
Lisa Ann Murkowski is an American attorney and politician serving as the senior United States senator from Alaska, having held the seat since 2002. She is the first woman to represent Alaska in the Senate and the Senate's second-most senior Republican woman, after Susan Collins of Maine. She became dean of Alaska's congressional delegation upon Representative Don Young's death.
The Democratic Senatorial Campaign Committee (DSCC) is the Democratic Hill committee for the United States Senate. Its purpose is to elect Democrats to the United States Senate. The DSCC's current Chair is Senator Gary Peters of Michigan, who succeeded Nevada's Catherine Cortez Masto after the 2020 Senate elections. DSCC's current executive director is Christie Roberts.

United States gubernatorial elections were held on November 7, 2006, in 36 states and two territories. The elections coincided with the midterm elections of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives.

Jefferson H. Van Drew is an American politician and dentist serving as the U.S. representative for New Jersey's 2nd congressional district since 2019. Formerly a Democrat, he has been a member of the Republican Party since 2020.
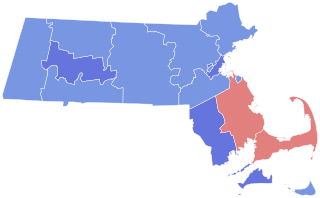
The 1984 United States Senate election in Massachusetts was held on November 6, to elect a member of the U.S. Senate from the State of Massachusetts. The election was won by Democrat John Kerry, the Lieutenant Governor of Massachusetts, who remained Senator until 2013, when he resigned to become United States Secretary of State. One-term incumbent Democratic Senator Paul Tsongas declined to seek re-election after developing cancer.

The 2008 United States Senate election in Massachusetts took place on November 4, 2008. Incumbent Democratic U.S. Senator John Kerry, who remained in the Senate after losing the presidency to incumbent President George W. Bush in the 2004 presidential election, won re-election to a fifth term in office. Kerry later resigned his seat in 2013 to become Secretary of State under the Obama administration.
The Delaware Democratic Party (DelDems) is the affiliate of the Democratic Party in the U.S. state of Delaware. It is headquartered in New Castle County and chaired by Erik Raser-Schramm.

The 1980 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 4. Republican presidential nominee Ronald Reagan defeated incumbent Democratic President Jimmy Carter in a landslide. Republicans picked up seats in both chambers of Congress and won control of the Senate, though Democrats retained a majority in the House of Representatives. The election is sometimes referred to as part of the "Reagan Revolution", a conservative realignment in U.S. politics and marked the start of the Reagan Era.

The 2010 United States Senate election in Alaska took place on November 2, 2010, to elect a member of the United States Senate to represent the State of Alaska, alongside 33 U.S. Senate elections in other states, elections in all states for the U.S. House of Representatives, as well as various state and local elections. The general election was preceded by primary elections which were held on August 24, 2010. Scott McAdams, the Mayor of Sitka, became the Democratic nominee; Joe Miller, an attorney and former federal magistrate, became the Republican nominee after defeating incumbent U.S. Senator Lisa Murkowski. Miller was endorsed by the Tea Party movement and former Governor Sarah Palin. Murkowski announced that despite her defeat in the primary, she would run in the general election as a write-in candidate.

The 2013 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 5, 2013. This off-year election cycle featured several special elections to the United States Congress; two gubernatorial races; state legislative elections in a few states; and numerous citizen initiatives, mayoral races, and a variety of other local offices on the ballot.

Joseph Patrick Kennedy III is an American politician and diplomat who has been the United States Special Envoy for Northern Ireland since 2022. Prior to this, Kennedy served as the U.S. representative for Massachusetts's 4th congressional district from 2013 to 2021. A member of the Democratic Party, he represented a district that extends from Boston's western suburbs to the state's South Coast. He worked as an assistant district attorney in the Cape and Islands and Middlesex County, Massachusetts, offices before his election to Congress. In January 2021, he became a CNN commentator.
The Tea Party movement, founded in 2009, is an American political movement that advocates strict adherence to the United States Constitution, reducing U.S. government spending and taxes, and reduction of the U.S. national debt and federal budget deficit.

