
The common shrew opossums are members of the family Caenolestidae. They are found in Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela. The most recently discovered species is C. sangay.

Jenynsia is a genus of freshwater fishes in the family Anablepidae. Like Anableps species, they are onesided livebearers: some sources indicate that they only mate on one side, right-"handed" males with left-"handed" females and vice versa. However, other sources dispute this. These South American fish are viviparous.

Rineloricaria is a genus of freshwater tropical catfish belonging to the family Loricariidae. They are commonly called whiptail catfish because of the long filament that grows out of the tip of the caudal fin that is characteristic of the genus. With the exception of R. altipinnis from Panama, they are native to the rivers of northern and central South America. Some species are regularly seen in the aquarium trade.

Gymnogeophagus is a genus of cichlid fishes from South America, where they are known from various river basins in southern Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay and northern Argentina. They are part of a group popularly known as eartheaters.

Phalloceros is a genus of poeciliids native to freshwater habitats in Brazil, Paraguay, Uruguay and northern Argentina. The majority are endemic to southern and southeastern Brazil. P. caudimaculatus has long been part of the aquarium industry and has been introduced to countries far from its native range.
Lepthoplosternum is a small genus of freshwater catfish in the Callichthyinae subfamily of the armored catfish family.
Epactionotus is a genus of armored catfishes native to South America.

Pimelodus is a genus of fish in the family Pimelodidae native to Central and South America.
Hisonotus is a genus of armored catfishes native to South America. Species of Hisonotus and Curculionichthys are the only representatives of the subfamily Otothyrinae having serrae on the posterior edge of the pectoral fin spine. These species are small fishes, generally found in small fast flowing streams, where they grasp to the branches and leaves of aquatic or subaquatic plants. The species of this genus mostly occur in Atlantic coastal streams of southern Brazil and the Paraguay-Paraná system of southern South America. They are also distributed in the Río de La Plata basin and coastal rivers of southeastern Brazil.
Microlepidogaster is a genus of armored catfishes native to South America.
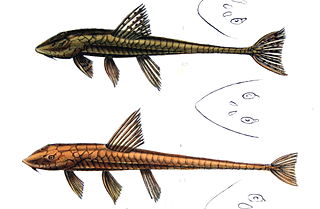
Loricariichthys is a genus of catfishes of the family Loricariidae.
Pareiorhaphis is a genus of catfish in the family Loricariidae native to South America. This genus can be readily distinguished from other neoplecostomines by the unique combination of having fleshy lobes on lateral margins of head ornamented with hypertrophied odontodes on nuptial males, caudal peduncle ovoid in cross section, abdomen usually naked, dorsal fin spinelet ovoid and adipose fin usually present. The color pattern is usually dark brown and mottled with the abdomen white. Most species in to Pareiorhaphis were originally described in Hemipsilichthys. In 1918, Alípio de Miranda-Ribeiro proposed the new genus Pareiorhaphis. Whether Pareiorhaphis is monophyletic or not is currently unknown.

Parotocinclus is a genus of fish in the family Loricariidae native to South America. This genus is distributed through almost all hydrographic systems in South America from the Guyana Shield drainages and Amazon Shield tributaries to the coastal drainages of eastern and southeastern Brazil, including the rio São Francisco basin. Most species have the caudal peduncle oval in cross section. It has been found that Characidium species may interact with P. maculicauda. The small Characidium will follow grazing P. maculicauda, which release particulate matter dislodged from the catfish's foraging.

Scleromystax is a genus of fish in the family Callichthyidae endemic to small tributaries from several coastal river basins draining the southern and southeastern regions in Brazil. Most of the species of Scleromystax are highly sexually dimorphic; males have developed odontodes inserted in fleshy papillae on the preopercular-opercular region and the dorsal and pectoral fins are 2–3 times as long as those of females. S. salmacis is an exception, as its sexually dimorphic features are subtle and non-remarkable.
Gelanoglanis is a genus of fish in the family Auchenipteridae native to South America.
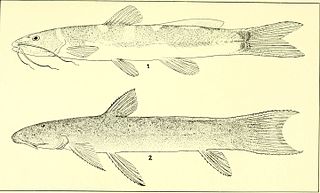
Rhamdella is a genus of three-barbeled catfishes native to South America.

Cnesterodon is a genus of poeciliids native to South America.
Cnesterodon raddai, the Resistencia toothcarp, is a species of poeciliid native to the Paraguay and lower Paraná River basins.
Cnesterodon hypselurus, the Cilida toothcarp, is a species of poeciliid native to the Paranapanema River basin in Brazil.
Cnesterodon omorgmatos, the Cilida toothcarp, is a species of poeciliid native to the Paranapanema River basin in Brazil.











