semi-nomadic Turkic peoples originating from Central Asia. There are few written records of the language and its features and characteristics are unknown. It is believed to have gradually become extinct by the 13th century AD as its speakers assimilated into neighboring Turkic-speaking populations.
Ernak was the last known ruler of the Huns, and the third son of Attila. After Attila's death in 453 AD, his Empire crumbled and its remains were ruled by his three sons, Ellac, Dengizich and Ernak. He succeeded his older brother Ellac in 454 AD, and probably ruled simultaneously over Huns in dual kingship with his brother Dengizich, but in separate divisions in separate lands.
Zabergan was the chieftain of the Kutrigur Bulgar Huns, a nomadic people of the Pontic–Caspian steppe, after Sinnion. His name is Iranian, meaning full moon. Either under pressure from incoming Avars, or in revolt against the Byzantine Empire, in the winter of 558, he led a large Kutrigur army that crossed the frozen Danube. The army was divided into three sections: one raided south far as Thermopylae, while two others the Thracian Chersonesus and the periphery of Constantinople. In March 559 Zabergan attacked Constantinople, and one part of his forces consisted of 7,000 horsemen, but Belisarius defeated him at the Battle of Melantias and he was forced to withdraw.
Khinialon or Chinialon or Chinialus was chieftain of the Kutrigurs. In 551 he came from the "western side of the Maeotic Lake" to assist the Gepids at the war with Lombards with 12,000 Kutrigurs. Later along with the Gepids they plundered the Byzantine lands. However, Byzantine emperor Justinian I through diplomatic persuasion and bribery dragged the Kutrigurs and Utigurs into mutual warfare. The Utigurs led by Sandilch attacked the Kutrigurs, who suffered great losses.
Charaton was one of the first kings of the Huns.

Uldin, also spelled Huldin is the first ruler of the Huns whose historicity is undisputed.

Ellac was the oldest son of Attila (434–453) and Kreka. After Attila's death in 453 AD, his Empire crumbled and its remains were ruled by his three sons, Ellac, Dengizich and Ernak. He ruled shortly, and died at the Battle of Nedao in 454 AD. Ellac was succeeded by brothers Dengizich and Ernak.
Octar or Ouptaros was a Hunnic ruler. He ruled in dual kingship with his brother Rugila, possibly with a geographical division, ruling the Western Huns while his brother ruled the Eastern Huns.

Laudaricus was a prominent Hunnic chieftain and general active in the first half of the 5th century.
The history of the Huns spans the time from before their first secure recorded appearance in Europe around 370 AD to after the disintegration of their empire around 469. The Huns likely entered Western Asia shortly before 370 from Central Asia: they first conquered the Goths and the Alans, pushing a number of tribes to seek refuge within the Roman Empire. In the following years, the Huns conquered most of the Germanic and Scythian barbarian tribes outside of the borders of the Roman Empire. They also launched invasions of both the Asian provinces of Rome and the Sasanian Empire in 375. Under Uldin, the first Hunnic ruler named in contemporary sources, the Huns launched a first unsuccessful large-scale raid into the Eastern Roman Empire in Europe in 408. From the 420s, the Huns were led by the brothers Octar and Ruga, who both cooperated with and threatened the Romans. Upon Ruga's death in 435, his nephews Bleda and Attila became the new rulers of the Huns, and launched a successful raid into the Eastern Roman Empire before making peace and securing an annual tribute and trading raids under the Treaty of Margus. Attila appears to have killed his brother and became sole ruler of the Huns in 445. He would go on to rule for the next eight years, launching a devastating raid on the Eastern Roman Empire in 447, followed by an invasion of Gaul in 451. Attila is traditionally held to have been defeated in Gaul at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, however some scholars hold the battle to have been a draw or Hunnic victory. The following year, the Huns invaded Italy and encountered no serious resistance before turning back.
Basich or Basikh was a Hun military commander who co-led an invasion of Persia in 395 AD together with Kursich.
Kursich was a Hun general and royal family member. He led a Hunnish army in the Hunnic invasion of Persia in 395 AD.
Glom was a Hun sub-king, or tribe king. He fought for the Sasanian Empire in the late 520s.
References
- ↑ Jeffreys, Elizabeth; Jeffreys, Michael; Scott, Roger (1986). The Chronicle of John Malalas. Brill. p. 369. ISBN 9789004344600 . Retrieved 15 November 2022.
- ↑ Evan Michael Schultheis (30 January 2019). The Battle of the Catalaunian Fields AD 451: Flavius Aetius, Attila the Hun and the Transformation of Gaul. ISBN 978-1526745668.
- ↑ Golden 1980, p. 258.
- ↑ Golden 1992, p. 106.
- ↑ Martindale, J.R. (1992). The Prosopography of the Later Roman Empire 2 Part Set: Volume 3, AD 527-641. Cambridge University Press. p. 1346. Retrieved 15 November 2022.
- ↑ Maenchen-Helfen, Otto J. (1973). The World of the Huns: Studies in Their History and Culture . Berkeley, Los Angeles and London: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520015968, pp. 391-392