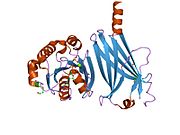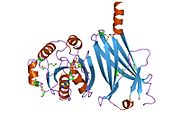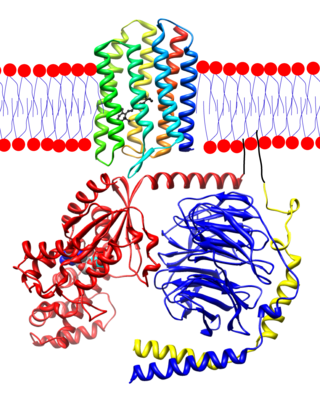
Transducin (Gt) is a protein naturally expressed in vertebrate retina rods and cones and it is very important in vertebrate phototransduction. It is a type of heterotrimeric G-protein with different α subunits in rod and cone photoreceptors.

Rod cells are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in lower light better than the other type of visual photoreceptor, cone cells. Rods are usually found concentrated at the outer edges of the retina and are used in peripheral vision. On average, there are approximately 92 million rod cells in the human retina. Rod cells are more sensitive than cone cells and are almost entirely responsible for night vision. However, rods have little role in color vision, which is the main reason why colors are much less apparent in dim light.
GTPase-activating proteins or GTPase-accelerating proteins (GAPs) are a family of regulatory proteins whose members can bind to activated G proteins and stimulate their GTPase activity, with the result of terminating the signaling event. GAPs are also known as RGS protein, or RGS proteins, and these proteins are crucial in controlling the activity of G proteins. Regulation of G proteins is important because these proteins are involved in a variety of important cellular processes. The large G proteins, for example, are involved in transduction of signaling from the G protein-coupled receptor for a variety of signaling processes like hormonal signaling, and small G proteins are involved in processes like cellular trafficking and cell cycling. GAP's role in this function is to turn the G protein's activity off. In this sense, GAPs function is opposite to that of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), which serve to enhance G protein signaling.
Visual phototransduction is the sensory transduction process of the visual system by which light is detected to yield nerve impulses in the rod cells and cone cells in the retina of the eye in humans and other vertebrates. It relies on the visual cycle, a sequence of biochemical reactions in which a molecule of retinal bound to opsin undergoes photoisomerization, initiates a cascade that signals detection of the photon, and is indirectly restored to its photosensitive isomer for reuse. Phototransduction in some invertebrates such as fruit flies relies on similar processes.

3′,5′-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterases (EC 3.1.4.17) are a family of phosphodiesterases. Generally, these enzymes hydrolyze a nucleoside 3′,5′-cyclic phosphate to a nucleoside 5′-phosphate:

Ran also known as GTP-binding nuclear protein Ran is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAN gene. Ran is a small 25 kDa protein that is involved in transport into and out of the cell nucleus during interphase and also involved in mitosis. It is a member of the Ras superfamily.

Ras-related protein Rap-1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAP1A gene.
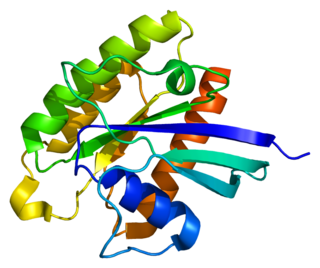
RHEB also known as Ras homolog enriched in brain (RHEB) is a GTP-binding protein that is ubiquitously expressed in humans and other mammals. The protein is largely involved in the mTOR pathway and the regulation of the cell cycle.

X-linked retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator is a GTPase-binding protein that in humans is encoded by the RPGR gene. The gene is located on the X-chromosome and is commonly associated with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP). In photoreceptor cells, RPGR is localized in the connecting cilium which connects the protein-synthesizing inner segment to the photosensitive outer segment and is involved in the modulation of cargo trafficked between the two segments.

Ran GTPase-activating protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RANGAP1 gene.

Rod cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase subunit beta is the beta subunit of the protein complex PDE6 that is encoded by the PDE6B gene. PDE6 is crucial in transmission and amplification of visual signal. The existence of this beta subunit is essential for normal PDE6 functioning. Mutations in this subunit are responsible for retinal degeneration such as retinitis pigmentosa or congenital stationary night blindness.

Rnd1 is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rnd subgroup of the Rho family of GTPases. It is encoded by the gene RND1.

Uncoordinated-119 (Unc-119) is a protein that has been identified in C. elegans, humans, mice, zebrafish, rabbits, pig, calf, monkey, and protozoa. They have been classified in the GMP phosphodiesterase, delta superfamily. Unc-119 proteins are categorized into their own family but are shown to be ancestrally related to PrBP and rhoGDI. It has been given many different names: Retinal Protein 4, HRG4, POC7 Centriolar Protein Homolog A, IMD13, POC7A, and RG4.

ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARL3 gene.

Retinal rod rhodopsin-sensitive cGMP 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase subunit gamma is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDE6G gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(t) subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAT1 gene.

Ras-related protein Rap-2b is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAP2B gene. RAP2B belongs to the Ras-related protein family.

ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARL2 gene.

Rod cGMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase subunit alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDE6A gene.

cAMP and cAMP-inhibited cGMP 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 10A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDE10A gene.