Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus. Signs and symptoms may include vomiting, abdominal pain, deep gasping breathing, increased urination, weakness, confusion and occasionally loss of consciousness. A person's breath may develop a specific "fruity" smell. The onset of symptoms is usually rapid. People without a previous diagnosis of diabetes may develop DKA as the first obvious symptom.

Diabetic coma is a life-threatening but reversible form of coma found in people with diabetes mellitus.
Tachypnea, also spelt tachypnoea, is a respiratory rate greater than normal, resulting in abnormally rapid and shallow breathing.
Apnea is the temporary cessation of breathing. During apnea, there is no movement of the muscles of inhalation, and the volume of the lungs initially remains unchanged. Depending on how blocked the airways are, there may or may not be a flow of gas between the lungs and the environment. If there is sufficient flow, gas exchange within the lungs and cellular respiration would not be severely affected. Voluntarily doing this is called holding one's breath. Apnea may first be diagnosed in childhood, and it is recommended to consult an ENT specialist, allergist or sleep physician to discuss symptoms when noticed; malformation and/or malfunctioning of the upper airways may be observed by an orthodontist.
A blood gas test or blood gas analysis tests blood to measure blood gas tension values, it also measures blood pH, and the level and base excess of bicarbonate. The source of the blood is reflected in the name of each test; arterial blood gases come from arteries, venous blood gases come from veins and capillary blood gases come from capillaries. The blood gas tension levels of partial pressures can be used as indicators of ventilation, respiration and oxygenation. Analysis of paired arterial and venous specimens can give insights into the aetiology of acidosis in the newborn.
Hyperventilation is irregular breathing that occurs when the rate or tidal volume of breathing eliminates more carbon dioxide than the body can produce. This leads to hypocapnia, a reduced concentration of carbon dioxide dissolved in the blood. The body normally attempts to compensate for this homeostatically, but if this fails or is overridden, the blood pH will rise, leading to respiratory alkalosis. The symptoms of respiratory alkalosis include dizziness, tingling in the lips, hands, or feet, headache, weakness, fainting, and seizures. In extreme cases, it may cause carpopedal spasms, a flapping and contraction of the hands and feet.
Acidosis is a biological process producing hydrogen ions and increasing their concentration in blood or body fluids. pH is the negative log of hydrogen ion concentration and so it is decreased by a process of acidosis.
The control of ventilation is the physiological mechanisms involved in the control of breathing, which is the movement of air into and out of the lungs. Ventilation facilitates respiration. Respiration refers to the utilization of oxygen and balancing of carbon dioxide by the body as a whole, or by individual cells in cellular respiration.

Ketoacidosis is a metabolic state caused by uncontrolled production of ketone bodies that cause a metabolic acidosis. While ketosis refers to any elevation of blood ketones, ketoacidosis is a specific pathologic condition that results in changes in blood pH and requires medical attention. The most common cause of ketoacidosis is diabetic ketoacidosis but it can also be caused by alcohol, medications, toxins, and rarely, starvation.

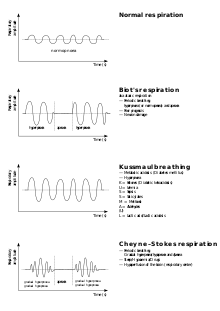
Cheyne–Stokes respiration is an abnormal pattern of breathing characterized by progressively deeper, and sometimes faster, breathing followed by a gradual decrease that results in a temporary stop in breathing called an apnea. The pattern repeats, with each cycle usually taking 30 seconds to 2 minutes. It is an oscillation of ventilation between apnea and hyperpnea with a crescendo-diminuendo pattern, and is associated with changing serum partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide.

Hypophosphatemia is an electrolyte disorder in which there is a low level of phosphate in the blood. Symptoms may include weakness, trouble breathing, and loss of appetite. Complications may include seizures, coma, rhabdomyolysis, or softening of the bones.

Metabolic acidosis is a serious electrolyte disorder characterized by an imbalance in the body's acid-base balance. Metabolic acidosis has three main root causes: increased acid production, loss of bicarbonate, and a reduced ability of the kidneys to excrete excess acids. Metabolic acidosis can lead to acidemia, which is defined as arterial blood pH that is lower than 7.35. Acidemia and acidosis are not mutually exclusive – pH and hydrogen ion concentrations also depend on the coexistence of other acid-base disorders; therefore, pH levels in people with metabolic acidosis can range from low to high.
Hyperpnea, or hyperpnoea, is increased volume of air taken during breathing. It can occur with or without an increase in respiration rate. It is characterized by deep breathing. It may be physiologic—as when required by oxygen to meet metabolic demand of body tissues —or it may be pathologic, as when sepsis is severe or during pulmonary edema. Hyperpnea is further characterized by the required use of muscle contraction during both inspiration and expiration. Thus, hyperpnea is intense active breathing as opposed to the passive process of normal expiration.

Respiratory alkalosis is a medical condition in which increased respiration elevates the blood pH beyond the normal range (7.35–7.45) with a concurrent reduction in arterial levels of carbon dioxide. This condition is one of the four primary disturbances of acid–base homeostasis.

Agonal respiration, gasping respiration, or agonal breathing is a distinct and abnormal pattern of breathing and brainstem reflex characterized by gasping labored breathing and is accompanied by strange vocalizations and myoclonus. Possible causes include cerebral ischemia, hypoxia, or anoxia. Agonal breathing is a severe medical sign requiring immediate medical attention, as the condition generally progresses to complete apnea and preludes death. The duration of agonal respiration can range from two breaths to several hours of labored breathing.

A respiratory examination, or lung examination, is performed as part of a physical examination, in response to respiratory symptoms such as shortness of breath, cough, or chest pain, and is often carried out with a cardiac examination.
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS), also known as hyperosmolar non-ketotic state (HONK), is a complication of diabetes mellitus in which high blood sugar results in high osmolarity without significant ketoacidosis. Symptoms include signs of dehydration, weakness, leg cramps, vision problems, and an altered level of consciousness. Onset is typically over days to weeks. Complications may include seizures, disseminated intravascular coagulopathy, mesenteric artery occlusion, or rhabdomyolysis.
In acid base physiology, the Davenport diagram is a graphical tool, developed by Horace W. Davenport, that allows a clinician or investigator to describe blood bicarbonate concentrations and blood pH following a respiratory and/or metabolic acid-base disturbance. The diagram depicts a three-dimensional surface describing all possible states of chemical equilibria between gaseous carbon dioxide, aqueous bicarbonate and aqueous protons at the physiologically complex interface of the alveoli of the lungs and the alveolar capillaries. Although the surface represented in the diagram is experimentally determined, the Davenport diagram is rarely used in the clinical setting, but allows the investigator to envision the effects of physiological changes on blood acid-base chemistry. For clinical use there are two recent innovations: an Acid-Base Diagram which provides Text Descriptions for the abnormalities and a High Altitude Version that provides text descriptions appropriate for the altitude.

High anion gap metabolic acidosis is a form of metabolic acidosis characterized by a high anion gap. Metabolic acidosis occurs when the body produces too much acid, or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body. Several types of metabolic acidosis occur, grouped by their influence on the anion gap.
Labored respiration or labored breathing is an abnormal respiration characterized by evidence of increased effort to breathe, including the use of accessory muscles of respiration, stridor, grunting, or nasal flaring.