
The skeleton is the body part that forms the supporting structure of an organism. It can also be seen as the bony frame work of the body which provides support, shape and protection to the soft tissues and delicate organs in animals. There are several different skeletal types: the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside the body, the hydroskeletonis a flexible skeleton supported by fluid pressure and the cytoskeleton is present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including bacteria, and archaea. The term comes from Greek σκελετός (skeletós), meaning 'dried up'.

A joint or articulation is the connection made between bones in the body which link the skeletal system into a functional whole. They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally.
Comp, COMP or Comps may refer to:

Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) is a category of otherwise unrelated drugs defined by their use in rheumatoid arthritis to slow down disease progression. The term is often used in contrast to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug and steroids.

Craniosacral therapy (CST) is a form of bodywork or alternative therapy using gentle touch to palpate the synarthrodial joints of the cranium. A practitioner of cranial-sacral therapy may also apply light touches to a patient's spine and pelvic bones. Practitioners say that this palpation regulates the flow of cerebrospinal fluid and aids in "primary respiration". CST has been characterized as pseudoscience, and its practice called quackery. According to the American Cancer Society, although CST may relieve the symptoms of stress or tension, "available scientific evidence does not support claims that craniosacral therapy helps in treating cancer or any other disease". Similarly, cranial osteopathy has no scientific basis for any claimed benefit.
Allotransplant is the transplantation of cells, tissues, or organs to a recipient from a genetically non-identical donor of the same species. The transplant is called an allograft, allogeneic transplant, or homograft. Most human tissue and organ transplants are allografts.

The hock, or gambrel, is the joint between the tarsal bones and tibia of a digitigrade or unguligrade quadrupedal mammal, such as a horse, cat, or dog. This joint may include articulations between tarsal bones and the fibula in some species, while in others the fibula has been greatly reduced and is only found as a vestigial remnant fused to the distal portion of the tibia. It is the anatomical homologue of the ankle of the human foot. While homologous joints occur in other tetrapods, the term is generally restricted to mammals, particularly long-legged domesticated species.
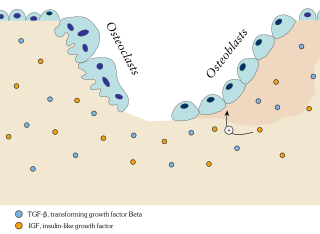
Ossification in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells called osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue: Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down of bone into the primitive connective tissue (mesenchyme), while endochondral ossification involves cartilage as a precursor. In fracture healing, endochondral osteogenesis is the most commonly occurring process, for example in fractures of long bones treated by plaster of Paris, whereas fractures treated by open reduction and internal fixation with metal plates, screws, pins, rods and nails may heal by intramembranous osteogenesis.
Pannus is an abnormal layer of fibrovascular tissue or granulation tissue. Common sites for pannus formation include over the cornea, over a joint surface, or on a prosthetic heart valve. Pannus may grow in a tumor-like fashion, as in joints where it may erode articular cartilage and bone.
An enchondroma is a cartilage cyst found in the bone marrow. Typically, enchondroma is discovered on an X-ray scan. Enchondromas have a characteristic appearance on Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) as well. They have also been reported to cause increased uptake on PET examination.
Osteochondrosis is a family of orthopedic diseases of the joint that occur in children, adolescents and other rapidly growing animals, particularly pigs, horses, dogs, and broiler chickens. They are characterized by interruption of the blood supply of a bone, in particular to the epiphysis, followed by localized bony necrosis, and later, regrowth of the bone. This disorder is defined as a focal disturbance of endochondral ossification and is regarded as having a multifactorial cause, so no one thing accounts for all aspects of this disease.

A meniscus is a crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous anatomical structure that, in contrast to an articular disk, only partly divides a joint cavity. In humans they are present in the knee, wrist, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular, and temporomandibular joints; in other animals they may be present in other joints.
Osteochondritis is a painful type of osteochondrosis where the cartilage or bone in a joint is inflamed.

The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word "sternum" originates from the Greek στέρνον, meaning "chest".
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to trauma and orthopaedics:











