Related Research Articles

Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea or dyspnoea, is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity", and recommends evaluating dyspnea by assessing the intensity of its distinct sensations, the degree of distress and discomfort involved, and its burden or impact on the patient's activities of daily living. Distinct sensations include effort/work to breathe, chest tightness or pain, and "air hunger". The tripod position is often assumed to be a sign.
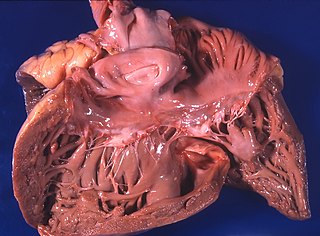
Pulmonary heart disease, also known as cor pulmonale, is the enlargement and failure of the right ventricle of the heart as a response to increased vascular resistance or high blood pressure in the lungs.

Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive liquid accumulation in the tissue and air spaces of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia and respiratory failure. It is due to either failure of the left ventricle of the heart to remove oxygenated blood adequately from the pulmonary circulation, or an injury to the lung tissue directly or blood vessels of the lung.
Salt water aspiration syndrome is a rare diving disorder suffered by scuba divers who inhale a mist of seawater, usually from a faulty demand valve, causing irritation of the lungs. It is not the same thing as aspiration of salt water as a bulk liquid, i.e. drowning. It can usually be treated by rest for several hours. If severe, medical assessment is required. First described by Carl Edmonds.
Orthopnea or orthopnoea is shortness of breath (dyspnea) that occurs when lying flat, causing the person to have to sleep propped up in bed or sitting in a chair. It is commonly seen as a late manifestation of heart failure, resulting from fluid redistribution into the central circulation, causing an increase in pulmonary capillary pressure and causing difficulty in breathing. It is also seen in cases of abdominal obesity or pulmonary disease. Orthopnea is the opposite of platypnea, shortness of breath that worsens when sitting or standing upright.

Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with nausea, sweating, or shortness of breath. It can be divided into heart-related and non-heart-related pain. Pain due to insufficient blood flow to the heart is also called angina pectoris. Those with diabetes or the elderly may have less clear symptoms.

Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this does not naturally close after birth it is referred to as a patent (open) foramen ovale (PFO). It is common in patients with a congenital atrial septal aneurysm (ASA).

Anasarca is a severe and generalized form of edema, with subcutaneous tissue swelling throughout the body. Unlike typical edema, which almost everyone will experience at some time and can be relatively benign, anasarca is a pathological process reflecting a severe disease state and can involve the cavities of the body in addition to the tissues.

Sinus bradycardia is a sinus rhythm with a reduced rate of electrical discharge from the sinoatrial node, resulting in a bradycardia, a heart rate that is lower than the normal range.

Valvular heart disease is any cardiovascular disease process involving one or more of the four valves of the heart. These conditions occur largely as a consequence of aging, but may also be the result of congenital (inborn) abnormalities or specific disease or physiologic processes including rheumatic heart disease and pregnancy.

Hypoxemia is an abnormally low level of oxygen in the blood. More specifically, it is oxygen deficiency in arterial blood. Hypoxemia has many causes, and often causes hypoxia as the blood is not supplying enough oxygen to the tissues of the body.
The abdominojugular test, also known as abdominojugular reflux (AJR), is a physical examination test useful in diagnosing right ventricle dysfunction, particularly right ventricular failure.

Unstable angina is a type of angina pectoris that is irregular or more easily provoked. It is classified as a type of acute coronary syndrome.
Postural drainage (PD) is the drainage of lung secretions using gravity. It is used to treat a variety of conditions that cause the build-up of secretions in the lungs.

Fat embolism syndrome occurs when fat enters the blood stream and results in symptoms. Symptoms generally begin within a day. This may include a petechial rash, decreased level of consciousness, and shortness of breath. Other symptoms may include fever and decreased urine output. The risk of death is about 10%.
In medicine, hepatopulmonary syndrome is a syndrome of shortness of breath and hypoxemia caused by vasodilation in the lungs of patients with liver disease. Dyspnea and hypoxemia are worse in the upright position.
Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea or paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea (PND) is an attack of severe shortness of breath and coughing that generally occurs at night. It usually awakens the person from sleep, and may be quite frightening. PND, as well as simple orthopnea, may be relieved by sitting upright at the side of the bed with legs dangling, as symptoms typically occur when the person is recumbent, or lying down.

In transfusion medicine, transfusion-associated circulatory overload is a transfusion reaction resulting in signs or symptoms of excess fluid in the circulatory system (hypervolemia) within 12 hours after transfusion. The symptoms of TACO can include shortness of breath (dyspnea), low blood oxygen levels (hypoxemia), leg swelling, high blood pressure (hypertension), and a high heart rate (tachycardia).

Anomalous pulmonary venous connection is a congenital defect of the pulmonary veins.
Platypnea–orthodeoxia syndrome is a condition in which a person has shortness of breath and low oxygen saturations when upright, but no symptoms when lying down. It can be caused by ventilation-perfusion mismatch, intracardiac shunting, or pulmonary shunting. In some cases, the cause is multifactorial.
References
- ↑ Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary (32 ed.). Elsevier Saunders. 2012. p. 1459. ISBN 978-0-8089-2418-0.
- ↑ Robin ED, McCauley RF (1997). "An analysis of platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome including a 'new' therapeutic approach". Chest. 112 (6): 1449–51. doi: 10.1378/chest.112.6.1449 . PMID 9404736.
- ↑ Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary (32 ed.). Elsevier Saunders. 2012. p. 1337. ISBN 978-0-8089-2418-0.
- 1 2 Cheng TO (2002). "Mechanisms of platypnea-orthodeoxia: what causes water to flow uphill?". Circulation. 105 (6): e47. doi: 10.1161/circ.105.6.e47 . hdl: 10553/76643 . PMID 11839642.
- ↑ Kubler P, Gibbs H, Garrahy P (2000). "Platypnoea-orthodeoxia syndrome". Heart. 83 (2): 221–3. doi:10.1136/heart.83.2.221. PMC 1729301 . PMID 10648502.