The 2016 United States Senate election in Alaska was held on November 8, 2016, to elect a member of the United States Senate to represent the State of Alaska, concurrently with the 2016 U.S. presidential election, as well as other elections to the United States Senate in other states and elections to the United States House of Representatives and various state and local elections.

The 2020 United States Senate elections were held on November 3, 2020, with the 33 class 2 seats of the Senate contested in regular elections. Of these, 21 were held by Republicans, and 12 by Democrats. The winners were elected to 6-year terms from January 3, 2021, to January 3, 2027. Two special elections for seats held by Republicans were also held in conjunction with the general elections: one in Arizona, to fill the vacancy created by John McCain's death in 2018; and one in Georgia, following Johnny Isakson's resignation in 2019. These elections ran concurrently with the 2020 United States presidential election in which incumbent president Donald Trump lost to Democratic nominee Joe Biden.
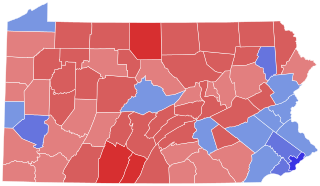
The 2018 United States Senate election in Pennsylvania took place on November 6, 2018, to elect a member of the United States Senate to represent the State of Pennsylvania, concurrently with other elections to the United States Senate, elections to the United States House of Representatives, and various state and local elections. This was one of ten Democratic-held Senate seats up for election in a state that Donald Trump won in the 2016 presidential election. The primary elections were held on May 15. Incumbent Democratic Senator Bob Casey Jr. ran for re-election to a third term. Casey, who faced no primary opposition, defeated the Republican nominee, Lou Barletta, Green Party nominee Neal Gale, and Libertarian Party nominee Dale Kerns. Casey was the first senator to be elected to a third term from Pennsylvania since Arlen Specter in 1992, and the first Pennsylvania Democrat to be popularly elected to three terms in the Senate.
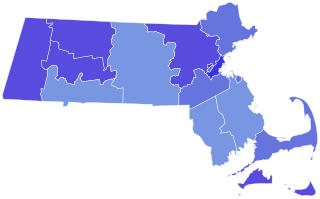
The 2020 United States Senate election in Massachusetts was held on November 3, 2020, to elect a member of the United States Senate to represent the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, concurrently with the 2020 U.S. presidential election, as well as elections to the United States Senate in other states, elections to the United States House of Representatives, and various state and local elections. On September 1, incumbent senator Ed Markey defeated U.S. Representative Joe Kennedy III in a competitive primary for the Democratic nomination, and Kevin O'Connor defeated Shiva Ayyadurai for the Republican nomination. Markey went on to win the general election with 66.2% of the vote, and was thus re-elected to a second full term in a landslide.

The 2022 United States Senate elections were held on November 8, 2022, concurrently with other midterm elections at the federal, state, and local levels. Regularly scheduled elections were held for 34 of the 100 seats in the U.S. Senate, the winners of which will serve 6-year terms beginning with the 118th United States Congress. 2 special elections were held to complete unexpired terms. While pundits considered the Republican Party a slight favorite to gain control of the Senate, the Democrats outperformed expectations and expanded the majority they had held since 2021, gaining a seat for a functioning 51–49 majority.

The 2022 United States Senate election in Alaska was held on November 8, 2022. Incumbent senator Lisa Murkowski won reelection to a fourth full term, defeating fellow Republican Kelly Tshibaka and Democrat Patricia Chesbro.

The 2024 United States presidential election in Iowa is scheduled to take place on Tuesday, November 5, 2024, as part of the 2024 United States elections in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia will participate. Iowa voters will choose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote. The state of Iowa has six electoral votes in the Electoral College, following reapportionment due to the 2020 United States census in which the state neither gained nor lost a seat.















