
Eurotiomycetes is a large class of ascomycetes with cleistothecial ascocarps within the subphylum Pezizomycotina, currently containing around 3810 species according to the Catalogue of Life. It is the third largest lichenized class, with more than 1200 lichen species that are mostly bitunicate in the formation of asci. It contains most of the fungi previously known morphologically as "Plectomycetes".

The Eurotiales are an order of sac fungi, also known as the green and blue molds. It was circumscribed in 1980.

The Trichocomaceae are a family of fungi in the order Eurotiales. Taxa are saprobes with aggressive colonization strategies, adaptable to extreme environmental conditions. Family members are cosmopolitan in distribution, ubiquitous in soil, and common associates of decaying plant and food material.

Aspergillus is a genus consisting of several hundred mould species found in various climates worldwide.

Paecilomyces is a genus of fungi. A number of species in this genus are plant pathogens.

Acrophialophora fusispora is a poorly studied ascomycete fungus found in soil, air and various plants. A. fusispora is morphologically similar to the genera Paecilomyces and Masonia, but differ in the presence of pigmented conidiophores, verticillate phialides, and frequent sympodial proliferation. Moreover, A. fusispora is distinguished by its pigmented spindle-shaped conidia, covered with spiral bands. The fungus is naturally found in soils of tropical to temperate regions. The fungus has been identified as a plant and animal pathogen, and has recently been recognized as an emerging opportunistic human pathogen. A. fusispora infection in human is rare and has few documented clinical cases, but due to the rarity of the fungus and potential misidentification, the infections may be underdiagnosed. Clinical cases of A. fusispora include cases of keratitis, pulmonary colonization and infection, and cerebral infections. The fungus also has two documented cases of infection in dogs.

Ramaria formosa, commonly known as the salmon coral, beautiful clavaria, handsome clavaria, yellow-tipped- or pink coral fungus, is a coral fungus found in Europe. It is widely held to be mildly poisonous if consumed, giving rise to acute gastrointestinal symptoms of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and colicky pain. It is a pinkish, much-branched coral-shape reaching some 20 cm (8 in) high. Similar forms collected in North America are now considered to represent a different species than the European Ramaria formosa.
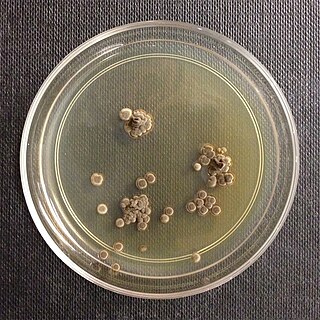
The Wallemiomycetes are a class of fungi in the division Basidiomycota. It consists of the single order Wallemiales, containing the single family Wallemiaceae, which in turn contains the single genus Wallemia. The phylogenetic origin of the lineage was placed to various parts of Basidiomycota, but according to the analysis of a larger dataset it is a sister group of Agaricomycotina. The genus contains species of xerophilic molds that are found worldwide. The seven described species are distinguished by conidial size, xerotolerance, halotolerance, chaotolerance, growth temperature regimes, extracellular enzyme activity profiles, and secondary metabolite patterns. They are typically isolated from low-moisture foods, indoor air dust, salterns and soil. W. sebi is thought to be one of the causes of the hypersensitivity pneumonitis known as the farmer's lung disease, but since the other species were recognised and separated from W. sebi only recently, their role in the disease cannot be excluded.
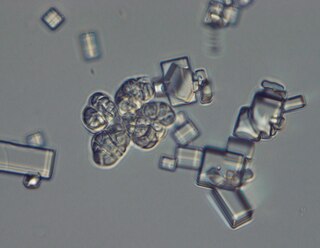
Wallemia ichthyophaga is one of the three species of fungi in the genus Wallemia, which in turn is the only genus of the class Wallemiomycetes. The phylogenetic origin of the lineage was placed to various parts of Basidiomycota, but according to the analysis of larger datasets it is a (495-million-years-old) sister group of Agaricomycotina. Although initially believed to be asexual, population genomics found evidence of recombination between strains and a mating type locus was identified in all sequenced genomes of the species.
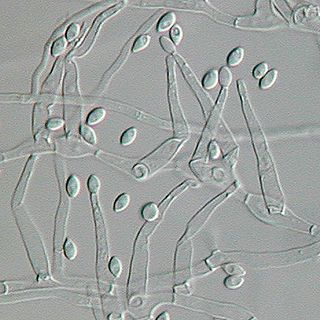
Paecilomyces variotii, also known by the name Byssochlamys spectabilis for the sexual state, is a common environmental mold from the Phylum Ascomycota. It is widespread in the environment and can be found in composts, soils and wood, as well es a common environmental contaminant in indoor air and carpet dust. Ascospores of the sexual state of P. variotii are strongly heat-resistant. As such the fungus is a common contaminant of heat-treated foods and juices. Paecilomyces variotii has been associated with a number of infective diseases of humans and animals.

