Sodium laureth sulfate (SLES), an accepted contraction of sodium lauryl ether sulfate (SLES), also called sodium alkylethersulfate, is an anionic detergent and surfactant found in many personal care products and for industrial uses. SLES is an inexpensive and very effective foaming agent. SLES, sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), ammonium lauryl sulfate (ALS), and sodium pareth sulfate are surfactants that are used in many cosmetic products for their cleaning and emulsifying properties. It is derived from palm kernel oil or coconut oil. In herbicides, it is used as a surfactant to improve absorption of the herbicidal chemicals and reduces time the product takes to be rainfast, when enough of the herbicidal agent will be absorbed.

Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension or interfacial tension between two liquids, a liquid and a gas, or a liquid and a solid. The word "surfactant" is a blend of surface-active agent, coined c. 1950. As they consist of a water-repellent and a water-attracting part, they enable water and oil to mix; they can form foam and facilitate the detachment of dirt.

Polyethylene glycol (PEG; ) is a polyether compound derived from petroleum with many applications, from industrial manufacturing to medicine. PEG is also known as polyethylene oxide (PEO) or polyoxyethylene (POE), depending on its molecular weight. The structure of PEG is commonly expressed as H−(O−CH2−CH2)n−OH.

Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the formula C2H4O. It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor. Because it is a strained ring, ethylene oxide easily participates in a number of addition reactions that result in ring-opening. Ethylene oxide is isomeric with acetaldehyde and with vinyl alcohol. Ethylene oxide is industrially produced by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of a silver catalyst.

In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether, where the ether forms a three-atom ring: two atoms of carbon and one atom of oxygen. This triangular structure has substantial ring strain, making epoxides highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often volatile.

Hexadecane (also called cetane) is an alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C16H34. Hexadecane consists of a chain of 16 carbon atoms, with three hydrogen atoms bonded to the two end carbon atoms, and two hydrogens bonded to each of the 14 other carbon atoms.
In organic chemistry, ethoxylation is a chemical reaction in which ethylene oxide adds to a substrate. It is the most widely practiced alkoxylation, which involves the addition of epoxides to substrates.
Cetyl alcohol, also known as hexadecan-1-ol and palmityl alcohol, is a C-16 fatty alcohol with the formula CH3(CH2)15OH. At room temperature, cetyl alcohol takes the form of a waxy white solid or flakes. The name cetyl derives from the whale oil (cetacea oil, from Latin: cetus, lit. 'whale', from Ancient Greek: κῆτος, romanized: kētos, lit. 'huge fish') from which it was first isolated.
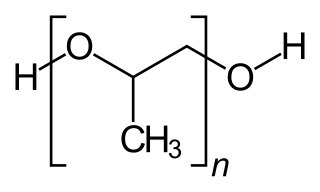
Polypropylene glycol or polypropylene oxide is the polymer of propylene glycol. Chemically it is a polyether, and, more generally speaking, it's a polyalkylene glycol (PAG) H S Code 3907.2000. The term polypropylene glycol or PPG is reserved for polymer of low- to medium-range molar mass when the nature of the end-group, which is usually a hydroxyl group, still matters. The term "oxide" is used for high-molar-mass polymer when end-groups no longer affect polymer properties. Between 60 and 70% of propylene oxide is converted to polyether polyols by the process called alkoxylation.
Glycol ethers are a class of chemical compounds consisting of alkyl ethers that are based on glycols such as ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. They are commonly used as solvents in paints and cleaners. They have good solvent properties while having higher boiling points than the lower-molecular-weight ethers and alcohols.
Polysorbate 20 is a polysorbate-type nonionic surfactant formed by the ethoxylation of sorbitan monolaurate. Its stability and relative nontoxicity allows it to be used as a detergent and emulsifier in a number of domestic, scientific, and pharmacological applications. As the name implies, the ethoxylation process leaves the molecule with 20 repeat units of polyethylene glycol; in practice these are distributed across 4 different chains, leading to a commercial product containing a range of chemical species.
PEG-16 macadamia glycerides is the polyethylene glycol derivative of the mono- and diglycerides derived from macadamia nut oil by ethoxylation with an average of ethylene glycol units. PEG-16 macadamia glycerides are commonly used in cosmetic formulations as an emollient, refatter, conditioner, solubilizer, and secondary emulsifier.
Jojoba wax esters are polyethylene glycol derivatives of the acids and alcohols obtained from the saponification of jojoba oil. With an average ethoxylation value of 80, it is known as jojoba wax PEG-80 esters or PEG-80 jojoba. With an average ethoxylation value of 120, it is known as jojoba wax PEG-120 esters or PEG-120 jojoba. Jojoba wax esters are used in cosmetic formulations as emollients.
The INCI names ceteareth-n (where n is a number) refer to polyoxyethylene ethers of a mixture of high molecular mass saturated fatty alcohols, mainly cetyl alcohol (m = 15) and stearyl alcohol (m = 17). The number n indicates the average number of ethylene oxide residues in the polyoxyethylene chain.
Octaethylene glycol monododecyl ether (C12E8) is a nonionic surfactant formed by the ethoxylation of dodecanol to give a material with 8 repeat units of ethylene glycol.
Within chemical compound surfactants, pentaethylene glycol monododecyl ether (C12E5) is a nonionic surfactant. It is formed by the ethoxylation chemical reaction of dodecanol to give a material with 5 repeat units of ethylene glycol.
Nonoxynols also known as nonaethylene glycol or polyethylene glycol nonyl phenyl ether are mixtures of nonionic surfactants used as detergents, emulsifiers, wetting agents or defoaming agents. The most commonly discussed compound nonoxynol-9 is a spermicide, formulated primarily as a component of vaginal foams and creams. Nonoxynol was found to metabolize into free nonylphenol when administered to lab animals. Arkopal-N60, with on average 6 ethylene glycol units is a related used surfactant.

A defoamer or an anti-foaming agent is a chemical additive that reduces and hinders the formation of foam in industrial process liquids. The terms anti-foam agent and defoamer are often used interchangeably. Strictly speaking, defoamers eliminate existing foam and anti-foamers prevent the formation of further foam. Commonly used agents are insoluble oils, polydimethylsiloxanes and other silicones, certain alcohols, stearates and glycols. The additive is used to prevent formation of foam or is added to break a foam already formed.
Isoceteth-20 is a polyethylene glycol ether formed by the ethoxylation of iso-cetyl alcohol; with the general formula HO(C2H4O)nC16H33 where n has an average value of 20. It is a nonionic surfactant used as an emulsifier in some personal care products. However, as iso-cetyl alcohol is rare in nature isoceteth-20 does not see widespread use.
C12-15 pareth-12 (INCI name) is an emulsifier and surfactant commonly used in cosmetics formulations. It is a polyethylene glycol ether formed by combining synthetic C12–C15 fatty alcohols with 12 moles of ethylene oxide.







