
Ricinus communis, the castor bean or castor oil plant, is a species of perennial flowering plant in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae. It is the sole species in the monotypic genus, Ricinus, and subtribe, Ricininae. The evolution of castor and its relation to other species are currently being studied using modern genetic tools. It reproduces with a mixed pollination system which favors selfing by geitonogamy but at the same time can be an out-crosser by anemophily or entomophily.

Jatropha is a genus of flowering plants in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae. The name is derived from the Greek words ἰατρός (iatros), meaning "physician", and τροφή (trophe), meaning "nutrition", hence the common name physic nut. Another common name is nettlespurge. It contains approximately 170 species of succulent plants, shrubs and trees. Most of these are native to the Americas, with 66 species found in the Old World. Plants produce separate male and female flowers. As with many members of the family Euphorbiaceae, Jatropha contains compounds that are highly toxic. Jatropha species have traditionally been used in basketmaking, tanning and dye production. In the 2000s, one species, Jatropha curcas, generated interest as an oil crop for biodiesel production and also medicinal importance when used as lamp oil; native Mexicans in the Veracruz area developed by selective breeding a Jatropha curcas variant lacking the toxic compounds, yielding a better income when used as source for biodiesel, because of its edible byproduct. Toxicity may return if edible Jatropha is pollinated by toxic types.

Pistia is a genus of aquatic plants in the arum family, Araceae. It is the sole genus in the tribe Pistieae which reflects its systematic isolation within the family. The single species it comprises, Pistia stratiotes, is often called water cabbage, water lettuce, Nile cabbage, or shellflower. Its native distribution is uncertain but is probably pantropical; it was first discovered from the Nile near Lake Victoria in Africa. It is now present, either naturally or through human introduction, in nearly all tropical and subtropical fresh waterways and is considered an invasive species as well as a mosquito breeding habitat. The genus name is derived from the Greek word πιστός (pistos), meaning "water," and refers to the aquatic nature of the plants. The specific epithet is also derived from a Greek word, στρατιώτης, meaning "soldier," which references the sword-shaped leaves of some plants in the Stratiotes genus.

Pogostemon is a large genus from the family Lamiaceae, first described as a genus in 1815. It is native to warmer parts of Asia, Africa, and Australia.

Peumus boldus, commonly known as boldo, is a species of tree in the family Monimiaceae and the only species in the genus Peumus. It is endemic to the central region of Chile, between 33° and 40° southern latitude. Boldo has also been introduced to Europe and North Africa, though it is not often seen outside botanical gardens.

Quassia amara, also known as amargo, bitter-ash, bitter-wood, or hombre grande is a species in the genus Quassia, with some botanists treating it as the sole species in the genus. The genus was named by Carl Linnaeus who named it after the first botanist to describe it: the Surinamese freedman Graman Quassi. Q. amara is used as insecticide, in traditional medicine and as additive in the food industry.

Mesembryanthemum tortuosum is a succulent plant in the family Aizoaceae native to the Cape Provinces of South Africa. It is known as kanna, channa, kougoed —which literally means, 'chew(able) things' or 'something to chew'.

Alstonia scholaris, commonly called blackboard tree, scholar tree, milkwood or devil's tree in English, is an evergreen tropical tree in the Dogbane Family (Apocynaceae). It is native to southern China, tropical Asia and Australasia, where it is a common ornamental plant. It is a toxic plant, but is used traditionally for myriad diseases and complaints.

Prenylated flavonoids or prenylflavonoids are a sub-class of flavonoids. They are widely distributed throughout the plant kingdom. Some are known to have phytoestrogenic or antioxidant properties. They are given in the list of adaptogens in herbalism. Chemically they have a prenyl group attached to their flavonoid backbone. It is usually assumed that the addition of hydrophobic prenyl groups facilitate attachment to cell membranes. Prenylation may increase the potential activity of its original flavonoid.

