Related Research Articles

Tietze syndrome is a benign inflammation of one or more of the costal cartilages. It was first described in 1921 by German surgeon Alexander Tietze and was subsequently named after him. The condition is characterized by tenderness and painful swelling of the anterior (front) chest wall at the costochondral, sternocostal, or sternoclavicular junctions. Tietze syndrome affects the true ribs and has a predilection for the 2nd and 3rd ribs, commonly affecting only a single joint.

Rheumatism or rheumatic disorders are conditions causing chronic, often intermittent pain affecting the joints or connective tissue. Rheumatism does not designate any specific disorder, but covers at least 200 different conditions, including arthritis and "non-articular rheumatism", also known as "regional pain syndrome" or "soft tissue rheumatism". There is a close overlap between the term soft tissue disorder and rheumatism. Sometimes the term "soft tissue rheumatic disorders" is used to describe these conditions.

Cauliflower ear is an irreversible condition that occurs when the external portion of the ear is hit and develops a blood clot or other collection of fluid under the perichondrium. This separates the cartilage from the overlying perichondrium that supplies its nutrients, causing it to die and resulting in the formation of fibrous tissue in the overlying skin. As a result, the outer ear becomes permanently swollen and deformed, resembling a cauliflower, hence the name.

Costochondritis, also known as chest wall pain syndrome or costosternal syndrome, is a benign inflammation of the upper costochondral and sternocostal joints. 90% of patients are affected in multiple ribs on a single side, typically at the 2nd to 5th ribs. Chest pain, the primary symptom of costochondritis, is considered a symptom of a medical emergency, making costochondritis a common presentation in the emergency department. One study found costochondritis was responsible for 30% of patients with chest pain in an emergency department setting.

Ear pain, also known as earache or otalgia, is pain in the ear. Primary ear pain is pain that originates from the ear. Secondary ear pain is a type of referred pain, meaning that the source of the pain differs from the location where the pain is felt.

Cristina Monet Zilkha, known during her recording career simply as Cristina, was an American singer and writer, best known for her no wave recordings made for ZE Records in the late 1970s and early 1980s in New York City. She "was a pioneer in blending the artsiness and attitude of punk with the joyful energy of disco and pop.... [which] helped pave the way for the massive successes of her contemporaries, like Madonna and Cyndi Lauper, and anticipated the rise of confrontational but danceable alt-pop acts..." in a mode that was at once "campy, self-aware, and infectious."
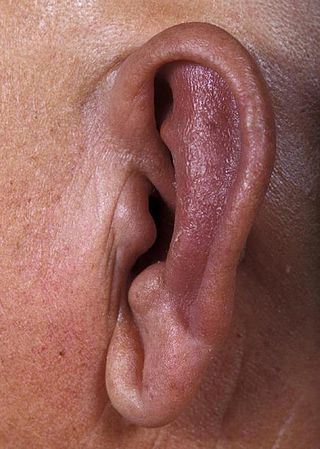
Relapsing polychondritis is a systemic disease characterized by repeated episodes of inflammation and in some cases deterioration of cartilage. The disease can be life-threatening if the respiratory tract, heart valves, or blood vessels are affected. The exact mechanism is poorly understood.
Chondropathy refers to a disease of the cartilage. It is frequently divided into 5 grades, with 0-2 defined as normal and 3-4 defined as diseased.

Saddle nose is a condition associated with nasal trauma, congenital syphilis, relapsing polychondritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, cocaine abuse, and leprosy, among other conditions. The most common cause is nasal trauma. It is characterized by a loss of height of the nose, because of the collapse of the nasal bridge. The depressed nasal dorsum may involve bony, cartilaginous, or both bony and cartilaginous components of the nasal dorsum.

Episcleritis is a benign, self-limiting inflammatory disease affecting part of the eye called the episclera. The episclera is a thin layer of tissue that lies between the conjunctiva and the connective tissue layer that forms the white of the eye (sclera). Episcleritis is a common condition, and is characterized by the abrupt onset of painless eye redness.

