 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
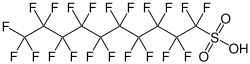
| Preferred IUPAC name 1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,9,9,10,10,10-Henicosafluoro-1-decanesulfonic acid | |
| Other names Henicosafluorodecanesulfonic acid, PFDS [1] | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.820 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10HF21O3S | |
| Molar mass | 600.14 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | black solid |
| Density | 1.8 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 224–255 [2] °C (435–491 °F; 497–528 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Perfluorodecanesulfonic acid is a chemical compound from the group of perfluorosulfonic acids within the per- and polyfluorinated alkyl compounds (PFAS). [3] [4] The chemical formula is C10F21SO3H. Perfluorodecanesulfonic acid is a persistent organic pollutant, known for its strong resistance to degradation. [5]