Rhizophagus is a genus of arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi that form symbiotic relationships (mycorrhizas) with plant roots. The genome of Rhizophagus irregularis was recently sequenced.
Aspergillus unguis is a species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus, and the asexual state (anamorph) of Emericella unguis. Aspergillus unguis is a filamentous soil-borne fungus found on decomposing plant matter and other moist substrates including with building materials and household dust. Aspergillus unguis occurs mainly in tropical and subtropical soils but has also been isolated from various marine and aquatic habitats. The species was first isolated in 1935 by Weill and L. Gaudin. Historically, A. unguis was assigned to the A. nidulans group, a common group of soil-borne fungi due to the resemblance of its ascospores and cleistothecia to those of Emericella nidulans. Aspergillus unguis is distinctive, however, in possessing spicular hyphae. A number of synonyms have been collapsed into this species, including Sterigmatocystis unguis, Aspergillus laokiashanensis and Aspergillus mellinus.

The genus Saproamanita contains about 24 species of agarics and is one of six genera in the family Amanitaceae, of which the similar Amanita is also a member. Saproamanita differs from Amanita in that its species are saprophytic, and not ectomycorrhizal.
Thermoascus is a genus of soil fungi in the family Trichocomaceae. Species in the genus are characterized by the production of heat-resistant ascospores. Thermoascus was circumscribed by German botanist Hugo Miehe in 1907.

Genomoviridae is a family of single stranded DNA viruses that mainly infect fungi. The genomes of this family are small. The genomes are circular single-stranded DNA and encode rolling-circle replication initiation proteins (Rep) and unique capsid proteins. In Rep-based phylogenies, genomoviruses form a sister clade to plant viruses of the family Geminiviridae. Ten genera are recognized in this family.
Paecilomyces marquandii is a soil-borne filamentous fungus distributed throughout temperate to tropical latitudes worldwide including forest, grassland, sewage sludge and strongly metal polluted area characterized by high tolerance in heavy metals. Simultaneous toxic action of zinc and alachlor result an increase in uptake of metal in this fungus but disrupts the cell membrane. Paecilomyces marquandii is known to parasitize the mushroom, Cuphophyllus virgineus, in the family, Hygrophoraceae. Paecilomyces marquandii is categorised as a biosafety risk group 1 in Canada and is not thought to be a significant pathogen of humans or animals.
Aspergillus sclerotiorum is a species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus. It is from the Circumdati section. The species was first described in 1933. A. sclerotiorum has been reported to produce penicillic acid, xanthomegnin, viomellein, and vioxanthin.

Fungal DNA barcoding is the process of identifying species of the biological kingdom Fungi through the amplification and sequencing of specific DNA sequences and their comparison with sequences deposited in a DNA barcode database such as the ISHAM reference database, or the Barcode of Life Data System (BOLD). In this attempt, DNA barcoding relies on universal genes that are ideally present in all fungi with the same degree of sequence variation. The interspecific variation, i.e., the variation between species, in the chosen DNA barcode gene should exceed the intraspecific (within-species) variation.
Fungal genomes are among the smallest genomes of eukaryotes. The sizes of fungal genomes range from less than 10 Mbp to hundreds of Mbp. The average genome size is approximately 37 Mbp in Ascomycota, 47 Mbp in Basidiomycota and 75 Mbp in Oomycota. The sizes and gene numbers of the smallest genomes of free-living fungi such as those of Wallemia ichthyophaga, Wallemia mellicola or Malassezia restricta are comparable to bacterial genomes. The genome of the extensively researched yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains approximately 12 Mbp and was the first completely sequenced eukaryotic genome. Due to their compact size fungal genomes can be sequenced with less resources than most other eukaryotic genomes and are thus important models for research. Some fungi exist as stable haploid, diploid, or polyploid cells, others change ploidy in response to environmental conditions and aneuploidy is also observed in novel environments or during periods of stress.
Paecilomyces paravariotii is a species of fungus in the genus Paecilomyces in the order of Eurotiales, closely related to Paecilomyces variotii.













