
Clupeiformes is the order of ray-finned fish that includes the herring family, Clupeidae, and the anchovy family, Engraulidae. The group includes many of the most important forage and food fish.

The ghost knifefishes are a family, Apteronotidae, of ray-finned fishes in the order Gymnotiformes. These fish are native to Panama and South America. They inhabit a wide range of freshwater habitats, but more than half the species in the family are found deep in rivers where there is little or no light.

Pristigasteridae is a family of ray-finned fish related to the herrings, including the genera Ilisha, Pellona, and Pristigaster. One common name for the taxon is longfin herring. The taxonomic classification of this family is in doubt; it was traditionally divided into two subfamilies, Pelloninae and Pristigasterinae, but molecular data indicates that these are not monophyletic.
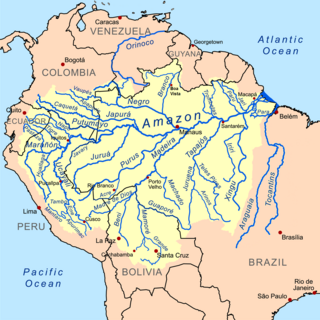
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about 7,000,000 km2 (2,700,000 sq mi), or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela, as well as the territory of French Guiana.

Glass knifefishes are fishes in the family Sternopygidae in the order Gymnotiformes. Species are also known as rattail knifefishes.

Sardinella is a genus of fish in the family Dorosomatidae found in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Ocean. They are abundant in warmer waters of the tropical and subtropical oceans. Adults are generally coastal, schooling, marine fish but juveniles are often found in lagoons and estuaries. These species are distinguished by their ranges and by specific body features, but they are often confused with one another. Fish of the genus have seven to 14 striped markings along the scales of the top of the head. The paddle-shaped supramaxilla bones are characteristic; they separate Sardinella from other genera and their shapes help distinguish species. They have paired predorsal scales and enlarged fin rays.

Brachyplatystoma is a genus of catfish from the family Pimelodidae. As the occasionally used common name goliath catfishes indicates, this genus includes some of the largest species of catfish, including the piraíba, B. filamentosum, which reaches up to 3.6 metres (12 ft) in length; though the other species don't reach this length. Brachyplatystoma are found in the Amazon and Orinoco basins, and other tropical freshwater and brackish habitats in South America. Many species are migratory. These fish are important as food fish and, to some extent, aquarium fish.

Alosa caspia is a species of alosid fish, one of the species of shad endemic to the Caspian Sea basin.

Pellona is a genus of ray-finned fishes in the family Pristigasteridae. The genus contains six species. Three of these are restricted to freshwater habitats in tropical and subtropical South America, while P. dayi and P. ditchela are found in coastal waters of the Indo-Pacific, and P. harroweri is found in coastal Atlantic waters from Panama to Brazil.

Ilisha is a genus of ray-finned fishes in the family Pristigasteridae. The genus contains 16 species. It is similar to Pellona but lacks a toothed hypo-maxilla. The genus has a worldwide distribution in tropical and subtropical coastal waters and estuaries. Some species also enter rivers, and I. amazonica and I. novacula are largely–if not entirely–restricted to tropical rivers.
Neoopisthopterus is a small genus of ray-finned fish in the family Pristigasteridae. There are currently two recognized species in this genus, both of which occur in tropical waters of the Western Hemisphere.
Odontognathus is a genus of longfin herrings in the family Pristigasteridae. Currently, three species are recognized for this genus, all of which are restricted to tropical waters of the Western Hemisphere.
Opisthopterus is a genus of longfin herring in the family Pristigasteridae. There are currently six species in this genus. They are found in Indo-Pacific.
Pliosteostoma is a monospecific genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Pristigasteridae, the longfin herrings. The only species in the genus is Pliosteostoma lutipinnis, the yellowfin herring, a species found along the Pacific coast of Central and South America between Mexico and Ecuador.

Raconda is a monospecific genus of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Pristigasteridae, the longfin herrings. The only species in the genus is Raconda russeliana, the raconda, a species found in the eastern Indian Ocean and far western Pacific Ocean.
Potamorhina is a genus of toothless characin from South America, with these currently described species:

The elongate ilisha, also known as the Chinese herring or slender shad, is a species of longfin herring native to the coastal waters and estuaries of North Indian Ocean and Northwest Pacific. It is a relatively large species, up to 45–60 centimetres (18–24 in) in total length. It is an important fishery species.

The Alosidae, or the shads, are a family of clupeiform fishes. The family currently comprises four genera worldwide, and about 32 species.

Amblygaster leiogaster, the smoothbelly sardinella, also known as blue sardine, blue sprat, bluebait, is a reef-associated marine species of sardinella in the herring family Clupeidae. It is one of the three species of genus Amblygaster. It is found in the marine waters along Indo-West Pacific regions south towards western Australia. The fish has 13 to 21 dorsal soft rays and 12 to 23 anal soft rays. It grows up to a maximum length of 23 cm. The flank is gold in fresh fish but becomes black while preservation. Belly is more rounded and scutes are not prominent. It is rather closely resemble Amblygaster clupeoides, but the latter has very few lower gill rakers than smoothbelly sardinella. The fish feeds on minute organisms like zooplankton.

Amblygaster sirm, the spotted sardinella, also known as the northern pilchard, spotted pilchard, spotted sardine, and trenched sardine, is a reef-associated marine species of sardinellas in the herring family Clupeidae.














