Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase 2-alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PI4K2A gene. [5] [6] [7]
Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase 2-alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PI4K2A gene. [5] [6] [7]
This gene encodes a phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase which catalyzes phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol at the D-4 position, yielding phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PI4P). Besides the fact, that PI4P serves as a precursor for other important phosphoinositides, such as phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, PI4P is an essential molecule in the cellular signaling and trafficking especially in the Golgi apparatus and the trans Golgi network.
Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases are evolutionary conserved among eukaryotes and include four human isoforms
Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase 2-alpha (PI4K2A) is the most abundant phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase in human cells and is responsible for the synthesis of approximately 50% of the total PI4P within the cell. PI4K2A is associated mainly with the membranes of the trans Golgi network and early and late endosomes; [8] its membrane association is achieved by a heavy palmitoylation within a specific cysteine-rich motif. [9] Besides the synthesis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, PI4K2A is involved in various cell processes including membrane trafficking, regulation of endosomal sorting promoting target protein recruitment to endosomes or trans Golgi network, or signal transduction. Particularly, it regulates e.g. targeting of clathrin adaptor complexes to the Golgi apparatus, [10] EGFR signaling, [11] or the Wnt signaling pathway. [12]
PI4K2A is important in lysosomal quality control. It is the first essential enzyme of the phosphoinositide-initiated membrane tethering and lipid transport (PITT) pathway for rapid lysosomal repair. [13] Upon lysosomal membrane damage, PI4K2A is strongly recruited to lysosomes, leading to robust lysosomal PI4P production. Such lysosomal PI4K2A/PI4P signaling drives rapid lysosomal repair through extensive membrane contacts between the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and damaged lysosomes as well as multiple ER-to-lysosomal lipid transfer processes.
Pi4k2a gene trap mouse show pre-mature aging and neurodegeneration, with increased lipofuscin accumulation. [14] PI4K2A-deleted patients have complex and severe developmental problems along with neurodegeneration. [15]
Dysfunction of PI4K2A may contribute to tumour growth, [16] spastic paraplegia, [14] Gaucher's disease, [17] or Alzheimer's disease. [18]

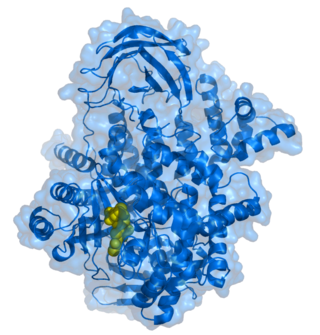
PI4K2A is composed of a proline-rich N-terminal region and a kinase domain located C-terminally. The proline-rich N-terminal region contains physiologically important binding sites for a ubiquitin ligase Itch [20] and clathrin adaptor complex 3, [21] but is likely disordered and dispensable for the kinase activity. [22] The kinase domain can be divided into N-terminal and C-terminal lobes with the ATP binding groove and putative phosphatidylinositol binding pocket in between. The C-lobe of the kinase domain contains an additional lateral hydrophobic pocket with no distinct function assigned yet. [19] [23]

Endosomes are a collection of intracellular sorting organelles in eukaryotic cells. They are parts of endocytic membrane transport pathway originating from the trans Golgi network. Molecules or ligands internalized from the plasma membrane can follow this pathway all the way to lysosomes for degradation or can be recycled back to the cell membrane in the endocytic cycle. Molecules are also transported to endosomes from the trans Golgi network and either continue to lysosomes or recycle back to the Golgi apparatus.
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which in turn are involved in cancer.
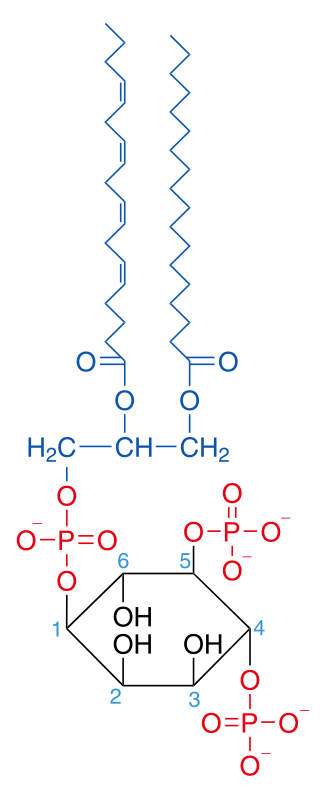
Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate or PtdIns(4,5)P2, also known simply as PIP2 or PI(4,5)P2, is a minor phospholipid component of cell membranes. PtdIns(4,5)P2 is enriched at the plasma membrane where it is a substrate for a number of important signaling proteins. PIP2 also forms lipid clusters that sort proteins.

