Glucono-delta-lactone (GDL), also known as gluconolactone, is an organic compound with the formula (HOCH)3(HOCH2CH)CO2. A colorless solid, it is an oxidized derivative of glucose.

Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of secondary metabolite providing antioxidant roles in plants. It belongs to the subgroup of polyphenols called flavonoids.

A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synthesis and have played a central role in the development of the field of organic chemistry by providing challenging synthetic targets. The term natural product has also been extended for commercial purposes to refer to cosmetics, dietary supplements, and foods produced from natural sources without added artificial ingredients.

Alkylresorcinols (ARs), also known as resorcinolic lipids, are amphiphilic phenolic lipids characterised by a non-polar odd-numbered alkyl side chain with up to 27 carbon atoms attached to a polar resorcinol (1,3-dihydroxybenzene) ring.

Ellagic acid is a polyphenol found in numerous fruits and vegetables. It is the dilactone of hexahydroxydiphenic acid.

Penicillium roqueforti is a common saprotrophic fungus in the genus Penicillium. Widespread in nature, it can be isolated from soil, decaying organic matter, and plants.

Citrinin is a mycotoxin which is often found in food. It is a secondary metabolite produced by fungi that contaminates long-stored food and it causes different toxic effects, like nephrotoxic, hepatotoxic and cytotoxic effects. Citrinin is mainly found in stored grains, but sometimes also in fruits and other plant products.
Mycotoxicology is the branch of mycology that focuses on analyzing and studying the toxins produced by fungi, known as mycotoxins. In the food industry it is important to adopt measures that keep mycotoxin levels as low as practicable, especially those that are heat-stable. These chemical compounds are the result of secondary metabolism initiated in response to specific developmental or environmental signals. This includes biological stress from the environment, such as lower nutrients or competition for those available. Under this secondary path the fungus produces a wide array of compounds in order to gain some level of advantage, such as incrementing the efficiency of metabolic processes to gain more energy from less food, or attacking other microorganisms and being able to use their remains as a food source.
Penicillium griseofulvum is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces patulin, penifulvin A, cyclopiazonic acid, roquefortine C, shikimic acid, griseofulvin, and 6-Methylsalicylic acid. Penicillium griseofulvum occurs on cereals and nuts.

Brevianamides are indole alkaloids that belong to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines produced as secondary metabolites of fungi in the genus Penicillium and Aspergillus. Structurally similar to paraherquamides, they are a small class compounds that contain a bicyclo[2.2.2]diazoctane ring system. One of the major secondary metabolites in Penicillium spores, they are responsible for inflammatory response in lung cells.

Penicillium chrysogenum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or water-damaged buildings. It has been recognised as a species complex that includes P. notatum, P. meleagrinum, and P. cyaneofulvum. Molecular phylogeny has established that Alexander Fleming's first discovered penicillin producing strain is of a distinct species, P. rubens, and not of P. notatum. It has rarely been reported as a cause of human disease. It is the source of several β-lactam antibiotics, most significantly penicillin. Other secondary metabolites of P. chrysogenum include roquefortine C, meleagrin, chrysogine, 6-MSA YWA1/melanin, andrastatin A, fungisporin, secalonic acids, sorbicillin, and PR-toxin.

In biochemistry, naturally occurring phenols are natural products containing at least one phenol functional group. Phenolic compounds are produced by plants and microorganisms. Organisms sometimes synthesize phenolic compounds in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research. Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants.

δ-Viniferin is a resveratrol dehydrodimer. It is an isomer of epsilon-viniferin. It can be isolated from stressed grapevine leaves. It is also found in plant cell cultures and wine. It can also be found in Rheum maximowiczii.
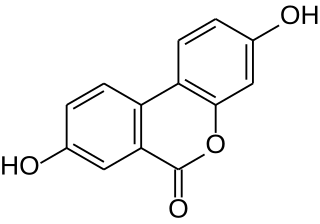
Urolithin A is a metabolite compound resulting from the transformation of ellagitannins by the gut bacteria. It belongs to the class of organic compounds known as benzo-coumarins or dibenzo-α-pyrones. Its precursors – ellagic acids and ellagitannins – are ubiquitous in nature, including edible plants, such as pomegranates, strawberries, raspberries, walnuts, and others.
Penicillium citrinum is an anamorph, mesophilic fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces tanzawaic acid A-D, ACC, Mevastatin, Quinocitrinine A, Quinocitrinine B, and nephrotoxic citrinin. Penicillium citrinum is often found on moldy citrus fruits and occasionally it occurs in tropical spices and cereals. This Penicillium species also causes mortality for the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus. Because of its mesophilic character, Penicillium citrinum occurs worldwide. The first statin (Mevastatin) was 1970 isolated from this species.
Penicillium corylophilum is a species of the genus of Penicillium which occurs in damp buildings in United States, Canada and western Europe but it can also be found in a variety of foods and mosquitoes. Penicillium corylophilum produces the alkaloid epoxyagroclavine and citrinin and is a pathogen to mosquitoes.

Penicillium solitum is an anamorphic, mesophilic, salinity-tolerant, and psychrotolerant species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is known to produce various compounds including polygalacturonase, compactin, cyclopenin, cyclopenol, cyclopeptin, dehydrocompactin, dihydrocyclopeptin, palitantin, solistatin, solistatinol, viridicatin, viridicatol.
Penicillium steckii is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces citrinin, tanzawaic acid E, tanzawaic acid F.
Penicillium striatisporum is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from the rhizosphere of chilli peppers. Penicillium striatisporum has a selective antifungal activity against Candida albicans This species produces striatisporin A, striatisporolide A, versiol, calbistrin C, deformylcalbistrin A, citromycetin, citromycin, fulvic acid, (-)-2,3-dihydrocitromycetin and (+)-hexylitaconic acid
Penicillium tulipae is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces penicillic acid, roquefortine C, roquefortine D, terrestric acid, glandicoline A, glandicoline B, meleagrin, oxaline, penitrem A and epineoxaline.











