
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract may include anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, inflammation of the eye, and fatigue. The skin rashes may be due to infections as well as pyoderma gangrenosum or erythema nodosum. Bowel obstruction may occur as a complication of chronic inflammation, and those with the disease are at greater risk of colon cancer and small bowel cancer.

Coeliac disease or celiac disease is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barley. Classic symptoms include gastrointestinal problems such as chronic diarrhoea, abdominal distention, malabsorption, loss of appetite, and among children failure to grow normally. Non-classic symptoms are more common, especially in people older than two years. There may be mild or absent gastrointestinal symptoms, a wide number of symptoms involving any part of the body, or no obvious symptoms. Coeliac disease was first described in childhood; however, it may develop at any age. It is associated with other autoimmune diseases, such as Type 1 diabetes mellitus and Hashimoto's thyroiditis, among others.

Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes. The name typically refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, drenching sweats, unintended weight loss, itching, and constantly feeling tired. The enlarged lymph nodes are usually painless. The sweats are most common at night.

A nut is a fruit consisting of a hard or tough nutshell protecting a kernel which is usually edible. In general usage and in a culinary sense, a wide variety of dry seeds are called nuts, but in a botanical context "nut" implies that the shell does not open to release the seed (indehiscent).

Iodobenzamide is a pharmaceutical drug used for diagnostic purposes. It is a dopamine antagonist and it can be used by nuclear medicine physicians as a radioactive tracer for SPECT where the radioactive isotope is iodine-123 or iodine-125. The main purpose of a brain study with IBZM is the differentiation of Parkinson's disease from other neurodegenerative diseases such as Lewy Body dementia and multiple system atrophy.

Kidney disease, or renal disease, technically referred to as nephropathy, is damage to or disease of a kidney. Nephritis is an inflammatory kidney disease and has several types according to the location of the inflammation. Inflammation can be diagnosed by blood tests. Nephrosis is non-inflammatory kidney disease. Nephritis and nephrosis can give rise to nephritic syndrome and nephrotic syndrome respectively. Kidney disease usually causes a loss of kidney function to some degree and can result in kidney failure, the complete loss of kidney function. Kidney failure is known as the end-stage of kidney disease, where dialysis or a kidney transplant is the only treatment option.
A medical condition is a broad term that includes all diseases and disorders.
Mathematical models can project how infectious diseases progress to show the likely outcome of an epidemic and help inform public health and plant health interventions. Models use basic assumptions or collected statistics along with mathematics to find parameters for various infectious diseases and use those parameters to calculate the effects of different interventions, like mass vaccination programs. The modelling can help decide which intervention(s) to avoid and which to trial, or can predict future growth patterns, etc.
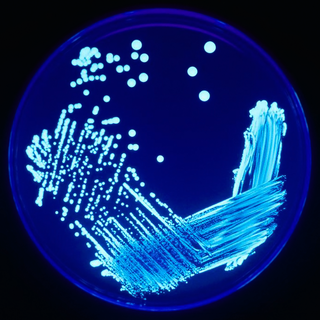
The Legionellales are an order of Pseudomonadota. Like all Pseudomonadota, they are Gram-negative. They comprise two families, typified by Legionella and Coxiella, both of which include notable pathogens. For example, Q fever is caused by Coxiella burnetii and Legionella pneumophila causes Legionnaires' disease and Pontiac fever.

Waterborne diseases are conditions caused by pathogenic micro-organisms that are transmitted by water. These diseases can be spread while bathing, washing, drinking water, or by eating food exposed to contaminated water. They are a pressing issue in rural areas amongst developing countries all over the world. While diarrhea and vomiting are the most commonly reported symptoms of waterborne illness, other symptoms can include skin, ear, respiratory, or eye problems. Lack of clean water supply, sanitation and hygiene (WASH) are major causes for the spread of waterborne diseases in a community. Therefore, reliable access to clean drinking water and sanitation is the main method to prevent waterborne diseases.
Venereology is a branch of medicine that is concerned with the study and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). The name derives from Roman goddess Venus, associated with love, beauty and fertility. A physician specializing in venereology is called a venereologist. In many areas of the world, the specialty is usually combined with dermatology.
Phytophthora citricola is a plant pathogen. It was first described by Kaneyoshi (Kenkichi) Sawada in 1927 when it was isolated from orange trees in present-day Taiwan. It has since been found causing disease on a wide variety of plants.
Phoma tracheiphila is a fungal plant pathogen. It causes a disease known as Mal secco on citrus trees. It occurs in dry, cool climates such as the Mediterranean, Black Sea and Asia Minor. It forms pycniospores that are carried short distances by rain, or by wind to new leaves, where germinated hyphae invade stomata or more likely fresh wounds.

Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens, and is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As the disease advances, symptoms can include problems with language, disorientation, mood swings, loss of motivation, self-neglect, and behavioral issues. As a person's condition declines, they often withdraw from family and society. Gradually, bodily functions are lost, ultimately leading to death. Although the speed of progression can vary, the typical life expectancy following diagnosis is three to nine years.

An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated that there are more than 80 recognized autoimmune diseases, with recent scientific evidence suggesting the existence of potentially more than 100 distinct conditions. Nearly any body part can be involved.

Pardoprunox (INN) is an antiparkinsonian drug developed by Solvay for the treatment of Parkinson's disease that reached phase III clinical trials before being discontinued. It was also being investigated for the treatment of depression and anxiety but these indications appear to have been abandoned as well.

Radequinil is a cognitive enhancer which acts as a partial inverse agonist of the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor. It was under development by Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and made it to phase II clinical trials but development seems to have been halted and it was never marketed.

Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2. The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quickly spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
Ghana Infectious Disease Centre (GIDC) is a centre built to improve the medical diagnostic and research capacity of Ghana with regard to infectious diseases. The facility was built due to the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic in Ghana. Establishing the centre was facilitated by the Ghana COVID-19 Private Sector Fund in collaboration with the Ghana Armed Forces at the Ga East Municipal Hospital in Accra. The old Shai Osudoku District Hospital was also renovated into one of the infectious diseases centres in the Shai Osudoku District in Dodowa. This shares a boundary with the Shai Osudoku District Health Directorate. The president, Nana Addo Dankwa Akuffo Addo, inspected the centre on 30 October 2020