Pleckstrin homology domain or (PHIP) is a protein domain of approximately 120 amino acids that occurs in a wide range of proteins involved in intracellular signaling or as constituents of the cytoskeleton.

Phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate is one of the seven phosphoinositides found in eukaryotic cell membranes. In quiescent cells, the PtdIns(3,5)P2 levels, typically quantified by HPLC, are the lowest amongst the constitutively present phosphoinositides. They are approximately 3 to 5-fold lower as compared to PtdIns3P and PtdIns5P levels, and more than 100-fold lower than the abundant PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2. PtdIns(3,5)P2 was first reported to occur in mouse fibroblasts and budding yeast S. cerevisiae in 1997. In S. cerevisiae PtdIns(3,5)P2 levels increase dramatically during hyperosmotic shock. The response to hyperosmotic challenge is not conserved in most tested mammalian cells except for differentiated 3T3L1 adipocytes.
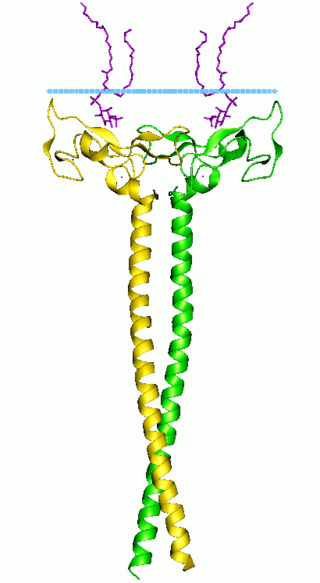
In molecular biology the FYVE zinc finger domain is named after the four cysteine-rich proteins: Fab 1, YOTB, Vac 1, and EEA1, in which it has been found. FYVE domains bind phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate, in a way dependent on its metal ion coordination and basic amino acids. The FYVE domain inserts into cell membranes in a pH-dependent manner. The FYVE domain has been connected to vacuolar protein sorting and endosome function.

Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3R1 gene.
In enzymology, a ceramide kinase, also abbreviated as CERK, is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:

Hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HGS gene.

Phospholipase C (PLC) is a class of membrane-associated enzymes that cleave phospholipids just before the phosphate group (see figure). It is most commonly taken to be synonymous with the human forms of this enzyme, which play an important role in eukaryotic cell physiology, in particular signal transduction pathways. Phospholipase C's role in signal transduction is its cleavage of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into diacyl glycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3), which serve as second messengers. Activators of each PLC vary, but typically include heterotrimeric G protein subunits, protein tyrosine kinases, small G proteins, Ca2+, and phospholipids.

Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 3-kinase C2 domain-containing alpha polypeptide is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIK3C2A gene.

Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PI4KB gene.

Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PI4KA gene.

PIKfyve, a FYVE finger-containing phosphoinositide kinase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIKFYVE gene.

Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase type-1 gamma is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIP5K1C gene.

Collagen type IV alpha-3-binding protein, also known as ceramide transfer protein (CERT) or StAR-related lipid transfer protein 11 (STARD11) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL4A3BP gene. The protein contains a pleckstrin homology domain at its amino terminus and a START domain towards the end of the molecule. It is a member of the StarD2 subfamily of START domain proteins.

Phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate 4-kinase type-2 alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIP4K2A gene.

Phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase type-1 alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIP5K1A gene.

Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type 2-beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PI4K2B gene.

In the field of biochemistry, PDPK1 refers to the protein 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1, an enzyme which is encoded by the PDPK1 gene in humans. It is implicated in the development and progression of melanomas.