Related Research Articles

Basidiomycota is one of two large divisions that, together with the Ascomycota, constitute the subkingdom Dikarya within the kingdom Fungi. Members are known as Basidiomycetes. More specifically, Basidiomycota includes these groups: mushrooms, puffballs, stinkhorns, bracket fungi, other polypores, jelly fungi, boletes, chanterelles, earth stars, smuts, bunts, rusts, mirror yeasts, and Cryptococcus, the human pathogenic yeast. Basidiomycota are filamentous fungi composed of hyphae and reproduce sexually via the formation of specialized club-shaped end cells called basidia that normally bear external meiospores. These specialized spores are called basidiospores. However, some Basidiomycota are obligate asexual reproducers. Basidiomycota that reproduce asexually can typically be recognized as members of this division by gross similarity to others, by the formation of a distinctive anatomical feature, cell wall components, and definitively by phylogenetic molecular analysis of DNA sequence data.

Saccharomycetales belongs to the kingdom of Fungi and the division Ascomycota. It is the only order in the class Saccharomycetes. There are currently 13 families recognized as belonging to Saccharomycetales. GBIF also includes; Alloascoideaceae, Eremotheciaceae (16) Trigonopsidaceae and Wickerhamomycetaceae.

Mortierella species are soil fungi belonging to the order Mortierellales within the subphylum Mortierellomycotina. The widespread genus contains about 85 species.

The Ustilaginomycotina is a subdivision within the division Basidiomycota of the kingdom Fungi. It consists of the classes Ustilaginomycetes and Exobasidiomycetes, and in 2014 the subdivision was reclassified and the two additional classes Malasseziomycetes and Moniliellomycetes added. The name was first published by Doweld in 2001; Bauer and colleagues later published it in 2006 as an isonym. Ustilagomycotina and Agaricomycotina are considered to be sister groups, and they are in turn sister groups to the subdivision Pucciniomycotina.
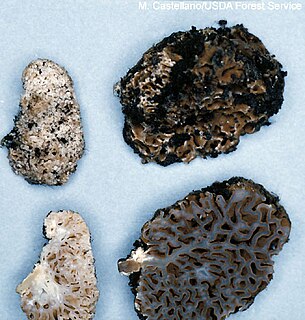
Gautieria is a genus of hypogeal fungi in the family Gomphaceae. They form mycorrhizae with various tree species, mostly from the family Pinaceae. Species are present over much of the world's temperate and boreal forest habitats. It is well documented that species from this genera are an important part of the diet of the northern flying squirrel. Also, some Australian marsupials, especially the rat-kangaroos, feed extensively on these fungi. The fungi also benefit from this relationship: not only do the squirrels help to disperse the spores and propagate the species, studies suggest that passage through the digestive tract of a mammal promotes germination of spores.
The Cystofilobasidiaceae are a family of fungi in the order Cystofilobasidiales. Phylogenetic analyses shows that this family is clearly distinct from other yeast-like families of the Tremellomycetes.

Tremella is a genus of fungi in the family Tremellaceae. All Tremella species are parasites of other fungi and most produce anamorphic yeast states. Basidiocarps, when produced, are gelatinous and are colloquially classed among the "jelly fungi". Over 100 species of Tremella are currently recognized worldwide. One species, Tremella fuciformis, is commercially cultivated for food.
Kernia is a genus of fungi in the family Microascaceae.
Koordersiella is a genus of fungi in the class Dothideomycetes. The relationship of this taxon to other taxa within the class is unknown.
Griggsia is a genus of fungi in the class Dothideomycetes. The relationship of this taxon to other taxa within the class is unknown. Also, the placement of this genus within the Dothideomycetes is uncertain. The genus name of Griggsia is in honour of American botanist Robert Fiske Griggs (1881–1962).
The Pichiaceae are a family of yeasts in the order Saccharomycetales. According to the 2007 Outline of Ascomycota, the family contains four genera, but GBIF lists 15 genera. The family was named by Zender in 1925.
Lasseria is a genus of fungi in the Helotiales order. The relationship of this taxon to other taxa within the order is unknown, and it has not yet been placed with certainty into any family.

Herman Jan Phaff was a scientist who specialised in yeast ecology. He was born in the Netherlands before moving to California at age of 26. He was active in Californian universities until his death. During his career he accumulated thousands of strains of yeast from the wild, and described 60 new taxa of yeast.
Holtermannia is a genus of fungi in the order Holtermanniales. Species produce groups of horn-like gelatinous basidiocarps on wood and have associated yeast states. The genus is distributed in southeast Asia and Brazil, and contains six species.

The Maleae are the apple tribe in the rose family, Rosaceae. The group includes a number of plants bearing commercially important fruits, such as apples and pears, while others are cultivated as ornamentals. Older taxonomies separated some of this group as tribe Crataegeae, as the Cydonia group, or some genera were placed in family Quillajaceae.
Kuraishia is a genus of two species of ascomycetous yeasts in the family Saccharomycetaceae. The type species Kuraishia capsulata was originally described as a member of Hansenula in 1953.

Ogataea is a genus of ascomycetous yeasts in the family Saccharomycetaceae. It was separated from the former genus Hansenula via an examination of their 18S and 26S rRNA partial base sequencings by Yamada et al. 1994.

Massalongia is a genus of lichen-forming fungi in the family Massalongiaceae. It has four species. The genus was circumscribed by German lichenologist Gustav Wilhelm Körber in 1855, with M. carnosa assigned as the type species.
The Phaffomycetaceae are a family of yeasts in the order Saccharomycetales that reproduce by budding. Species in the family have a widespread distribution.
Wickerhamomyces is a genus of fungi within the Saccharomycetales order. It is placed within the familyof Phaffomycetaceae.
References
- ↑ Lumbsch TH, Huhndorf SM. (December 2007). "Outline of Ascomycota – 2007". Myconet. Chicago, USA: The Field Museum, Department of Botany. 13: 1–58.
- ↑ "Phaffomyces Y.Yamada, 1997". www.gbif.org. Retrieved 30 July 2022.
- ↑ Phaff, H. J. (1986). "My Life With Yeasts". Annual Review of Microbiology. 40: 1–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.000245 . PMID 3535641.
- ↑ Burkhardt, Lotte (2022). Eine Enzyklopädie zu eponymischen Pflanzennamen [Encyclopedia of eponymic plant names](pdf) (in German). Berlin: Botanic Garden and Botanical Museum, Freie Universität Berlin. doi:10.3372/epolist2022. ISBN 978-3-946292-41-8 . Retrieved January 27, 2022.