 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
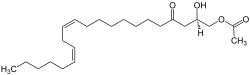
| Preferred IUPAC name (2R,12Z,15Z)-2-Hydroxy-4-oxohenicosa-12,15-dien-1-yl acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H40O4 | |
| Molar mass | 380.569 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Persin is a fungicidal toxin present in the avocado. [1] Persin is an oil-soluble compound structurally similar to a fatty acid, a colourless oil, and it leaches into the body of the fruit from the seeds.
Contents
The relatively low concentrations of persin in the ripe pulp of the avocado fruit is generally considered harmless to humans. Negative effects in humans are primarily in allergic individuals. When persin is consumed by domestic animals through the leaves or bark of the avocado tree, or skins and seeds of the avocado fruit, it is toxic and dangerous. [2] [3]