The costal margin, also known as the costal arch, is the lower edge of the chest (thorax) formed by the bottom edge of the rib cage.

Laryngotracheal stenosis refers to abnormal narrowing of the central air passageways. This can occur at the level of the larynx, trachea, carina or main bronchi. In a small number of patients narrowing may be present in more than one anatomical location.
Pseudocyst of the auricle, also known as auricular pseudocyst, endochondral pseudocyst, cystic chondromalacia, intracartilaginous auricular seroma cyst, and benign idiopathic cystic chondromalacia, is a cutaneous condition characterized by a fluctuant, tense, noninflammatory swelling on the upper half of the ear, known as the auricle or pinna. Pseudocysts of the auricle are nontender, noninflammatory cystic lesions that progress over a 4- to 12-week period, ranging from 1 to 5 cm in diameter. They are usually unilateral, often on the right ear, but can also present bilaterally.

Perichondritis is inflammation of the perichondrium, a layer of connective tissue which surrounds cartilage. A common form, auricular perichondritis involves infection of the pinna due to infection of traumatic or surgical wound or the spread of inflammation into depth. It may lead to severe deformation of the pinna if not treated vigorously with IV antibiotics. The causative organism is usually Pseudomonas aeruginosa. A rare form is laryngeal perichondritis. It develops suddenly due to an injury, virulent organisms or compromised immune status of the host, and also affects cartilage of the larynx. This may result in deformations and stenoses.
Mouth and genital ulcers with inflamed cartilage syndrome or MAGIC syndrome refers to a condition in which an individual exhibits symptoms of both relapsing polychondritis (RP) and Behcet's disease (BD). Inflammatory ulcers in the mouth, genitalia, and skin are the hallmark of Behcet's disease (BD), a multisystem illness that is chronic and relapsing. Autoimmune recurrent chondritis of the larynx, tracheobronchial tree, nose, ears, and mouth is known as relapsing polychondritis (RP).
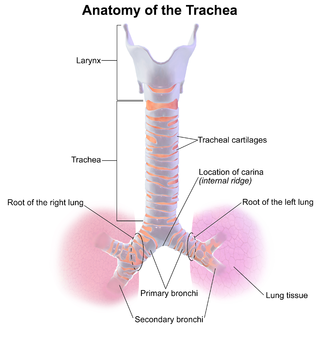
Tracheobronchomalacia (TBM) is a condition characterized by flaccidity of the tracheal support cartilage which leads to tracheal collapse. This condition can also affect the bronchi. There are two forms of this condition: primary TBM and secondary TBM. Primary TBM is congenital and starts as early as birth. It is mainly linked to genetic causes. Secondary TBM is acquired and starts in adulthood. It is mainly developed after an accident or chronic inflammation.

Tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica (TO) is a rare benign disease of unknown cause, in which multiple cartilaginous or bony submucosal nodules project into the trachea and proximal bronchi. The nodules usually spare the posterior wall of the airway because they are of cartilaginous origin, while the posterior wall of the airway is membranous (does not contain cartilage). This is as opposed to tracheobronchial amyloidosis, which does not spare the posterior wall.
Chondrolysis [ICD Code M94.3] is the process of breakdown of cartilage. It can occur as a result of trauma. Intra-articular infusions of certain local anesthetic agents such as bupivacaine, lidocaine, ropivacaine and levobupivacaine can also lead to this effect.
VEXAS syndrome is an adult-onset autoinflammatory disease primarily affecting males, caused by a somatic mutation of the UBA1 gene in hematopoietic progenitor cells. The name VEXAS is an acronym deriving from the core features of disease:

David B. Beck is an American physician-scientist, clinical geneticist, and researcher who co-discovered VEXAS Syndrome. He holds dual appointments as an assistant professor in the Department of Medicine and the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, and is a member of the Center for Human Genetics and Genomics and the Division of Rheumatology at New York University Grossman School of Medicine and NYU Langone Health.