
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceans, with an area of about 106,460,000 km2 (41,100,000 sq mi). It covers approximately 20 percent of Earth's surface and about 29 percent of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" from the "New World" in the European perception of the World.
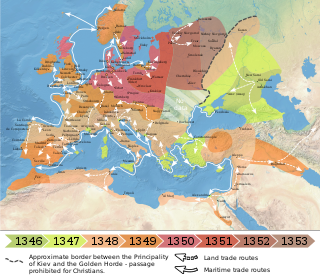
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Afro-Eurasia from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causing the death of 75–200 million people in Eurasia and North Africa, peaking in Europe from 1347 to 1351. Bubonic plague is caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, but it may also cause septicaemic or pneumonic plagues.

Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France to the south. Its capital, Luxembourg City, is one of the four official capitals of the European Union and the seat of the Court of Justice of the European Union, the highest judicial authority in the EU. Its culture, people, and languages are highly intertwined with its neighbors, making it a mixture of French and German cultures. It has three official languages: French, German, and the national language of Luxembourgish.

Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is silvery with a hint of blue; it tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements.

Paris is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,175,601 residents as of 2018, in an area of more than 105 square kilometres. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of Europe's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, science and arts. The City of Paris is the centre and seat of government of the region and province of Île-de-France, or Paris Region, which has an estimated population of 12,174,880, or about 18 percent of the population of France as of 2017. The Paris Region had a GDP of €709 billion in 2017. According to the Economist Intelligence Unit Worldwide Cost of Living Survey in 2018, Paris was the second most expensive city in the world, after Singapore and ahead of Zürich, Hong Kong, Oslo and Geneva. Another source ranked Paris as most expensive, on a par with Singapore and Hong Kong, in 2018.

The Proto-Indo-Europeans were a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction.

Ashkenazi Jews, also known as Ashkenazic Jews or, by using the Hebrew plural suffix -im,Ashkenazim are a Jewish diaspora population who coalesced in the Holy Roman Empire around the end of the first millennium.

Alain de Benoist – also known as Fabrice Laroche, Robert de Herte, David Barney, and other pen names – is a French journalist and political philosopher, a founding member of the Nouvelle Droite, and the leader of the ethno-nationalist think tank GRECE.
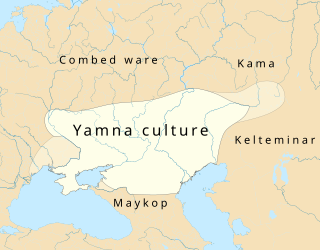
The Yamnaya culture (/ˈjamnaja/), also known as the Yamnaya Horizon, Yamna culture, Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological culture of the region between the Southern Bug, Dniester, and Ural rivers, dating to 3300–2600 BC. Its name derives from its characteristic burial tradition: Я́мная is a Russian adjective that means 'related to pits (yama)', and these people used to bury their dead in tumuli (kurgans) containing simple pit chambers. The people of the Yamnaya culture were likely the result of a genetic admixture between the descendants of Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers and people related to hunter-gatherers from the Caucasus. People with this ancestral component are known as Western Steppe Herders. Their material culture was very similar to the Afanasevo culture, and the populations of both cultures are genetically indistinguishable. They lived primarily as nomads, with a chiefdom system and wheeled carts and wagons that allowed them to manage large herds.

The Indo-Aryan migrations were the migrations into the Indian subcontinent of Indo-Aryan peoples, an ethnolinguistic group that spoke Indo-Aryan languages, the predominant languages of today's North India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and the Maldives. Indo-Aryan population movements into the region and Anatolia from Central Asia are considered to have started after 2000 BCE, as a slow diffusion during the Late Harappan period, which led to a language shift in the northern Indian subcontinent. The Iranian languages were brought into the Iranian plateau by the Iranians, who were closely related to the Indo-Aryans.
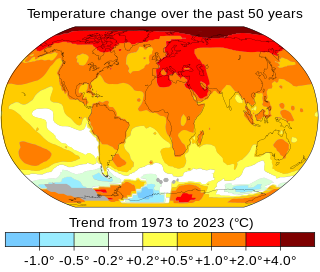
Climate change includes both global warming driven by human-induced emissions of greenhouse gases and the resulting large-scale shifts in weather patterns. Though there have been previous periods of climatic change, humans have since the mid-20th century had an unprecedented impact on Earth's climate system and have caused change on a global scale.

France, officially the French Republic, is a country primarily located in Western Europe, consisting of metropolitan France and several overseas regions and territories. The metropolitan area of France extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. The overseas territories include French Guiana in South America and several islands in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg and Germany to the northeast, Switzerland, Monaco and Italy to the east, Andorra and Spain to the south, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname and Brazil in the Americas. The country's eighteen integral regions span a combined area of 643,801 km2 (248,573 sq mi) and a total population of 67.413 million. France is a unitary semi-presidential republic with its capital in Paris, the country's largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. Other major urban areas include Lyon, Marseille, Toulouse, Bordeaux, Lille and Nice. France, including its overseas territories, has the most time zones of any country, with a total of twelve.
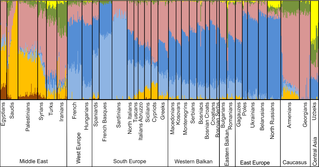
The most significant recent dispersal of modern humans from Africa gave rise to an undifferentiated "non-African" lineage by some 70-50 ka. By about 50-40 ka a basal West Eurasian lineage had emerged, as had a separate East Asian lineage. Both basal East and West Eurasians acquired Neanderthal admixture in Europe and Asia.
The genetic history of the British Isles is the subject of research within the larger field of human population genetics. It has developed in parallel with DNA testing technologies capable of identifying genetic similarities and differences between both modern and ancient populations. The conclusions of population genetics regarding the British Isles in turn draw upon and contribute to the larger field of understanding the history of the human occupation of the area, complementing work in linguistics, archaeology, history and genealogy.

Dominique Venner was a French historian, journalist and essayist. Venner was a member of the Organisation armée secrète and later became a European nationalist, founding Europe-Action, before withdrawing from politics to focus on a career as a historian. He specialized in military and political history. At the time of his death, he was the editor of the La Nouvelle Revue d'Histoire, a bimonthly history magazine. On 21 May 2013, Venner committed suicide inside the cathedral of Notre Dame de Paris.
Haplogroup R1a, or haplogroup R-M420, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup which is distributed in a large region in Eurasia, extending from Scandinavia and Central Europe to southern Siberia and South Asia.
Haplogroup R1b (R-M343), also known as Hg1 and Eu18, is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup.

Neanderthals are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic humans who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago. They most likely went extinct due to assimilation into the modern human genome, great climatic change, disease, or a combination of these factors. They were fully replaced by early European modern humans.

Overseas France consists of all the French-administered territories outside Europe, mostly remains of the French colonial empire. It includes island territories in the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans, French Guiana on the South American continent, and several peri-Antarctic islands as well as a claim in Antarctica. Excluding the district of Adélie Land, where French sovereignty is effective de jure by French law, but where the French exclusive claim on this part of Antarctica is frozen by the Antarctic Treaty, overseas France covers a land area of 119,396 km2 (46,099 sq mi) and accounts for 18.0% of the French Republic's land territory. Its exclusive economic zone (EEZ) of 9,825,538 km2 (3,793,661 sq mi) accounts for 96.7% of the EEZ of the French Republic.
La République En Marche !, sometimes called simply En Marche ! as its original name, is a centrist and liberal political party in France.














