Related Research Articles
The Goths were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. They were first reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 3rd century AD, living north of the Danube in what is now Ukraine, Moldova and Romania. From here they conducted raids into Roman territory, and large numbers of them joined the Roman military. These early Goths lived in the regions where archaeologists find the Chernyakhov culture, which flourished throughout this region during the 3rd and 4th centuries.

The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part of Scythia at the time. By 370 AD, the Huns had arrived on the Volga, causing the westwards movement of Goths and Alans. By 430, they had established a vast, but short-lived, empire on the Danubian frontier of the Roman empire in Europe. Either under Hunnic hegemony, or fleeing from it, several central and eastern European peoples established kingdoms in the region, including not only Goths and Alans, but also Vandals, Gepids, Heruli, Suebians and Rugians.

The Ostrogoths were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Western Roman Empire, drawing upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under Theodoric the Great.
Fritigern was a Thervingian Gothic chieftain whose decisive victory at Adrianople during the Gothic War (376–382) led to favourable terms for the Goths when peace was made with Gratian and Theodosius I in 382.

The Gepids were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary, and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava, and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion and language of the Goths and Vandals.

The Battle of Nedao was fought in Pannonia in 454 CE between the Huns and their former Germanic vassals. Nedao is believed to be a tributary of the Sava River.

Hervarar saga ok Heiðreks is a legendary saga from the 13th century combining matter from several older sagas in Germanic heroic legend. It tells of wars between the Goths and the Huns during the 4th century. The final part of the saga, which was likely composed separately from and later than the rest, is a source for Swedish medieval history.

The Sciri, or Scirians, were a Germanic people. They are believed to have spoken an East Germanic language. Their name probably means "the pure ones".

Hlöd or Hlod was the illegitimate son of Heidrek, the king of the Geats, in Norse mythology.

The sack of Rome on 24 August 410 AD was undertaken by the Visigoths led by their king, Alaric. At that time, Rome was no longer the administrative capital of the Western Roman Empire, having been replaced in that position first by Mediolanum in 286 and then by Ravenna in 402. Nevertheless, the city of Rome retained a paramount position as "the eternal city" and a spiritual center of the Empire. This was the first time in almost 800 years that Rome had fallen to a foreign enemy, and the sack was a major shock to contemporaries, friends and foes of the Empire alike.

Uldin, also spelled Huldin is the first ruler of the Huns whose historicity is undisputed.
Valamir or Valamer was an Ostrogothic king in the former Roman province of Pannonia from AD 447 until his death. During his reign, he fought alongside the Huns against the Roman Empire and then, after Attila the Hun's death, fought against the Huns to consolidate his independent control over a large group of Goths.
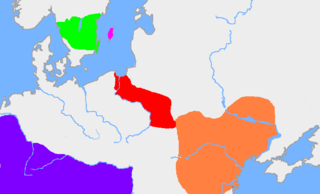
The Greuthungi were a Gothic people who lived on the Pontic steppe between the Dniester and Don rivers in what is now Ukraine, in the 3rd and the 4th centuries. They had close contacts with the Tervingi, another Gothic people, who lived west of the Dniester River. To the east of the Greuthungi, living near the Don river, were the Alans.

The Taifals or Tayfals were a people group of Germanic or Sarmatian origin, first documented north of the lower Danube in the mid third century AD. They experienced an unsettled and fragmented history, for the most part in association with various Gothic peoples, and alternately fighting against or for the Romans. In the late fourth century some Taifali were settled within the Roman Empire, notably in western Gaul in the modern province of Poitou. They subsequently supplied mounted units to the Roman army and continued to be a significant source of cavalry for early Merovingian armies. By the sixth century their region of western Gaul had acquired a distinct identity as Thifalia.

Balamber was ostensibly a chieftain of the Huns, mentioned by Jordanes in his Getica. Jordanes simply called him "king of the Huns" and writes the story of Balamber crushing the tribes of the Ostrogoths in the 370s; somewhere between 370 and more probably 376 AD.

Athanaric or Atanaric was king of several branches of the Thervingian Goths for at least two decades in the 4th century. Throughout his reign, Athanaric was faced with invasions by the Roman Empire, the Huns and a civil war with Christian rebels. He is considered the first king of the Visigoths, who later settled in Iberia, where they founded the Visigothic Kingdom.

The history of the Huns spans the time from before their first secure recorded appearance in Europe around 370 AD to after the disintegration of their empire around 469. The Huns likely entered Western Asia shortly before 370, from Central Asia: they first conquered the Goths and the Alans, pushing a number of tribes to seek refuge within the Roman Empire. In the following years, the Huns conquered most of the Germanic and Scythian tribes outside of the borders of the Roman Empire. They also launched invasions of both the Asian provinces of Rome and the Sasanian Empire in 375. Under Uldin, the first Hunnic ruler named in contemporary sources, the Huns launched a first unsuccessful large-scale raid into the Eastern Roman Empire in Europe in 408. From the 420s, the Huns were led by the brothers Octar and Ruga, who both cooperated with and threatened the Romans. Upon Ruga's death in 435, his nephews Bleda and Attila became the new rulers of the Huns, and launched a successful raid into the Eastern Roman Empire before making peace and securing an annual tribute and trading raids under the Treaty of Margus. Attila appears to have killed his brother, and became sole ruler of the Huns in 445. He would go on to rule for the next eight years, launching a devastating raid on the Eastern Roman Empire in 447, followed by an invasion of Gaul in 451. Attila is traditionally held to have been defeated in Gaul at the Battle of the Catalaunian Fields, however some scholars hold the battle to have been a draw or Hunnic victory. The following year, the Huns invaded Italy and encountered no serious resistance before turning back.
The Battle of Dibaltum was fought between the Roman army and an army of Goths, Huns, and Alans in the summer of 377. The battle took place outside the city of Dibaltum in Thrace and resulted in a Gothic victory.
Sifka or Sifeca is a Hun princess in Norse mythology, the mother of the warrior Hlöd by Heidrek, King of the Geats.
Chelchal was a Hun commander serving as lieutenant general under the Byzantine Empire.
References
- ↑ History of the Goths. University of California Press. 13 February 1990. ISBN 9780520069831 . Retrieved 5 April 2012.