Kangaroos are marsupials from the family Macropodidae. In common use the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, the red kangaroo, as well as the antilopine kangaroo, eastern grey kangaroo, and western grey kangaroo. Kangaroos are indigenous to Australia and New Guinea. The Australian government estimates that 42.8 million kangaroos lived within the commercial harvest areas of Australia in 2019, down from 53.2 million in 2013.

Macropodidae is a family of marsupials that includes kangaroos, wallabies, tree-kangaroos, wallaroos, pademelons, quokkas, and several other groups. These genera are allied to the suborder Macropodiformes, containing other macropods, and are native to the Australian continent, New Guinea and nearby islands.

The red kangaroo is the largest of all kangaroos, the largest terrestrial mammal native to Australia, and the largest extant marsupial. It is found across mainland Australia, except for the more fertile areas, such as southern Western Australia, the eastern and southeastern coasts, and the rainforests along the northern coast.

The parma wallaby is a small marsupial macropod mammal native to forests and densely-vegetated areas of northeastern New South Wales, Australia, close to the border with Queensland. There is also an introduced population found in and around Rodney District, just north of Auckland, New Zealand. About the size of a stout cat, it lives mainly under thick plant cover, and is only active at night when it emerges to feed on grasses and small plants. It is the smallest of the wallabies and carries its young in a pouch, as with other marsupials. Shy and elusive, it was believed extinct until its rediscovery in the 1960s.

Wallaroo is a common name for several species of moderately large macropods, intermediate in size between the kangaroos and the wallabies. The word "wallaroo" is from the Dharug walaru with spelling influenced by the words "kangaroo" and "wallaby".

The tammar wallaby, also known as the dama wallaby or darma wallaby, is a small macropod native to South and Western Australia. Though its geographical range has been severely reduced since European colonisation, the tammar wallaby remains common within its reduced range and is listed as "Least Concern" by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). It has been introduced to New Zealand and reintroduced to some areas of Australia where it had been previously extirpated. Skull variations differentiate between tammar wallabies from Western Australia, Kangaroo Island, and mainland South Australia, making them distinct population groups.

Potoroidae is a family of marsupials, small Australian animals known as bettongs, potoroos, and rat-kangaroos. All are rabbit-sized, brown, jumping marsupials and resemble a large rodent or a very small wallaby.

Macropus is a marsupial genus in the family Macropodidae. It has two extant species of large terrestrial kangaroos. The term is derived from the Ancient Greek μάκρος, makros "long" and πους, pous "foot". Thirteen known extinct species are recognised. The type species is the eastern grey kangaroo.

The Macropodiformes, also known as macropods, are one of the three suborders of the large marsupial order Diprotodontia. They may in fact be nested within one of the suborders, Phalangeriformes. Kangaroos, wallabies and allies, bettongs, potoroos and rat kangaroos are all members of this suborder.

Lagorchestes is a genus of small, rabbit-like mammals commonly known as hare-wallabies. It includes four species native to Australia and New Guinea, two of which are extinct. Hare-wallabies belong to the macropod family (Macropodidae) which includes kangaroos, wallabies, and other marsupials.

The western brush wallaby, also known as the black-gloved wallaby, is a species of wallaby found in the southwestern coastal region of Western Australia. The wallaby's main threat is predation by the introduced red fox. The IUCN lists the western brush wallaby as Least Concern, as it remains fairly widespread and the population is believed to be stable or increasing, as a result of red fox control programs.

The antilopine kangaroo, also known as the antilopine wallaroo or the antilopine wallaby, is a species of macropod found in northern Australia: in Cape York Peninsula in Queensland, the Top End of the Northern Territory, and the Kimberley region of Western Australia. It is a locally common, gregarious grazer.

The black wallaroo, also known as Woodward's wallaroo, is a species of macropod restricted to a small, mountainous area in Arnhem Land, Northern Territory, Australia, between South Alligator River and Nabarlek. It classified as near threatened, mostly due to its limited distribution. A large proportion of the range is protected by Kakadu National Park.

The common wallaroo, also known as the euro, hill wallaroo, or simply wallaroo, is a species of macropod. The word euro is particularly applied to one subspecies.

The northern or sandy nail-tail wallaby is a species of macropod found across northern Australia on arid and sparsely wooded plains. The largest species of the genus Onychogalea, it is a solitary and nocturnal herbivorous browser that selects its food from a wide variety of grasses and succulent plant material. Distinguished by a slender and long-limbed form that resembles the typical and well known kangaroos, although their standing height is shorter, around half of one metre, and their weight is less than nine kilograms. As with some medium to large kangaroo species, such as Osphranter rufus, they have an unusual pentapedal motion at slow speeds by stiffening the tail for a fifth limb. When fleeing a disturbance, they hop rapidly with the tail curled back and repeatedly utter the sound "wuluhwuluh". Their exceptionally long tail has a broad fingernail-like protuberance beneath a dark crest of hair at its end, a peculiarity of the genus that is much broader than the other species. The name unguifera, meaning claw, is a reference to this extraordinary attribute, the purpose of which is unknown.

Macropod hybrids are hybrids of animals within the family Macropodidae, which includes kangaroos and wallabies. Several macropod hybrids have been experimentally bred, including:

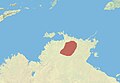
The eastern short-eared rock-wallaby or Wilkins' rock-wallaby is a species of rock-wallaby found in the northernmost parts of the Northern Territory of Australia, and is common in the Kakadu and Litchfield National Parks. It was thought to be a subpopulation of the short-eared rock-wallaby Petrogale brachyotis found in the Kimberley, but recent genetic and morphological studies have shown it to be distinct. Wilkins' rock-wallaby is smaller, has more distinct grey/brown markings on its head and sides, and more colourful limbs than the western species.

Notamacropus is a genus of small marsupials in the family Macropodidae, commonly known as wallabies. The term is derived from the Latin nota "stripe" and macropus "kangaroo", referencing the distinct facial stripe of many extant genus members and their phylogenetic relationship to other kangaroos.
Macropus pan is a species of marsupial that existed during the Pliocene in Australia, known only from fossils located at several sites across Australia. The species is recognised as allied to the modern grey kangaroos, the western Macropus fuliginosus and eastern Macropus giganteus, in a clade initially named as subgenus Macropus (Macropus) Dawson & Flannery. The first description was provided by Charles W. De Vis in 1895, emerging from the author's examination of fossil material held at the Queensland Museum. Fossil specimens of Quanbun local fauna, named for a site in Western Australia, were also identified as this species. The origin of the type specimen was not recorded, although based on comparisons to material with a known provenance it is assumed to have excavated at Chinchilla, Queensland. A larger macropod than any modern species, the standing height was estimated to be over two metres.