
Strophanthus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described as a genus in 1802. It is native primarily to tropical Africa, extending to South Africa, with a few species in Asia from southern India to New Guinea and southern China. The genus name is a compound of the Greek words στρόφος (stróphos) "twisted cord" and ἄνθος (ánthos) "flower", in reference to the corolla lobes which, in some species - notably S. petersianus - resemble long twisted ribbons or threads and can reach a length of 30–35 cm. This trait, in addition to colouring involving combinations of bright pinks, purples and oranges, combine to make the flowers among the most ornamental in the plant kingdom.
Ctenolophon is the only genus in the flowering plant family Ctenolophonaceae. It has two recognized species:

Ancistrocladus is a genus of woody lianas in the monotypic family Ancistrocladaceae. The branches climb by twining other stems or by scrambling with hooked tips. They are found in the tropics of the Old World.

Synsepalum is a genus of trees and shrubs in the chicle family, Sapotaceae described as a genus in 1852.

The African river martin is a passerine bird, one of two members of the river martin subfamily of the swallow family, Hirundinidae. When discovered, it was not initially recognised as a swallow, and its structural differences from most of its relatives, including its stout bill and robust legs and feet, have led to its current placement in a separate subfamily shared only with the Asian white-eyed river martin. The African river martin is a large swallow, mainly black with a blue-green gloss to the head and a greener tint to the back and wings. The under-wings are brownish, the underparts are purple-black, and the flight feathers are black. This martin has red eyes, a broad orange-red bill and a black, square tail. Young birds are similar in appearance to the adults, but have browner plumage. This species has a variety of unmusical calls, and displays both in flight and on the ground, although the purpose of the terrestrial display is unknown.
The mouselike pipistrelle is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae. It is found in Cameroon, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Gabon. Its natural habitats are subtropical and tropical dry and moist lowland forests.

Thomandersia is the sole genus in the Thomandersiaceae, an African family of flowering plants. Thomandersia is a genus of shrubs and small trees, with six species native to Central and West Africa.

The Gabon talapoin, also known as the northern talapoin, is a small species of African monkey native to riparian habitats in Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, the western Republic of the Congo and the far western Democratic Republic of Congo. It may have been introduced to Bioko and the Canary Islands. Classified in the genus Miopithecus, it was given the name Miopithecus ogouensis, based on the River Ogooué, distinguishing it from the other species, the Angolan talapoin, also known as Miopithecus talapoin.
Hunteria is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1824. It is native to Africa and to South and Southeast Asia.
- Hunteria ballayiHua - Central African Republic, Republic of Congo, Cameroon, Gabon
- Hunteria camerunensisK.Schum. ex Hallier f. - Republic of Congo, Cameroon, Gabon
- Hunteria congolanaPichon - Republic of Congo, Zaïre, Kenya
- Hunteria densifloraPichon - Zaïre
- Hunteria ghanensisJ.B.Hall & Leeuwenb. - Ivory Coast, Ghana
- Hunteria hexaloba(Pichon) Omino - Gabon
- Hunteria macrosiphonOmino - Republic of Congo, Gabon
- Hunteria myrianthaOmino - Zaïre
- Hunteria oxyanthaOmino - Republic of Congo, Zaïre, Gabon
- Hunteria simii(Stapf) H.Huber - Guinea, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Sierra Leone
- Hunteria umbellata(K.Schum) Hallier f. - W + C Africa from Senegal to Zaïre
- Hunteria zeylanica(Retz.) Gardner ex Thwaites - Somalia, Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambique, S China, India, Sri Lanka, Andaman & Nicobar Islands, Indochina, W Malaysia, Sumatra
Lecomtedoxa is a genus of plant in family Sapotaceae described as a genus in 1914.

Marantochloa is a genus of plant in family Marantaceae described as a genus in 1860. It is native to tropical Africa and to islands in the Indian Ocean.
Eremospatha is a genus of climbing flowering plants in the palm family found in tropical Africa. These rattans are uncommon in cultivation and poorly understood by taxonomists. Closely related to Laccosperma, they are differentiated by the near complete absence of bracts and bracteoles. The name is from Greek meaning 'without a spathe'.
Podococcus is a genus of palms found in tropical Africa. It includes two recognized species:
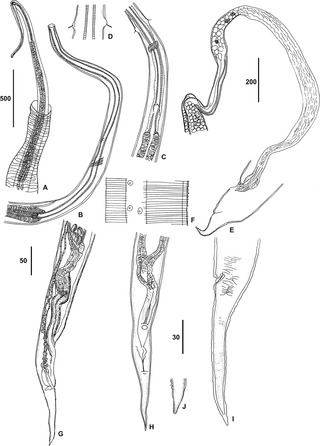
Thelazioidea is a superfamily of spirurian nematodes in the large order Spirurida. Like all nematodes, they have neither a circulatory nor a respiratory system.

Coniostola is a genus of moths belonging to the subfamily Olethreutinae of the family Tortricidae.

Boulengeromyrus is a monospecific genus of freshwater ray-finned fish belonging to the family Mormyridae, the elephantfishes. The only species in the genus is Knoepffler's elephantfish. It occurs only in the Ivindo River and the Ntem River basins of Gabon and Cameroon. It reaches a maximum length of about 41 cm (16 in).
Copelatus pederzanii is a species of diving beetle. It is part of the genus Copelatus in the subfamily Copelatinae of the family Dytiscidae. It was described by Bilardo & Rocchi in 1995.

Craterispermum is a genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. It contains 16 species that occur in tropical Africa and Seychelles. It is the only genus in the tribe Craterispermeae, of which the divergence time is estimated at 34.8 million years ago.

Englerophytum is a group of trees in the family Sapotaceae described as a genus in 1914.

Landolphia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apocynaceae first described as a genus in 1806. They take the form of vines that scramble over host trees. Landolphia is native to tropical Africa.












