
Starfish or sea stars are star-shaped echinoderms belonging to the class Asteroidea. Common usage frequently finds these names being also applied to ophiuroids, which are correctly referred to as brittle stars or basket stars. Starfish are also known as asteroids due to being in the class Asteroidea. About 1,900 species of starfish live on the seabed in all the world's oceans, from warm, tropical zones to frigid, polar regions. They are found from the intertidal zone down to abyssal depths, at 6,000 m (20,000 ft) below the surface.

The California spiny lobster is a species of spiny lobster found in the eastern Pacific Ocean from Monterey Bay, California, to the Gulf of Tehuantepec, Mexico. It typically grows to a length of 30 cm (12 in) and is a reddish-brown color with stripes along the legs, and has a pair of enlarged antennae but no claws. The interrupted grooves across the tail are characteristic for the species.

Asterias amurensis, also known as the Northern Pacific seastar and Japanese common starfish, is a seastar found in shallow seas and estuaries, native to the coasts of northern China, Korea, far eastern Russia, Japan, Alaska, the Aleutian Islands and British Columbia in Canada. Two forms are recognised: the nominate and formarobusta from the Strait of Tartary. It mostly preys on large bivalve molluscs, and it is mostly preyed on by other species of starfish. Population booms in Japan can affect the harvest of mariculture operations and are costly to combat.

Solaster paxillatus, the orange sun star, is a species of starfish found at varying depths in the northern Pacific Ocean. It is a natural predator of the starfish Asterias amurensis.

The common starfish, common sea star or sugar starfish is the most common and familiar starfish in the north-east Atlantic. Belonging to the family Asteriidae, it has five arms and usually grows to between 10–30 cm across, although larger specimens are known. The common starfish is usually orange or brownish in color, and sometimes violet; specimens found in deeper waters are pale. The common starfish is found on rocky and gravelly substrates where it feeds on mollusks and other benthic invertebrates.

The common sunstar is a species of sea star belonging to the family Solasteridae. It is found in the northern parts of both the Atlantic and the Pacific Oceans.

The Brisingids are deep-sea-dwelling starfish in the order Brisingida.

Poraniopsis is a genus of starfish in the family Poraniidae in the order Valvatida. Poraniopsis echinaster is the type species.

Luidia senegalensis, the nine-armed sea star, is a tropical species of starfish in the family Luidiidae found in the western Atlantic Ocean.
Stylasterias is a genus of starfish in the family Asteriidae. Stylasterias forreri, the velcro star, is the only species in the genus. It is found on the Pacific coast of Canada and the United States.

Orthasterias is a genus of sea stars in the family Asteriidae. Orthasterias koehleri, the rainbow star or red-banded sea star, is the only species in the genus. It is found in the North Pacific Ocean.

Pteraster militaris, the wrinkled star, is a species of starfish in the family Pterasteridae. It is found in the northern Pacific Ocean, the Arctic Ocean, the Barents Sea, and the northern Atlantic Ocean.

Marthasterias is a genus of starfish in the family Asteriidae. Both species in the genus are commonly known as the spiny starfish.
Trophodiscus almus is a species of starfish in the family Astropectinidae. It is found in fairly deep waters in the Sea of Okhotsk, the Sea of Japan and around the Japanese island of Hokkaido. It is very unusual among starfish in that it broods its young on its upper surface. Its common name in Japanese is "Komochi-momiji".
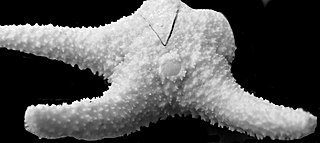
Bathyporania ascendens is a species of starfish in the family Poraniidae, and the only species of the genus Bathyporania. It is native to the Pacific Ocean and is found in deep water off the coast of North America.

Clavaporania fitchorum is a species of starfish in the family Poraniidae. It is the only known species of the genus Clavaporania. It is native to the South Pacific Ocean and is found in deep water off the coast of Australia.

The Pacific spiny dogfish is a common species of the Squalidae (dogfish) family of sharks and are among the most abundant species of sharks in the world. This species is closely related to Squalus acanthias and for many years they were treated as a single species. Recent research, using meristic, morphological and molecular data led to the resurrection of the Pacific spiny dogfish as a separate species. The American Fisheries Society recommends the common name "Pacific spiny dogfish" for Squalus suckleyi over alternatives such as "spotted spiny dogfish" and "North Pacific spiny dogfish" and "spiny dogfish" for Squalus acanthias.
Paulasterias mcclaini is a species of starfish in the family Paulasteriidae. It is found in deep water at hydrothermal vents.

Meyenaster is a genus of starfish in the family Asteriidae. It is a monotypic genus and the only species is Meyenaster gelatinosus which was first described by the Prussian botanist and zoologist Franz Julius Ferdinand Meyen in 1834. It is found in the southeastern Pacific Ocean on the coasts of South America.

Rathbunaster is a monospecific genus of sea stars in the family Asteriidae. The genus name was given by Walter Kenrick Fisher to honor the starfish biologist Richard Rathbun of the Smithsonian Institution. He originally ranged this genus under the family Pycnopididae, synonymous with Asteriidae.

