Daphnin is a plant toxin with the chemical formula C15H16O9 and is one of the active compounds present in the Eurasian and North African genus Daphne of the Thymelaeaceae, a plant family with a predominantly Southern Hemisphere distribution with concentrations in Australia and tropical Africa.

Derris taiwaniana is a perennial climbing shrub belonging to the genus Derris. It is known by several synonyms, including Millettia pachycarpa and M. taiwaniana. It is widely used in traditional practices, such as for poisoning fish, agricultural pesticide, blood tonic, and treatments of cancer and infertility. The bark fiber is used for making strong ropes.

Dendrophthoe falcata is one of the hemiparasitic plants that belong to the mistletoe family Loranthaceae. It is the most common of all the mistletoes that occur in India. At the moment reports say that it has around 401 plant hosts. The genus Dendrophthoe comprises about 31 species spread across tropical Africa, Asia, and Australia among which 7 species are found in India.

Zanthoxylum zanthoxyloides, also called Senegal prickly-ash or artar root, is a plant species in the genus Zanthoxylum.

Nimbin is a triterpenoid isolated from Neem. Nimbin is thought to be responsible for much of the biological activities of neem oil, and is reported to have anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, fungicidal, antihistamine and antiseptic properties.

Clausena anisata (Willd.) Hook.f. ex Benth. is a deciduous shrub or small tree, belonging to the Rutaceae or Citrus family, and widespread in the Afrotropical realm or Sub-Saharan Africa, but absent from the drier regions. It is also found in tropical and South-East Asia, growing in India and Sri Lanka and extending as far as Queensland in north-eastern Australia and some Pacific islands. It is cultivated in Malaysia and Indonesia. As with other plants useful to mankind its large range of medicinal properties has led to a global distribution and its growth wherever the climate is suitable. It grows in higher-rainfall regions in savanna, thickets, riverine forest, disturbed areas and secondary forest, up to an altitude of 3000 m. The leaves, which are foetid when bruised, give rise to the common name 'Horsewood' or the more descriptive Afrikaans common name 'Perdepis', meaning 'horse urine'.

Platostoma is a genus of flowering plants in the mint family, Lamiaceae, first described as a genus in 1818. It is native to tropical parts of Africa, southern Asia, Papuasia, and Australia. Mesona and Acrocephalus has been known as its synonyms.
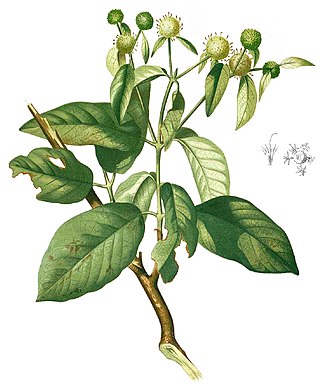
Mitragyna diversifolia is a tree species in the family Rubiaceae and found in Asia. The Catalogue of Life lists no subspecies.

Platostoma hispidum is a species of flowering plant in the mint family, Lamiaceae. It is found in Kashmir to Nepal, Bhutan, Western Ghats, Indo-China,and Malaysia. It is commonly known as hairy gomphrena.

Actinoscirpus is a monospecific genus in the family Cyperaceae which contains only the species Actinoscirpus grossus, the greater club rush. It is found across East and South Asia and is known in China as 大藨草; da biao cao, rumput menderong in Malaysian, and kasheruka within Ayurvedic medicine, which uses the tubers as an antiemetic and treatment for liver and digestive diseases. It is a perennial plant that grows rapidly with long rhizomes that end in small tubers. A. grossus is considered a "principal" weed of rice in some Southeast Asian countries. It is abundant in swampy or inundated areas, such as marshes and ditches, and is capable of dominating wetlands and rice patties. It is also a host of Chilo polychrysus, the dark-headed rice borer.

Chuquiraga spinosa, common name huamanpinta in Spanish, is a species of flowering plant of the family Asteraceae. Native to Perú and Bolivia, it is used in traditional medicine for its anti-inflammatory properties.



















