
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. Ecuador also includes the Galápagos Islands in the Pacific, about 1,000 kilometers (621 mi) west of the mainland. The country's capital is Quito and its largest city is Guayaquil.

Chusquea is a genus of evergreen bamboos in the grass family. Most of them are native to mountain habitats in Latin America, from Mexico to southern Chile and Argentina.

The Colombia national football team, nicknamed Los Cafeteros, represents Colombia in men's international football and is managed by the Colombian Football Federation, the governing body for football in Colombia. They are a member of CONMEBOL and are currently ranked 9th in the FIFA World Rankings. The team are nicknamed Los Cafeteros due to the coffee production in their country. The national team has been a symbol of nationalism, pride and passion for many Colombians worldwide. Colombia is known for having a passionate fan base, and the team's dances during goal celebrations have been symbolic.

Aganisia is a small South American genus in the orchid family (Orchidaceae), subfamily Epidendroideae.
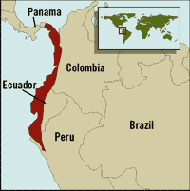
Tumbes-Chocó-Magdalena is a biodiversity hotspot, which includes the tropical moist forests and tropical dry forests of the Pacific coast of South America and the Galapagos Islands. The region extends from easternmost Panama to the lower Magdalena Valley of Colombia, and along the Pacific coast of Colombia and Ecuador to the northwestern corner of Peru. Formerly called the Chocó-Darién-Western Ecuador Hotspot, it has been expanded to include several new areas, notably the Magdalena Valley in northern Colombia. It is bounded on the east by the Andes Mountains. The Tumbes-Choco-Magdalena Hotspot is 1,500 km long and encircles 274,597 km2. Tumbes-Choco-Magdalena is near the Pacific Ocean. The factors that threaten Tumbes-Choco-Magdalena are farming encroachment, deforestation, illegal crops, and population growth. Whereas the Panamanian and Colombian portion of the hotspot are relatively intact, approximately 98% of native forest in coastal Ecuador has been cleared, rendering it the most threatened tropical forest in the world. The hotspot includes a wide variety of habitats, ranging from mangroves, beaches, rocky shorelines, and coastal wilderness to some of the world's wettest rain forests in the Colombian Chocó. The hotspot includes a number of ecoregions:

Luis Fernando Suárez Guzmán is a Colombian football manager and former player who played as a defender. He is the current manager of Deportivo Pereira. Suárez has managed in six Latin American countries: Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Honduras, Mexico and Costa Rica.

Pitcairnia is a genus of plants in the family Bromeliaceae, subfamily Pitcairnioideae. It was named for William Pitcairn, Scottish physician and gardener (1711–1791). The genus Pitcairnia ranks as the second most prolific of the bromeliad family. They are most abundant in Colombia, Peru and Brazil, but can also be found in areas from Cuba and Mexico south to Argentina. One species, Pitcairnia feliciana, is found in tropical West Africa and is the only member of the family Bromeliaceae not native to the Americas.

Wallisia cyanea, or pink quill, is a species of plant of the genus Wallisia in the bromeliad family, native to the rainforests of Ecuador. An epiphytic perennial growing to 50 cm (20 in) high by 50 cm (20 in) wide, it has stemless rosettes of thin, recurved leaves and paddle-shaped spikes of 20 pink bracts with violet flowers, in spring and autumn.
The 1972 Federation Cup was the tenth edition of the most important competition between national teams in women's tennis. 31 nations participated in the tournament, which was held at Ellis Park in Johannesburg, South Africa from 20–25 March. South Africa defeated Great Britain in the final, in what was the first final not featuring United States or Australia, giving South Africa their first title. South Africa became the first team other than United States or Australia to win the Fed Cup.

Diglossopis was a genus of blue flowerpiercers in the family Thraupidae. They are now usually placed in the genus Diglossa. They were formerly classified in the bunting and American sparrow family Emberizidae, more recent studies have shown it to belong in the Thraupidae. They are restricted to highland forest and woodland from Venezuela and Colombia, through Ecuador and Peru, to Bolivia.

Gran Colombia, or Greater Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central America from 1819 to 1831. It included present-day Colombia, mainland Ecuador, Panama, and Venezuela, along with parts of northern Peru, northwestern Brazil, and claimed the Essequibo region. The terms Gran Colombia and Greater Colombia are used historiographically to distinguish it from the current Republic of Colombia, which is also the official name of the former state.

Wettinia is a genus of flowering plants in the palm family Arecaceae. The genus, established in 1837, contains some 20 species, but more seem to await discovery considering that 4 species - W. aequatorialis, W. lanata, W. minima and W. panamensis - were described as late as 1995. The genus is broadly divided into two groups. One group has the fruits tightly packed, while the other, formerly classified as genus Catoblastus, has fruits scattered along the inflorescence branches. It is not known whether these groups are both monophyletic. The genus is named after Frederick Augustus II of Saxony, of the House of Wettin.

The masked flowerpiercer is a species of bird in the tanager family, Thraupidae. It is found in humid montane forest and scrub in Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru and Bolivia. Flowerpiercers got their name from the fact that they have a sharp hook on the tip of their upper mandible which they use to slice open the base of flowers to get at the nectar.
The Colombia national under-17 football team represents Colombia in international under-17 football competitions and is overseen by the Colombian Football Federation.

Brunellia is a genus of trees. They are distributed in the mountainous regions of southern Mexico, Central America, West Indies, and South America. Brunellia is the only genus in the family Brunelliaceae. As of 2001 there were about 54 species.

Colombia–Ecuador relations refers to the bilateral relations between the neighbouring Colombia and Ecuador. The present territory of both countries was part of the Spanish Empire from the sixteenth to nineteenth centuries. After the wars for independence against Spain led by Simón Bolívar, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela became part of the Republic of Gran Colombia in 1819. Both nations are members of the Community of Latin American and Caribbean States, Organization of Ibero-American States, and Organization of American States.
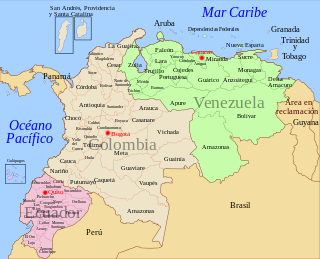
The 2008 Andean diplomatic crisis was a diplomatic stand-off involving the South American countries of Ecuador, Colombia and Venezuela. It began with an incursion into Ecuadorian territory across the Putumayo River by the Colombian military on March 1, 2008, leading to the deaths of over twenty militants, including Raúl Reyes and sixteen other members of the Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC). This incursion led to increased tension between Colombia and Ecuador and the movement of Venezuelan and Ecuadorian troops to their borders with Colombia.

Aganisia cyanea is a showy species of orchid native to Colombia, Venezuela, Peru and Brazil and widely cultivated elsewhere as an ornamental. It is remarkable because some cultivars of this species produce blue flowers, the color blue being quite rare among the orchids. They are considered difficult to maintain in cultivation without a controlled growing environment.
A. tricolor may refer to:
















