Related Research Articles
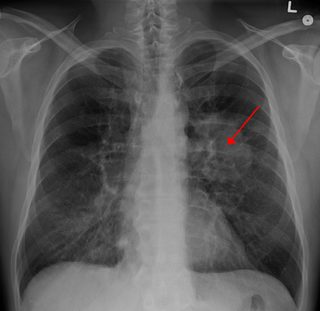
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. This growth can spread beyond the lung by the process of metastasis into nearby tissue or other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in the lung, known as primary lung cancers, are carcinomas. The two main types are small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) and non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). The most common symptoms are coughing, weight loss, shortness of breath, and chest pains.

René-Théophile-Hyacinthe Laennec was a French physician and musician. His skill of carving his own wooden flutes led him to invent the stethoscope in 1816, while working at the Hôpital Necker. He pioneered its usage in diagnosing various chest conditions. He became a lecturer at the Collège de France in 1822 and professor of medicine in 1823. His final appointments were that of head of the medical clinic at the Hôpital de la Charité and professor at the Collège de France. He died of tuberculosis in 1826 at the age of 45.

The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and many other animals including a few fish and some snails. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their different muscles to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the main muscle of respiration that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocal sounds including human speech possible.

The circulatory system, also called the cardiovascular system or the vascular system, is an organ system that permits blood to circulate and transport nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood cells to and from the cells in the body to provide nourishment and help in fighting diseases, stabilize temperature and pH, and maintain homeostasis.

The respiratory system is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In land animals the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in millions of small air sacs; in mammals and reptiles these are called alveoli, and in birds they are known as atria. These microscopic air sacs have a very rich blood supply, thus bringing the air into close contact with the blood. These air sacs communicate with the external environment via a system of airways, or hollow tubes, of which the largest is the trachea, which branches in the middle of the chest into the two main bronchi. These enter the lungs where they branch into progressively narrower secondary and tertiary bronchi that branch into numerous smaller tubes, the bronchioles. In birds the bronchioles are termed parabronchi. It is the bronchioles, or parabronchi that generally open into the microscopic alveoli in mammals and atria in birds. Air has to be pumped from the environment into the alveoli or atria by the process of breathing which involves the muscles of respiration.

Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is inflammation of the membranes that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity (pleurae). This can result in a sharp chest pain while breathing. Occasionally the pain may be a constant dull ache. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, fever or weight loss, depending on the underlying cause.
A wheeze is a continuous, coarse, whistling sound produced in the respiratory airways during breathing. For wheezes to occur, some part of the respiratory tree must be narrowed or obstructed, or airflow velocity within the respiratory tree must be heightened. Wheezing is commonly experienced by persons with a lung disease; the most common cause of recurrent wheezing is asthma, though it can also be a symptom of lung cancer, congestive heart failure, and certain types of heart diseases.

A respiratory examination, or lung examination, is performed as part of a physical examination, in response to respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath, cough, or chest pain, and is often carried out with a cardiac examination.

Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli, pleurae, pleural cavity, and the nerves and muscles of respiration. Respiratory diseases range from mild and self-limiting, such as the common cold, influenza, and pharyngitis to life-threatening diseases such as bacterial pneumonia, pulmonary embolism, tuberculosis, acute asthma, lung cancer, and severe acute respiratory syndromes, such as COVID-19. Respiratory diseases can be classified in many different ways, including by the organ or tissue involved, by the type and pattern of associated signs and symptoms, or by the cause of the disease.

Respiratory sounds refer to the specific sounds generated by the movement of air through the respiratory system. These may be easily audible or identified through auscultation of the respiratory system through the lung fields with a stethoscope as well as from the spectral chacteristics of lung sounds. These include normal breath sounds and adventitious or "added" sounds such as crackles, wheezes, pleural friction rubs, stertor, and stridor.
Egophony is an increased resonance of voice sounds heard when auscultating the lungs, often caused by lung consolidation and fibrosis. It is due to enhanced transmission of high-frequency sound across fluid, such as in abnormal lung tissue, with lower frequencies filtered out. It results in a high-pitched nasal or bleating quality in the affected person's voice.
Sylvia Sapira was an American harpsichordist. She performed both the Baroque repertoire as well as contemporary compositions by composers such as Alan Hovhaness.
Biceps reflex is a reflex test that examines the function of the C5 reflex arc and the C6 reflex arc. The test is performed by using a tendon hammer to quickly depress the biceps brachii tendon as it passes through the cubital fossa. Specifically, the test activates the stretch receptors inside the biceps brachii muscle which communicates mainly with the C5 spinal nerve and partially with the C6 spinal nerve to induce a reflex contraction of the biceps muscle and jerk of the forearm.
Emmanuel Sapira (1900–1943) was a Romanian-born Belgian chess master.
Doi's sign is a clinical sign in which absent deep tendon reflexes can be elicited after a short period of maximal muscle contraction. This occurs in patients with Eaton-Lambert syndrome, but is not seen in patients with neuropathy.

Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of obstructive lung disease characterized by long-term breathing problems and poor airflow. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and cough with sputum production. COPD is a progressive disease, meaning it typically worsens over time. Eventually, everyday activities such as walking or getting dressed become difficult. Chronic bronchitis, and emphysema are older terms used for different types of COPD. The term "chronic bronchitis" is still used to define a productive cough that is present for at least three months each year for two years. Those with such a cough are at a greater risk of developing COPD. The term "emphysema" is also used for the abnormal presence of air or other gas within tissues.

The Tel Aviv central bus station massacre was an attack which occurred on January 5, 2003 in which two Palestinian suicide bombers blew themselves up outside the Tel Aviv Central Bus Station in Tel Aviv, Israel, killing 23 civilians and injuring over 100.
The limbus sign is a ring of dystrophic calcification evident as a "milky precipitate" at the corneal limbus. The corneal limbus is the part of the eye where the cornea (front/center) meets the sclera. Thought to be caused by increased calcium concentration in the blood, this sign however persists after calcium phosphate concentration returns to normal. Compare the limbus sign (calcification) with arcus senilis (lipid).
Guttman Shmuel Landau was a leader of the Bessarabian Jewish community, active in the Moldavian Democratic Republic and Romania. His social work was tied to the city of Chișinău, where he was also a civil servant and merchant. A member of the Moldavian Republic's legislature in 1918, he returned to prominence during World War II, designated by the antisemitic regime of Ion Antonescu as President of the Chișinău Judenrat, effectively answering for the Chișinău Ghetto. He was unable to prevent his constituents' deportation and indiscriminate killing in Transnistria Governorate, but was spared their fate until May 20, 1942. He committed suicide the following day; his wife attempted the same, but was rescued and survived the war.
References
- ↑ Orient, Jane M.; Sapira, Joseph D. (2010). Sapira's Art & Science of Bedside Diagnosis. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 9781605474113.
- ↑ " pectoriloquy " at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
| This respiratory system article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| This medical sign article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |