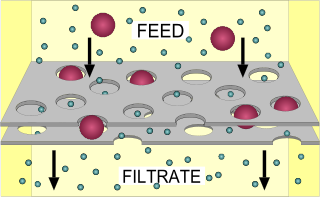
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a filter medium that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are described as oversize and the fluid that passes through is called the filtrate. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as blinding. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective pore size of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles. Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms.

Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, including being safely returned to the environment. Water treatment removes contaminants and undesirable components, or reduces their concentration so that the water becomes fit for its desired end-use. This treatment is crucial to human health and allows humans to benefit from both drinking and irrigation use.

Activated carbon, also called activated charcoal, is a form of carbon commonly used to filter contaminants from water and air, among many other uses. It is processed (activated) to have small, low-volume pores that increase the surface area available for adsorption or chemical reactions. Activation is analogous to making popcorn from dried corn kernels: popcorn is light, fluffy, and has a surface area that is much larger than the kernels. Activated is sometimes replaced by active.

Wastewater treatment is a process used to remove contaminants from wastewater and convert it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once returned to the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on the environment or is reused for various purposes. The treatment process takes place in a wastewater treatment plant. There are several kinds of wastewater which are treated at the appropriate type of wastewater treatment plant. For domestic wastewater, the treatment plant is called a sewage treatment plant. For industrial wastewater, treatment either takes place in a separate industrial wastewater treatment plant, or in a sewage treatment plant. Further types of wastewater treatment plants include agricultural wastewater treatment plants and leachate treatment plants.

The activated sludgeprocess is a type of biological wastewater treatment process for treating sewage or industrial wastewaters using aeration and a biological floc composed of bacteria and protozoa. It uses air and microorganisms to biologically oxidize organic pollutants, producing a waste sludge containing the oxidized material.

Industrial wastewater treatment describes the processes used for treating wastewater that is produced by industries as an undesirable by-product. After treatment, the treated industrial wastewater may be reused or released to a sanitary sewer or to a surface water in the environment. Some industrial facilities generate wastewater that can be treated in sewage treatment plants. Most industrial processes, such as petroleum refineries, chemical and petrochemical plants have their own specialized facilities to treat their wastewaters so that the pollutant concentrations in the treated wastewater comply with the regulations regarding disposal of wastewaters into sewers or into rivers, lakes or oceans. This applies to industries that generate wastewater with high concentrations of organic matter, toxic pollutants or nutrients such as ammonia. Some industries install a pre-treatment system to remove some pollutants, and then discharge the partially treated wastewater to the municipal sewer system.
An aerated lagoon is a simple wastewater treatment system consisting of a pond with artificial aeration to promote the biological oxidation of wastewaters.
Enhanced biological phosphorus removal (EBPR) is a sewage treatment configuration applied to activated sludge systems for the removal of phosphate.

Secondary treatment is the removal of biodegradable organic matter from sewage or similar kinds of wastewater. The aim is to achieve a certain degree of effluent quality in a sewage treatment plant suitable for the intended disposal or reuse option. A "primary treatment" step often precedes secondary treatment, whereby physical phase separation is used to remove settleable solids. During secondary treatment, biological processes are used to remove dissolved and suspended organic matter measured as biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). These processes are performed by microorganisms in a managed aerobic or anaerobic process depending on the treatment technology. Bacteria and protozoa consume biodegradable soluble organic contaminants while reproducing to form cells of biological solids. Secondary treatment is widely used in sewage treatment and is also applicable to many agricultural and industrial wastewaters.

Sequencing batch reactors (SBR) or sequential batch reactors are a type of activated sludge process for the treatment of wastewater. SBR reactors treat wastewater such as sewage or output from anaerobic digesters or mechanical biological treatment facilities in batches. Oxygen is bubbled through the mixture of wastewater and activated sludge to reduce the organic matter. The treated effluent may be suitable for discharge to surface waters or possibly for use on land.

Sewage sludge treatment describes the processes used to manage and dispose of sewage sludge produced during sewage treatment. Sludge treatment is focused on reducing sludge weight and volume to reduce transportation and disposal costs, and on reducing potential health risks of disposal options. Water removal is the primary means of weight and volume reduction, while pathogen destruction is frequently accomplished through heating during thermophilic digestion, composting, or incineration. The choice of a sludge treatment method depends on the volume of sludge generated, and comparison of treatment costs required for available disposal options. Air-drying and composting may be attractive to rural communities, while limited land availability may make aerobic digestion and mechanical dewatering preferable for cities, and economies of scale may encourage energy recovery alternatives in metropolitan areas.
Wet oxidation is a form of hydrothermal treatment. It is the oxidation of dissolved or suspended components in water using oxygen as the oxidizer. It is referred to as "Wet Air Oxidation" (WAO) when air is used. The oxidation reactions occur in superheated water at a temperature above the normal boiling point of water (100 °C), but below the critical point (374 °C).

