Related Research Articles

Prions are misfolded proteins with the ability to transmit their misfolded shape onto normal variants of the same protein. They characterize several fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in humans and many other animals. It is not known what causes the normal protein to misfold, but the abnormal three-dimensional structure is suspected of conferring infectious properties, collapsing nearby protein molecules into the same shape. The word prion derives from "proteinaceous infectious particle". The hypothesized role of a protein as an infectious agent stands in contrast to all other known infectious agents such as viroids, viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites, all of which contain nucleic acids.

An infection is the invasion of an organism's body tissues by disease-causing agents, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agents and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection.

Tenosynovitis is the inflammation of the fluid-filled sheath that surrounds a tendon, typically leading to joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. Tenosynovitis can be either infectious or noninfectious. Common clinical manifestations of noninfectious tenosynovitis include de Quervain tendinopathy and stenosing tenosynovitis
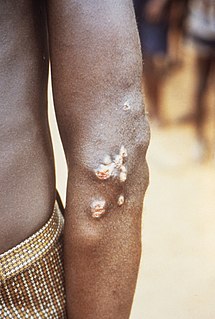
Yaws is a tropical infection of the skin, bones, and joints caused by the spirochete bacterium Treponema pallidum pertenue. The disease begins with a round, hard swelling of the skin, 2 to 5 cm in diameter. The center may break open and form an ulcer. This initial skin lesion typically heals after 3–6 months. After weeks to years, joints and bones may become painful, fatigue may develop, and new skin lesions may appear. The skin of the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet may become thick and break open. The bones may become misshapen. After 5 years or more, large areas of skin may die, leaving scars.
Rheumatism or rheumatic disorders are conditions causing chronic, often intermittent pain affecting the joints or connective tissue. Rheumatism does not designate any specific disorder, but covers at least 200 different conditions, including arthritis and "non-articular rheumatism", also known as "regional pain syndrome" or "soft tissue rheumatism". There is a close overlap between the term soft tissue disorder and rheumatism. Sometimes the term "soft tissue rheumatic disorders" is used to describe these conditions.

Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the feet, spine, and hips are most commonly involved in adults.

The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system provides form, support, stability, and movement to the body.

Blastomycosis is a fungal infection caused by inhaling Blastomyces dermatitidis spores. If it involves only the lungs, it is called pulmonary blastomycosis. Only about half of people with the disease have symptoms, which can include fever, cough, night sweats, muscle pains, weight loss, chest pain, and feeling tired. These symptoms usually develop between three weeks and three months after breathing in the spores. Blastomycosis can affect both immunocompetent and immunosuppressed individuals. In those with weak immune systems, the disease can spread to other areas of the body, including the skin and bones.

Eumycetoma, also known as Madura foot, is a persistent fungal infection of the skin and the tissues just under the skin, affecting most commonly the feet, although it can occur in hands and other body parts. It starts as a painless wet nodule, which may be present for years before ulceration, swelling, grainy discharge and weeping from sinuses and fistulae, followed by bone deformity.

An arthropathy is a disease of a joint.

The Young Sick Bacchus, also known as the Sick Bacchus or the Self-Portrait as Bacchus, is an early self-portrait by the Baroque artist Michelangelo Merisi da Caravaggio, dated between 1593 and 1594. It now hangs in the Galleria Borghese in Rome. According to Caravaggio's first biographer, Giovanni Baglione, it was a cabinet piece painted by the artist using a mirror.
Osteitis is inflammation of bone. More specifically, it can refer to one of the following conditions:
Paratyphoid fever, also known simply as paratyphoid, is a bacterial infection caused by one of the three types of Salmonella enterica. Symptoms usually begin 6–30 days after exposure and are the same as those of typhoid fever. Often, a gradual onset of a high fever occurs over several days. Weakness, loss of appetite, and headaches also commonly occur. Some people develop a skin rash with rose-colored spots. Without treatment, symptoms may last weeks or months. Other people may carry the bacteria without being affected; however, they are still able to spread the disease to others. Typhoid and paratyphoid are of similar severity. Paratyphoid and typhoid fever are types of enteric fever.
Talaromycosis is a fungal infection that presents with painless skin lesions of face and neck, fever, anaemia, large lymph glands and liver.

Children's National Hospital is a nationally ranked, freestanding, 323-bed, pediatric acute care children's hospital located in Washington D.C.. It is affiliated with the George Washington University School of Medicine and the Howard University College of Medicine. The hospital provides comprehensive pediatric specialties and subspecialties to infants, children, teens, and young adults aged 0–21 throughout the region. The hospital features an ACS verified level I pediatric trauma center, the only in the District of Columbia. Its regional pediatric intensive-care unit and neonatal intensive care units serve the region. The hospital also has a rooftop helipad for critical pediatric transport.
A skin infection is an infection of the skin in humans and other animals, that can also affect the associated soft tissues such as loose connective tissue and mucous membranes. They comprise a category of infections termed skin and skin structure infections (SSSIs), or skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs), and acute bacterial SSSIs (ABSSSIs). They are distinguished from dermatitis. although skin infections can result in skin inflammation.

A pathologic fracture is a bone fracture caused by weakness of the bone structure that leads to decrease mechanical resistance to normal mechanical loads. This process is most commonly due to osteoporosis, but may also be due to other pathologies such as: cancer Multiple Myeloma, infection, inherited bone disorders, or a bone cyst. Only a small number of conditions are commonly responsible for pathological fractures, including osteoporosis, osteomalacia, Paget's disease, Osteitis, osteogenesis imperfecta, benign bone tumours and cysts, secondary malignant bone tumours and primary malignant bone tumours.

The Bone River is a short river in the U.S. state of Washington. It is about 6 miles (9.7 km) long.
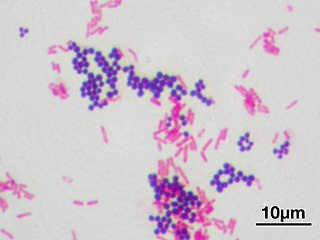
Infectious diseases, also known as infectiology, is a medical specialty dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of complex infections. An infectious disease specialist's practice consists of managing nosocomial (healthcare-acquired) infections or community-acquired infections and is historically associated with travel medicine and tropical medicine.
References
- ↑ Root, Richard K. (1999). Clinical Infectious Diseases: A Practical Approach. Oxford University Press. p. 741. ISBN 9780195081039 . Retrieved 5 December 2017.