
Millets are a group of highly variable small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food.
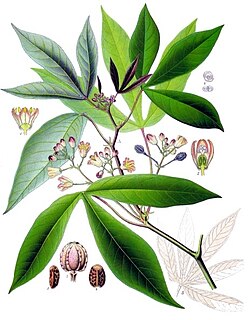
Manihot esculenta, commonly called cassava, manioc, or yuca is a woody shrub native to South America of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated as an annual crop in tropical and subtropical regions for its edible starchy tuberous root, a major source of carbohydrates. Though it is often called yuca in parts of Spanish America and in the United States, it is not related to yucca, a shrub in the family Asparagaceae. Cassava is predominantly consumed in boiled form, but substantial quantities are used to extract cassava starch, called tapioca, which is used for food, animal feed, and industrial purposes. The Brazilian farinha, and the related garri of West Africa, is an edible coarse flour obtained by grating cassava roots, pressing moisture off the obtained grated pulp, and finally drying it.

Convolvulaceae, known commonly as the bindweed or morning glory family, is a family of about 60 genera and more than 1,650 species of mostly herbaceous vines, but also trees, shrubs and herbs, and also including the sweet potato and a few other food tubers.

Bombacaceae were long recognised as a family of flowering plants or Angiospermae. The family name was based on the type genus Bombax. As is true for many botanical names, circumscription and status of the taxon has varied with taxonomic point of view, and currently the preference is to transfer most of the erstwhile family Bombacaceae to the subfamily Bombacoideae within the family Malvaceae in the order Malvales. The rest of the family were transferred to other taxa, notably the new family Durionaceae. Irrespective of current taxonomic status, many of the species originally included in the Bombacaceae are of considerable ecological, historical, horticultural, and economic importance, such as balsa, kapok, baobab and durian.

Chinese cabbage can refer to two cultivar groups of leaf vegetables often used in Chinese cuisine: the Pekinensis Group and the Chinensis Group.

Colocasia esculenta is a tropical plant grown primarily for its edible corms, a root vegetable most commonly known as taro, kalo, dasheen, madhumbe, marope, magogoya, patra or godere. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, and petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in African, Oceanic, and South Asian cultures, and taro is believed to have been one of the earliest cultivated plants.

Yam is the common name for some plant species in the genus Dioscorea that form edible tubers. Yams are perennial herbaceous vines cultivated for the consumption of their starchy tubers in many temperate and tropical regions, especially in Africa, South America and the Caribbean, Asia, and Oceania. The tubers themselves, also called "yams", come in a variety of forms owing to numerous cultivars and related species.

Vegetables are parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. The original meaning is still commonly used and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including the flowers, fruits, stems, leaves, roots, and seeds. An alternate definition of the term is applied somewhat arbitrarily, often by culinary and cultural tradition. It may exclude foods derived from some plants that are fruits, flowers, nuts, and cereal grains, but include savoury fruits such as tomatoes and courgettes, flowers such as broccoli, and seeds such as pulses.

Grasim Industries Limited is an Indian manufacturing company based in Mumbai, Maharashtra. Grasim Industries was ranked 154th in a list of the world's best regarded firms compiled by Forbes. It was started in 1947 as a textile manufacturer. Since then Grasim has diversified into Viscose Staple Fiber (VSF), cement, sponge iron, chemicals and Diversified Financial Services.

Linnaea is a plant genus in the honeysuckle family Caprifoliaceae. Until 2013, the genus included a single species, Linnaea borealis. In 2013, on the basis of molecular phylogenetic evidence, the genus was expanded to include species formerly placed in Abelia, Diabelia, Dipelta, Kolkwitzia and Vesalea. However, this is rejected by the majority of subsequent scientific literature and flora.

Rhodognaphalon is a genus of flowering plant in the family Malvaceae: found in tropical Africa.

Operculina is a genus of plants in the morning-glory family which that are found throughout the world.

Melanthera, squarestem, is a genus of flowering plants in the daisy family, Asteraceae, native to North and South America, as well as Africa, Asia and Oceania, including Hawaiʻi.

Periploca is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae, first described for modern science by Linnaeus in 1753. It is native to Europe, Asia, and Africa.
- Periploca aphyllaDecne. - Middle East from Sinai to Pakistan
- Periploca calophylla(Wight) Falc. - S China, Nepal, Bhutan, Assam, E Himalayas, Vietnam
- Periploca chevalieriBrowicz - Cape Verde Islands
- Periploca chrysanthaD.S. Yao, X.D. Chen & J.W. Ren - Gansu Province in China
- Periploca floribundaTsiang - Yunnan, Vietnam
- Periploca forrestiiSchltr. - Guangxi, Guizhou, Qinghai, Sichuan, Tibet, Yunnan, India, Kashmir, Myanmar, Nepal
- Periploca graecaL. - Mediterranean
- Periploca hydaspidisFalc. - Kashmir
- Periploca laevigataAiton - Canary Islands, Savage Islands
- Periploca linearifoliaQuart.-Dill. & A. Rich - Ethiopia
- Periploca nigrescensAfzel. - W Africa
- Periploca refractifoliaGilli - Tanzania
- Periploca sepiumBunge - widespread across much of China
- Periploca tsiangiiD. Fang & H.Z. Ling - Guangxi Province in China
- Periploca visciformis(Vatke) K. Schum. - Somalia
Jerry Lynn Williams (1948–2005) was a rock music singer and composer. He wrote such hits as "Forever Man," "See What Love Can Do," "Something's Happening," "Running on Faith" and "Pretending" for Eric Clapton. He contributed two songs, "Real Man" and "I Will Not Be Denied" to Bonnie Raitt's 1989 Grammy Award winning album Nick of Time. He had previously written material for Raitt's 1986 album Nine Lives. He also wrote songs for Robert Plant, B.B. King, Stevie Ray Vaughan and Jimmie Vaughan. As a performer, he released albums on Warner Bros. Records and CBS Records during the 1970s, and his break as a songwriter came when Delbert McClinton's cover of a song from his second album, "Givin' It Up for Your Love," reached the Top 40.

This is a categorically-organized list of foods. Food is any substance consumed to provide nutritional support for the body. It is produced either by Plants or Animals, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ingested by an organism and assimilated by the organism's cells in an effort to produce energy, maintain life, or stimulate growth.

A staple food, food staple, or simply a staple, is a food that is eaten routinely and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for a given person, supplying a large fraction of energy needs and generally forming a significant proportion of the intake of other nutrients as well. A staple food of a specific society may be eaten as often as every day or every meal, and most people live on a diet based on just a small number of food staples. Specific staples vary from place to place, but typically are inexpensive or readily available foods that supply one or more of the macronutrients needed for survival and health: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals, and vitamins. Typical examples include tubers and roots, grains, legumes, and seeds. Among them, cereals, legumes, tubers and roots account for about 90% of the world's food calories intake.
Tridynamia is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Convolvulaceae.
Cordisepalum is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Convolvulaceae.
Enneatypus is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Polygonaceae.
