Sewage treatment is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable for discharge to the surrounding environment or an intended reuse application, thereby preventing water pollution from raw sewage discharges. Sewage contains wastewater from households and businesses and possibly pre-treated industrial wastewater. There are a high number of sewage treatment processes to choose from. These can range from decentralized systems to large centralized systems involving a network of pipes and pump stations which convey the sewage to a treatment plant. For cities that have a combined sewer, the sewers will also carry urban runoff (stormwater) to the sewage treatment plant. Sewage treatment often involves two main stages, called primary and secondary treatment, while advanced treatment also incorporates a tertiary treatment stage with polishing processes and nutrient removal. Secondary treatment can reduce organic matter from sewage, using aerobic or anaerobic biological processes.
Membrane bioreactor (MBR) is a combination of membrane processes like microfiltration or ultrafiltration with a biological wastewater treatment process, the activated sludge process. It is now widely used for municipal and industrial wastewater treatment. In general, there are two different MBR configurations: (1) submerged membrane bioreactor (SMBR) and (2) side stream membrane bioreactor. In the first configuration, the membrane is located inside the biological reactor, submerged in the wastewater. In the latter configuration, the membrane is located outside the reactor, as an additional step after biological treatment.

A rotating biological contactor or RBC is a biological fixed-film treatment process used in the secondary treatment of wastewater following primary treatment. The primary treatment process involves removal of grit, sand and coarse suspended material through a screening process, followed by settling of suspended solids. The RBC process allows the wastewater to come in contact with a biological film in order to remove pollutants in the wastewater before discharge of the treated wastewater to the environment, usually a body of water. A rotating biological contactor is a type of secondary (biological) treatment process. It consists of a series of closely spaced, parallel discs mounted on a rotating shaft which is supported just above the surface of the wastewater. Microorganisms grow on the surface of the discs where biological degradation of the wastewater pollutants takes place.
Mixed liquor suspended solids (MLSS) is the concentration of suspended solids, in an aeration tank during the activated sludge process, which occurs during the treatment of waste water. The units MLSS is primarily measured in milligram per litre (mg/L), but for activated sludge its mostly measured in gram per litre [g/L] which is equal to kilogram per cubic metre [kg/m3]. Mixed liquor is a combination of raw or unsettled wastewater or pre-settled wastewater and activated sludge within an aeration tank. MLSS consists mostly of microorganisms and non-biodegradable suspended matter. MLSS is an important part of the activated sludge process to ensure that there is a sufficient quantity of active biomass available to consume the applied quantity of organic pollutant at any time. This is known as the food to microorganism ratio, more commonly notated as the F/M ratio. By maintaining this ratio at the appropriate level the biomass will consume high percentages of the food. This minimizes the loss of residual food in the treated effluent. In simple terms, the more the biomass consumes the lower the biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) will be in the discharge. It is important that MLSS removes COD and BOD in order to purify water for clean surface waters, and subsequently clean drinking water and hygiene. Raw sewage enters in the water treatment process with a concentration of sometimes several hundred mg/L of BOD. Upon being treated by screening, pre-settling, activated sludge processes or other methods of treatment, the concentration of BOD in water can be lowered to less than 2 mg/L, which is considered to be clean, safe to discharge to surface waters or to reuse water.

Sludge is a semi-solid slurry that can be produced from a range of industrial processes, from water treatment, wastewater treatment or on-site sanitation systems. For example, it can be produced as a settled suspension obtained from conventional drinking water treatment, as sewage sludge from wastewater treatment processes or as fecal sludge from pit latrines and septic tanks. The term is also sometimes used as a generic term for solids separated from suspension in a liquid; this 'soupy' material usually contains significant quantities of 'interstitial' water. Sludge can consist of a variety of particles, such as animal manure.
The adsorption/bio-oxidation process is a two-stage modification of the activated sludge process used for wastewater treatment. It consists of a high-loaded A-stage and low-loaded B-stage. The process is operated without a primary clarifier, with the A-stage being an open dynamic biological system. Both stages have separate settling tanks and sludge recycling lines, thus maintaining unique microbial communities in both reactors.

Moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) is a type of wastewater treatment process that was first invented by Prof. Hallvard Ødegaard at Norwegian University of Science and Technology in the late 1980s. It was commercialized by Kaldnes Miljöteknologi. There are over 700 wastewater treatment systems installed in over 50 countries. Currently, there are various suppliers of MBBR systems.














