
The Chao Phraya River is the major river in Thailand, with its low alluvial plain forming the centre of the country. It flows through Bangkok and then into the Gulf of Thailand.

The Russian Far East is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Eastern Federal District, which encompasses the area between Lake Baikal and the Pacific Ocean. The area's largest city is Khabarovsk, followed by Vladivostok. The region shares land borders with the countries of Mongolia, China, and North Korea to its south, as well as maritime boundaries with Japan to its southeast, and with the United States along the Bering Strait to its northeast.

Cyprinus is the genus of typical carps in family Cyprinidae. Most species in the genus are of East Asia origin with only the common carp in Western Asia and Europe; this invasive species has also been introduced to many other regions around the world. Cyprinus are closely related to some more barb-like genera, such as Cyclocheilichthys and Barbonymus (tinfoils). The crucian carps (Carassius) of western Eurasia, which include the goldfish, are apparently not as closely related.

The Acrochordidae, commonly known as wart snakes, Java wart snakes, file snakes, elephant trunk snakes, or dogface snakes are a monogeneric family created for the genus Acrochordus. This is a group of basal aquatic snakes found in Australia and tropical Asia. Currently, three species are recognized.

Trachypithecus is a genus of Old World monkeys containing species known as lutungs, langurs, or leaf monkeys. Their range is much of Southeast Asia.

The Chinese pond heron is an East Asian freshwater bird of the heron family, (Ardeidae). It is one of six species of birds known as "pond herons". It is parapatric with the Indian pond heron to the west and the Javan pond heron to the south, and these three are presumed to form a superspecies. As a group they are variously affiliated with the squacco heron or the Malagasy pond heron. As of mid-2011 there are no published molecular analyses of pond heron interrelationships and osteological data is likewise not analyzed for all relevant comparison taxa.

The Asian house shrew is a shrew species native to South and Southeast Asia that has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List since 2008 because of its large population and wide distribution. It has been introduced in several West Asian and East African countries. It is considered an invasive species and implicated in the demise of several island lizard species.

The red giant flying squirrel or common giant flying squirrel is a species of rodent in the family Sciuridae (squirrels). It is found in a wide variety of forest–types, plantations and more open habitats with scattered trees in Southeast Asia, ranging north to the Himalayas and southern and central China. One of the largest arboreal squirrels, all populations have at least some reddish-brown above and pale underparts, but otherwise there are significant geographic variations in the colours. The taxonomic position of those in the Sundaic region is generally agreed upon, but there is considerable uncertainty about the others, which variously have been included in this or other species, or recognized as their own species.

Python is a genus of constricting snakes in the Pythonidae family native to the tropics and subtropics of the Eastern Hemisphere.

The moonrat is a southeast Asian species of mammal in the family Erinaceidae. It is the only species in the genus Echinosorex. The moonrat is a fairly small, primarily carnivorous animal which, despite its name, is not closely related to rats or other rodents. The scientific name is sometimes given as Echinosorex gymnurus, but this is incorrect.

The Eurasian Steppe, also called the Great Steppe or The Steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Hungary, Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova, Ukraine, southern Russia, Kazakhstan, Xinjiang, Mongolia and Manchuria, with one major exclave, the Pannonian steppe, located mostly in Hungary.
Paralaubuca s a genus of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Xenocyprididae, the East Asian minnows or sharpbellies. The species in this genus are found in Asia.
Paralaubuca harmandi is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Xenocyprididae, the East Asian minnows or sharpbellies. This fish is from south east Asia. It occurs in the Mekong and Chao Praya in Thailand, Laos, Cambodia and Vietnam. It is a solitary species which is normally found as scattered individuals in the shallow and medium depths of large rivers. It feeds on zooplankton and insects of larger size than the other species in Paralaubuca. It moves into floodplains during the monsoon to feed and maybe to breed, and it has also been recorded undertaking short migrations upstream in rivers. It is fished for by both commercial and subsistence fisheries and it is processed into fermented products in Cambodia while elsewhere it is salted and dried. This species is rare in the aquarium trade.
Paralaubuca riveroi is a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Xenocyprididae, the East Asian minnows or sharpbellies. This fish occurs in Southeast Asia.
Paralaubuca typusis a species of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Xenocyprididae, the East Asian minnows or sharpbellies. This fish occurs in south-east Asia. It is found in Thailand in the basins of the Chao Phraya, Tapi, Mekong and Mae Klong and in the Mekong on Laos and Cambodia, as well as Vietnam where it is also found in the La Ngà River. It is one of the most abundant fish species in the lower Mekong.
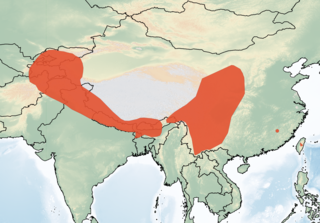
The eastern barbastelle or Asian barbastelle is a species of vesper bat found throughout much of Asia, from Afghanistan to Taiwan.

Oligodon deuvei is a species of snake in the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to Southeast Asia.

Oligodon barroni, or Barron's kukri snake, is a species of snake in the subfamily Colubrinae of the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to Southeast Asia.
Strelkov's long-eared bat is a species of vesper bat found in mountainous regions of Central Asia.














