
The Mongol Empire invaded and conquered much of Kievan Rus' in the mid-13th century, sacking numerous cities including the largest: Kiev and Chernigov. The siege of Kiev in 1240 by the Mongols is generally held to mark the end of the state of Kievan Rus', which had already been undergoing fragmentation. Many other principalities and urban centres in the northwest and southwest escaped complete destruction or suffered little to no damage from the Mongol invasion, including Galicia–Volhynia, Novgorod, Pskov, Smolensk, Polotsk, Vitebsk, and probably Rostov and Uglich.

The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the division of the Mongol Empire after 1259, it became a functionally separate khanate. It is also known as the Kipchak Khanate or the Ulus of Jochi, and replaced the earlier, less organized Cuman–Kipchak confederation.

Yury (Georgy) Danilovich was Prince of Moscow from 1303 to 1325 and Grand Prince of Vladimir from 1318 to 1322. He contested the title of Grand Prince of Vladimir with his uncle Mikhail of Tver. As Yury's father had never held the title, he had no legitimate claim. Despite two failed campaigns by Mikhail to subdue Yury, the latter allied with the Golden Horde and married the khan's sister Konchaka, and was made grand prince after Mikhail's execution in 1318.
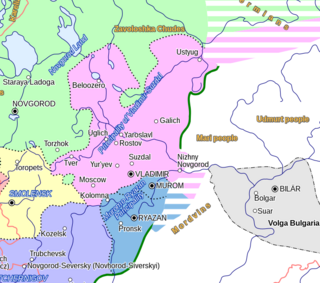
Vladimir-Suzdal, formally known as the Principality of Vladimir-Suzdal or Grand Principality of Vladimir (1157–1331), also as Suzdalia or Vladimir-Suzdalian Rus', was one of the major principalities emerging from Kievan Rus' in the late 12th century, centered in Vladimir-on-Klyazma. With time the principality grew into a grand principality divided into several smaller principalities. After being conquered by the Mongol Empire, the principality became a self-governed state headed by its own nobility. A governorship of the principality, however, was prescribed by a jarlig issued from the Golden Horde to a Rurikid sovereign.

Mikhail Yaroslavich, also known as Michael, was Prince of Tver from 1285 and Grand Prince of Vladimir from 1304 to 1314 and again from 1315 until his death in 1318. He was canonized and counted among the saints of the Russian Orthodox Church.
Yaroslav II Vsevolodovich, also transliterated as Iaroslav, was Grand Prince of Vladimir from 1238 to 1246. He collaborated with Batu Khan following the Mongol invasion, before he was ultimately poisoned.

In Russian historiography the term Upper Oka Principalities traditionally applies to about a dozen tiny and ephemeral polities situated along the upper course of the Oka River at the turn of the 14th and 15th centuries. They were reigned by the "upper princes", each of which descended from Mikhail Vsevolodovich of Chernigov. Nowadays, the areas concerned lie within the bounds of the Tula Oblast, Kaluga Oblast, Oryol Oblast and Bryansk Oblast of the Russian Federation.

The Principality of Ryazan, later known as the Grand Principality of Ryazan, was a principality from 1129 to 1521. Its capital was the city of Ryazan, now known as Old Ryazan, which was destroyed in 1237 during the Mongol invasions. The capital was moved to Pereyaslavl-Ryazansky, later renamed Ryazan.

The siege of Moscow in 1382 was a battle between the Principality of Moscow and Tokhtamysh, khan of the Golden Horde.
The Prince of Moscow, later known as the Grand Prince of Moscow, was the title of the ruler of the Principality of Moscow, initially a part of the grand principality of Vladimir-Suzdal. By the late 14th century, the grand principality was inherited by the prince of Moscow; the monarch bore the title of grand prince of Vladimir and Moscow and later the title of grand prince of Vladimir, Moscow and all Russia.
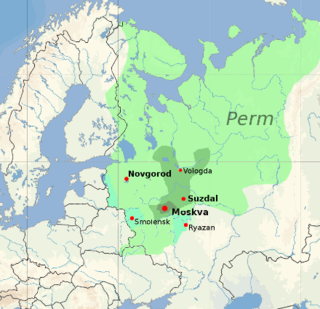
The Principality of Moscow or Grand Duchy of Moscow, also known simply as Muscovy, was a principality of the Late Middle Ages centered on Moscow. It eventually evolved into the Tsardom of Russia in the early modern period. The princes of Moscow were descendants of the first prince Daniel, referred to in modern historiography as the Daniilovichi, a branch of the Rurikids.

The Rurik dynasty, also known as the Rurikid or Riurikid dynasty, as well as simply Rurikids or Riurikids, was a noble lineage allegedly founded by the Varangian prince Rurik, who, according to tradition, established himself at Novgorod in the year 862. The Rurikids were the ruling dynasty of Kievan Rus' and its principalities following its disintegration.

Daniil Aleksandrovich, also known as Daniil of Moscow, was the youngest son of Alexander Nevsky and forefather of all Princes of Moscow. His descendants are known as the Daniilovichi.

Boris Aleksandrovich of Tver or Boris the Great was a Grand Prince of Tver from 22 April 1426 until his death.

The Battle of Kulikovo was fought between the forces of Mamai, a powerful Mongol military commander of the Golden Horde, and Russian forces led by Grand Prince Dmitry of Moscow. The battle took place on 8 September 1380, at Kulikovo Field near the Don River and was won by Dmitry, who became known as Donskoy after the battle.

The Muscovite War of Succession, or Muscovite Civil War, was a war of succession in the Grand Duchy of Moscow (Muscovy) from 1425 to 1453. The two warring parties were Vasily II, the son of the previous Grand Prince of Moscow Vasily I, and on the other hand his uncle, Yury Dmitrievich, the Prince of Zvenigorod, and the sons of Yuri Dmitrievich, Vasily Kosoy and Dmitry Shemyaka. In the intermediate stage, the party of Yury conquered Moscow, but in the end, Vasily II regained his crown.
The Prince of Vladimir, from 1186 Grand Prince of Vladimir, also translated as Grand Duke of Vladimir, was the title of the monarch of Vladimir-Suzdal. The title was passed to the prince of Moscow in 1389.

The Lithuanian–Muscovite War, known in the Rogozh Chronicle as Litovschina, encompasses three raids by Algirdas, Grand Duke of Lithuania, to the Principality of Moscow in 1368, 1370, and 1372. Algirdas organized the raids against Dmitry Donskoy in support of the Principality of Tver, chief rival of Moscow. In 1368 and 1370, Lithuanians besieged Moscow and burned the posad, but did not succeed in taking the city's Kremlin. In 1372, the Lithuanian army was stopped near Lyubutsk where, after a standoff, the Treaty of Lyubutsk was concluded. Lithuanians agreed to cease their aid to Tver, which was defeated in 1375. Mikhail II of Tver had to acknowledge Dmitry as "elder brother".

The Great Troubles, also known as the Golden Horde Dynastic War, was a war of succession in the Golden Horde from 1359 to 1381.




















