Paraconger is a genus of eels in the family Congridae. It currently contains the following species:
Chlopsis longidens is an eel in the family Chlopsidae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899, originally under the genus Atopichthys. It is known from a single leptocephalus specimen collected from between Ecuador and the Galapagos Islands, in the central eastern Pacific Ocean. From that specimen. the species is known to dwell in a tropical, marine climate at a maximum depth of 3,184 m. The specimen may possibly be a larval bicolor false moray.

The shorttail conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Charles Barkley Wade in 1946, originally under the genus Chiloconger. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, the Galapagos Islands, Panama, and Revillagigedo. It dwells at a depth range of 108–150 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 30 centimetres.
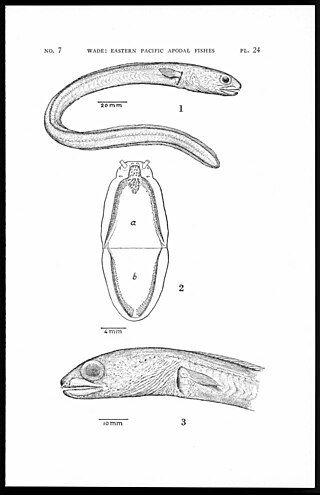
The shortsnout conger, also known as the thicklip conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899, originally under the genus Atopichthys. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, and Panama. It leads a reclusive, benthic, burrowing lifestyle, and typically dwells at a depth range of 27–2198 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 30 centimetres.
The Californian conger, also known as the ringeye conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, and Peru. It is known to dwell at a depth of 50 metres. Males reach an average total length of 40 centimetres, but can reach a maximum TL of 60 cm.
The margintail conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Felipe Poey in 1867, originally under the genus Echelus. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including the United States, Bahamas, the Gulf of Mexico, Cuba, Venezuela, and Colombia. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 35–75 meters, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting sand and mud in the neritic zone. Males reach an average total length of 35 centimeters, but can reach a maximum TL of 51 cm.
The blackspot conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1870, originally under the genus Conger. It is a subtropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Madeira and Azores. It dwells at a depth range of 30–100 meters and burrows into sand. Males can reach a maximum total length of 50 centimetres.
The Guinean conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Robert H. Kanazawa in 1961. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from Senegal to Angola, in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 25–50 metres, and inhabits benthic sand, which it burrows into backwards. Males can reach a maximum total length of 62.7 centimetres.
The largehead conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899, originally under the genus Uroconger. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from southern Canada to Chile, in the eastern Pacific Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 165–935 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 100 centimetres.
The neighbor conger is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899, originally under the genus Uroconger. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel that is known from the southwestern and western central Atlantic Ocean, including the Bahamas, Brazil, Cuba, and Mexico. It dwells at a depth range of 101–503 metres (331–1,650 ft). Males can reach a maximum total length of 46.2 centimetres (18.2 in).
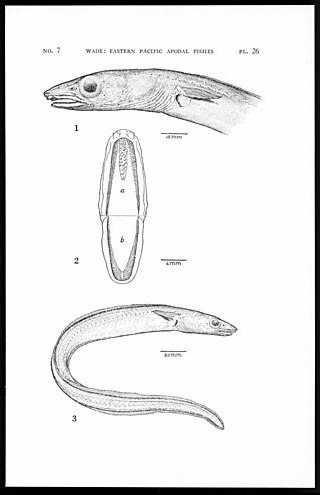
Gnathophis cinctus, the hardtail conger or Catalina conger, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899, originally under the genus Atopichthys. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Peru, and the United States. It dwells at a depth range of 9–336 metres, and leads a benthic lifestyle, burrowing into loose sand. Males can reach a maximum total length of 42 cm.
Hoplunnis sicarius is an eel in the family Nettastomatidae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899, originally under the genus Atopichthys. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including Mazatlan, Mexico, and Panama. It is known to dwell at a depth of 1,431 metres (4,695 ft), and inhabits substrates. Unlike many eel species, it does not form burrows.
The Longtailed sand-eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1870, originally under the genus Ophichthys. It is a marine, tropical eel, which is known from Aden to Natal, South Africa, in the western Indian Ocean. Males can reach a maximum total length of 54 centimetres (21 in).
Myrichthys xysturus is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Henry Gilbert in 1882, originally under the genus Ophichthys. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including the Gulf of California; Baja California Sur, Mexico; and the Galapagos Islands.
The death-banded snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including the central Gulf of California, Colombia, Costa Rica, Mexico and Panama. It dwells at a depth range of 35–760 metres, and forms burrows in sandy and muddy bottoms. Males can reach a maximum total length of 86 centimetres.
The Misol snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1872, originally under the genus Ophichthys. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western central Pacific Ocean.
The thin sand-eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1870, originally under the genus Ophichthys. It is a tropical, marine and freshwater eel which is known from the western Indian Ocean, including the Red Sea, South Africa, Mauritius and Réunion. Males can reach a maximum total length of 53 centimetres (21 in).
Avocettina bowersii is an eel in the family Nemichthyidae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from California, U.S.A.; Peru, and Chile. It dwells at a depth range of 92–641 metres, although the type specimen was collected from a depth of 2,692 metres.

Serrivomer sector, known commonly as the sawtooth eel, the saw-tooth snipe or the deep-sea eel, is an eel in the family Serrivomeridae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the eastern and western Pacific Ocean, including Japan, Chile, and California, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 3,243 metres, most often around 305 metres (1,001 ft). Males can reach a maximum total length of 76 centimetres (30 in).
Leptochilichthys agassizii, or Agassiz' smooth-head, is a species of fish in the family Alepocephalidae. It is named for the scientist and engineer Alexander Agassiz (1835–1910), who commanded the 1899 survey aboard the USS Albatross on which the fish was discovered.


