Steroid hormone receptors are found in the nucleus, cytosol, and also on the plasma membrane of target cells. They are generally intracellular receptors and initiate signal transduction for steroid hormones which lead to changes in gene expression over a time period of hours to days. The best studied steroid hormone receptors are members of the nuclear receptor subfamily 3 (NR3) that include receptors for estrogen and 3-ketosteroids. In addition to nuclear receptors, several G protein-coupled receptors and ion channels act as cell surface receptors for certain steroid hormones.
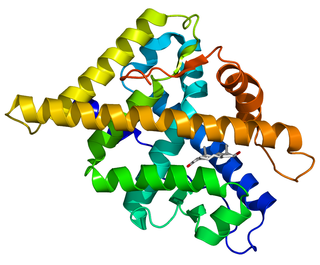
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4, is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone, in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor.

Transcription factor Sp1, also known as specificity protein 1* is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SP1 gene.

Proline-, glutamic acid- and leucine-rich protein 1 (PELP1) also known as modulator of non-genomic activity of estrogen receptor (MNAR) and transcription factor HMX3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PELP1 gene. is a transcriptional corepressor for nuclear receptors such as glucocorticoid receptors and a coactivator for estrogen receptors.

Estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), also known as NR3A1, is one of two main types of estrogen receptor, a nuclear receptor that is activated by the sex hormone estrogen. In humans, ERα is encoded by the gene ESR1.
The ERRs are orphan nuclear receptors, meaning the identity of their endogenous ligand has yet to be unambiguously determined. They are named because of sequence homology with estrogen receptors, but do not appear to bind estrogens or other tested steroid hormones.

Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HDAC1 gene.

The small heterodimer partner (SHP) also known as NR0B2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR0B2 gene. SHP is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors. SHP is unusual for a nuclear receptor in that it lacks a DNA binding domain. Therefore, it is technically neither a transcription factor nor nuclear receptor but nevertheless it is still classified as such due to relatively high sequence homology with other nuclear receptor family members.
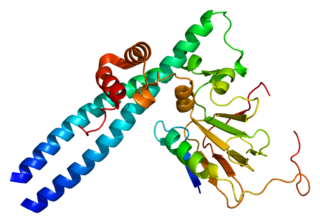
Transcription factor E2F1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the E2F1 gene.

Nuclear receptor-interacting protein 1 (NRIP1) also known as receptor-interacting protein 140 (RIP140) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NRIP1 gene.

Proliferation-associated protein 2G4 (PA2G4) also known as ErbB3-binding protein 1 (EBP1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PA2G4 gene.

Estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRα), also known as NR3B1, is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the ESRRA gene. ERRα was originally cloned by DNA sequence homology to the estrogen receptor alpha, but subsequent ligand binding and reporter-gene transfection experiments demonstrated that estrogens did not regulate ERRα. Currently, ERRα is considered an orphan nuclear receptor.

The testicular receptor 2 (TR2) also known as NR2C1 is protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2C1 gene. TR2 is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors.

Testicular receptor 4 also known as NR2C2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2C2 gene.

Retinoblastoma-like 1 (p107), also known as RBL1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBL1 gene.

E3 SUMO-protein ligase PIAS3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PIAS3 gene.

Prohibitin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PHB2 gene.

Forkhead box protein A1 (FOXA1), also known as hepatocyte nuclear factor 3-alpha (HNF-3A), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXA1 gene.

The retinoblastoma protein is a tumor suppressor protein that is dysfunctional in several major cancers. One function of pRb is to prevent excessive cell growth by inhibiting cell cycle progression until a cell is ready to divide. When the cell is ready to divide, pRb is phosphorylated, inactivating it, and the cell cycle is allowed to progress. It is also a recruiter of several chromatin remodeling enzymes such as methylases and acetylases.

Steroid Receptor Associated and Regulated Protein (SRARP) in humans is a protein encoded by a gene of the same name with two exons that is located on chromosome 1p36.13. SRARP contains 169 amino acids and has a molecular weight of 17,657 Da.



















