
Huntsman spiders, members of the family Sparassidae, are known by this name because of their speed and mode of hunting. They are also called giant crab spiders because of their size and appearance. Larger species sometimes are referred to as wood spiders, because of their preference for woody places. In southern Africa the genus Palystes are known as rain spiders or lizard-eating spiders. Commonly, they are confused with baboon spiders from the Mygalomorphae infraorder, which are not closely related.

Uloboridae is a family of non-venomous spiders, known as cribellate orb weavers or hackled orb weavers. Their lack of venom glands is a secondarily evolved trait. Instead, they wrap their prey thoroughly in silk, cover it in regurgitated digestive enzymes, and then ingest the liquified body.

Atypidae, also known as atypical tarantulas or purseweb spiders, is a spider family containing only three genera. They are accomplished ambush predators that spend most of their time in a sock-like, silken retreat on the ground from where they kill their prey.

Philodromidae, also known as philodromid crab spiders and running crab spiders, is a family of araneomorph spiders first described by Tord Tamerlan Teodor Thorell in 1870. It contains over 600 species in thirty genera. Most are dull colored- brown, gray, yellowish or mottled with a leaf-like cardiac mark on the anterior dorsal abdomen, and seldom reach above 10 millimetres (0.39 in) long. None of the species build webs, but they do use silk for draglines and egg sacs.
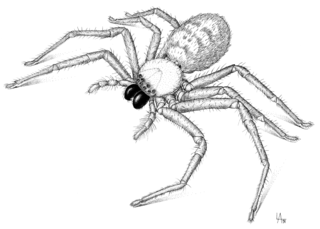
Delena cancerides, the flat huntsman or social huntsman, is a large, brown huntsman spider native to Australia. It has been introduced to New Zealand, where it is sometimes known as the Avondale spider as they are commonly found in the suburb of Avondale, Auckland. This was the species used in the beginning of the 2002 movie Spider-Man, a part in Australian movie Napoleon and widely in Arachnophobia, and all films depict them as having a deadly venomous bite, but they are generally considered harmless to humans in real-life. It was first described by Charles Athanase Walckenaer in 1837.

Gasteracantha is a genus of orb-weaver spiders first named by Carl Jakob Sundevall in 1833. The females of most species are brightly colored with six prominent spines on their broad, hardened, shell-like abdomens. The name Gasteracantha is derived from the Greek gaster (γαστήρ), meaning "belly, abdomen", and akantha (άκανθα), meaning "thorn, spine". Spiny-backed orb-weavers are sometimes colloquially called "crab spiders" because of their shape, but they are not closely related to the true crab spiders. Other colloquial names for certain species include thorn spider, star spider, kite spider, or jewel spider.

Grammostola is a genus of South American tarantulas that was first described by Eugène Louis Simon in 1892. These medium- to large-sized spiders are native to tropical South America, and are usually brown in color, with pinkish or orangish-red hairs. The very docile Chilean rose tarantulas are popular as a beginner's spider among tarantula enthusiasts.

Pelegrina is a spider genus of the family Salticidae. They are found throughout North America. Many of the species in Pelegrina were previously placed in the genera Metaphidippus, and before that, Dendryphantes. The genus was originally described in 1930 by the Spanish arachnologist Pelegrín Franganillo Balboa, who named it after himself.

Delena is a genus of South Pacific huntsman spiders that was first described by Charles Athanase Walckenaer in 1837.

Thomisus is a genus of crab spiders with around 150 species described. The genus includes species that vary widely in their ecology, with some that ambush predators that feed on insects visiting flowers. Like several other genera in the family Thomisidae, they are sometimes referred to as flower crab spiders, from their crab-like motion and their way of holding their front legs, reminiscent of a crab spreading its claws as a threat.

The skeleton tarantula, Ephebopus murinus, is a species of spider belonging to the family Theraphosidae (tarantulas), sub-family Aviculariinae. A New World species, it is native to several South American countries. Its common name is derived from the skeleton-like markings on its legs.

Arkys, also known as triangular spider or ambush spider, is a genus of Australian araneomorph spiders in the family Arkyidae, first described by Charles Athanase Walckenaer in 1837. They are often small, with a triangular shaped abdomen, and are found in Australia and some of its surrounding islands. They don't build webs, but can often be found on leaves and tips of flower heads. Their egg sacs are pinkish-orange and spherical, and are made late in the summer.

Arkys lancearius, the triangular spider, is a common Australian spider belonging to the family Arkyidae. It is an ambush hunter, commonly found resting on leaves and ferns or hanging from just a few threads of silk. The front two pairs of legs are large, suited for grabbing small insects, while the rear pairs of legs are much smaller.

Desis is a genus of intertidal spiders that was first described by Charles Athanase Walckenaer in 1837. It is found in Australasia, the Pacific, Japan, eastern and southern Africa, and India. They are truly marine spiders, living in the intertidal zone and only emerging at night on the ebb tide to hunt for invertebrates and small fish. In the day and during high tides, they hide in an air chamber sealed with silk.

Artema is a genus of cellar spiders that was first described by Charles Athanase Walckenaer in 1837.

Tigrosa is a genus of spiders in the family Lycosidae, found in North America.

Dolophones is a genus of orb-weaver spiders first described by Charles Athanase Walckenaer in 1837.
Clastes is a monotypic genus of huntsman spiders containing the single species, Clastes freycineti. It was first described by Charles Athanase Walckenaer in 1837, and is found in Papua New Guinea and on the Moluccas.

Sergiolus is a genus of ground spiders that was first described by Eugène Simon in 1892. They are 3.3 to 9 millimetres long.

Pelegrina aeneola is a species of jumping spider in the family Salticidae. It is found in North America.



















