Related Research Articles

Aspidistra is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Nolinoideae, native to eastern and southeastern Asia, particularly China and Vietnam. They grow in shade under trees and shrubs. Their leaves arise more or less directly from ground level, where their flowers also appear. The number of species known has increased considerably from the 1980s onwards, with around 100 accepted as of July 2013. Aspidistra elatior is common worldwide as a foliage house plant that is very tolerant of neglect. It and other species can also be grown in shade outside, where they are generally hardy to −5 °C (23 °F).

The Boletaceae are a family of mushroom-forming fungi, primarily characterised by small pores on the spore-bearing hymenial surface, instead of gills as are found in most agarics. Nearly as widely distributed as the agarics, the family is renowned for hosting some prime edible species highly sought after by mushroom hunters worldwide, such as the cep or king bolete . A number of rare or threatened species are also present in the family, that have become the focus of increasing conservation concerns. As a whole, the typical members of the family are commonly known as boletes.

The Polyporaceae are a family of poroid fungi belonging to the Basidiomycota. The flesh of their fruit bodies varies from soft to very tough. Most members of this family have their hymenium in vertical pores on the underside of the caps, but some of them have gills or gill-like structures. Many species are brackets, but others have a definite stipe – for example, Polyporus badius.
Dactylella is a genus comprising 72 species of mitosporic fungi in the family Orbiliaceae. They are notable for trapping and eating nematodes.

Ohmefentanyl is an extremely potent opioid analgesic drug which selectively binds to the µ-opioid receptor.

Triplophysa is a genus of fish in the family Nemacheilidae found mainly in and around the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in China. Currently, the genus is a mixed assemblage of species. Some lineages have been identified and treated as subgenera, but as Wikipedia follows Fishbase for fish species all but Hedinichthys have been treated as subgenera in Wikipedia, although Kottelat in his revision of the loaches did recognise them as valid. FishBase, however, includes these in Triplophysa without specifying subgenera and treats the names given by Kottelat as synonyms.
Holmiella is a genus of fungi in the order Patellariales.

Cunninghamella is a genus of fungi in the order Mucorales, and the family Cunninghamellaceae. The genus was circumscribed by French mycologist Alphonse Louis Paul Matruchot in Ann. Mycol. Vol.1 on page 47 in 1903.
Caprettia is a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Monoblastiaceae. The genus was circumscribed by Augusto Chaves Batista and Heraldo da Silva Maia in 1965, with Caprettia amazonensis assigned as the type species.

Thelephora is a genus of fungi in the family Thelephoraceae. The genus has a widespread distribution and contains about 50 species. Fruit bodies of species are leathery, usually brownish at maturity, and range in shape from coral-like tufts to having distinct caps. Almost all species in the genus are thought to be inedible, but Thelephora ganbajun is a gourmet fungus in Yunnan province of southwest China.
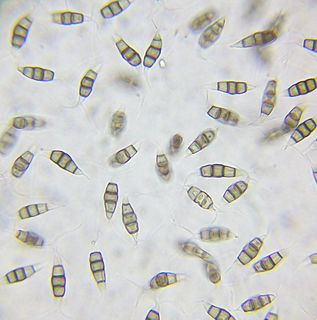
Pestalotiopsis is a genus of ascomycete fungi. Pestalotiopsis species are known as plant pathogens.

Rhizoctonia is a genus of fungi in the order Cantharellales. Species form thin, effused, corticioid basidiocarps, but are most frequently found in their sterile, anamorphic state. Rhizoctonia species are saprotrophic, but some are also facultative plant pathogens, causing commercially important crop diseases. Some are also endomycorrhizal associates of orchids. The genus name was formerly used to accommodate many superficially similar, but unrelated fungi.

Sutorius is a genus of fungi in the family Boletaceae. Its type species is the widely distributed Sutorius eximius. The Asian Boletus obscureumbrinus, found in Japan and China, was described by Japanese mycologist Tsuguo Hongo in 1968, moved to genus Sutorius in 2016, but then reclassified into genus Neoboletus in 2019. The Australian Sutorius australiensis and the southern Chinese Sutorius subrufus also belong to the genus.

Hortiboletus is a genus of fungi in the family Boletaceae. It was circumscribed in 2015 by Giampaolo Simonini, Alfredo Vizzini, and Matteo Gelardi. The erection of Hortiboletus follows recent molecular studies that outlined a new phylogenetic framework for the Boletaceae. Hortiboletus is derived from the Latin word hortus "garden", referring to a typical habitat of the type species, Hortiboletus rubellus. The bolete H. bubalinus, originally described as a Boletus and later placed in Xerocomus, was transferred to the genus by Bálint Dima. In 2015, Alona Yu. Biketova transferred Boletus campestris and Boletus engelii to Hortiboletus.
Nomuraea is a genus of fungi in the family Clavicipitaceae.

Massalongia is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Massalongiaceae. It has four species. The genus was circumscribed by German lichenologist Gustav Wilhelm Körber in 1855, with M. carnosa assigned as the type species.
References
- ↑ Shunsuke Nozawa, Kaoru Yamaguchi, Le Thi Hoang Yen, Duong Van Hop, Nyunt Phay, Katsuhiko Ando, Kyoko Watanabe, Identification of two new species and a sexual morph from the genus Pseudopestalotiopsis, Mycoscience, 2017, ISSN 1340-3540
- ↑ Burkhardt, Lotte (2022). Eine Enzyklopädie zu eponymischen Pflanzennamen [Encyclopedia of eponymic plant names](pdf) (in German). Berlin: Botanic Garden and Botanical Museum, Freie Universität Berlin. doi:10.3372/epolist2022. ISBN 978-3-946292-41-8 . Retrieved January 27, 2022.
- ↑ "Search Page - Pestalosphaeria". www.speciesfungorum.org. Species Fungorum. Retrieved 8 September 2022.