
Theridiidae, also known as the tangle-web spiders, cobweb spiders and comb-footed spiders, is a large family of araneomorph spiders first described by Carl Jakob Sundevall in 1833. This diverse, globally distributed family includes over 3,000 species in 124 genera, and is the most common arthropod found in human dwellings throughout the world.

Long-jawed orb weavers or long jawed spiders (Tetragnathidae) are a family of araneomorph spiders first described by Anton Menge in 1866. They have elongated bodies, legs, and chelicerae, and build small orb webs with an open hub with few, wide-set radii and spirals with no signal line or retreat. Some species are often found in long vegetation near water.

The blacktailed red sheetweaver, also known as red grass spider, is a species of dwarf spider. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Florinda. It was first described by Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1896, and has only been found in Mexico, the West Indies, and the United States. It is common in the southeastern United States, inhabiting grasslands, lawns, and agricultural fields.

Theridiosoma is a genus of ray spiders that was first described by Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1879. They use their web as a high speed slingshot to actively hunt for prey.

Metaphidippus is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Frederick Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1901. The name is combined from Ancient Greek μετά "after, beside" and the salticid genus Phidippus.

Phiale is a genus of jumping spiders that was first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1846. P. albovittata has been considered a junior synonym of Freya perelegans since 2006.

Zygiella is a genus of orb-weaver spiders first described by F. O. Pickard-Cambridge in 1902. In 2015, Parazygiella was determined to be a taxonomic synonym of Zygiella, and its species were moved to Zygiella.

Coneweb spiders (Diguetidae) are six-eyed haplogyne spiders that live in tangled space webs, fashioning a cone-like central retreat where they hide and lay eggs. It is a small family, containing only two genera split between a range in the Southwestern United States and Mexico and a range in South America. Members of the genus Diguetia usually build their webs in shrubs or between cactus pads. They have the same eye arrangement as the venomous recluse spiders, but none are known to be harmful to humans.
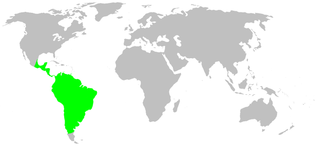
Senoculus is a genus of araneomorph spiders in the family Senoculidae, and was first described by Władysław Taczanowski in 1872. It is the only genus in the family Senoculidae.

Metepeira is a genus of orb-weaver spiders first described by F. O. Pickard-Cambridge in 1903. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek μετά and the obsolete genus name Epeira, denoting a genus similar to Epeira.
Melpomene is a genus of funnel weavers first described by O. Pickard-Cambridge in 1898. They range from southwestern U.S. to Panama and can grow up to 7 to 8.5 millimetres long. Roth and Brame noted that, with many undescribed species, the genus appears to be a catchall or "wastebasket taxon" for several unrelated species that may represent several genera.

Colonus is a genus of spiders in the jumping spider family, Salticidae. Colonus species are endemic to North and South America, ranging from New York to Argentina. All members of the genus have two pairs of bulbous spines on the ventral side of the first tibiae. The function of these spines is unknown. Colonus was declared a junior synonym of Thiodina by Eugène Simon in 1903, but this was reversed by Bustamante, Maddison, and Ruiz in 2015.

Linyphia is a genus of dwarf spiders that was first described by Pierre André Latreille in 1804. The name is Greek, and means "thread-weaver" or "linen maker".

Leucauge fastigata, the pear-shaped leucauge, is a species of spiders in the family Tetragnathidae. Its native range extends from India to the Philippines and Sulawesi.

Hentziectypus is a genus of comb-footed spiders that was first described by Allan Frost Archer in 1946. Originally placed with Theridion, it was moved to Achaearanea in 1955, and to its own genus in 2008. These spiders most resemble members of Cryptachaea, but are distinguished by a median apophysis that is broadly attached to the tegulum. Spiders of Parasteatoda have a median apophysis attached to the embolus, while those of Achaearanea have a hooked paracymbium on the pedipalps of males.
Epeirotypus is a genus of ray spiders that was first described by Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1894.
Epilineutes is a monotypic genus of South and Central American ray spiders containing the single species, Epilineutes globosus. The genus was first described by Jonathan A. Coddington in 1986. The single species was first described in 1896 under the name Andasta globosa, but has also been referred to as Theridiosoma globosum.

Ogulnius is a genus of ray spiders that was first described by Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1882.
Metabus is a genus of long-jawed orb-weavers that was first described by Octavius Pickard-Cambridge in 1899.














