
An endosymbiont or endobiont is an organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism. Typically the two organisms are in a mutualistic relationship. Examples are nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which live in the root nodules of legumes, single-cell algae inside reef-building corals and bacterial endosymbionts that provide essential nutrients to insects.

The heterotrichs are a class of ciliates. They typically have a prominent adoral zone of membranelles circling the mouth, used in locomotion and feeding, and shorter cilia on the rest of the body. Many species are highly contractile, and are typically compressed or conical in form. These include some of the largest protozoa, such as Stentor and Spirostomum, as well as many brightly pigmented forms, such as certain Blepharisma.

The green sulfur bacteria are a phylum, Chlorobiota, of obligately anaerobic photoautotrophic bacteria that metabolize sulfur.

A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and eukaryotic organisms. Most prokaryotes are unicellular and are classified into bacteria and archaea. Many eukaryotes are multicellular, but some are unicellular such as protozoa, unicellular algae, and unicellular fungi. Unicellular organisms are thought to be the oldest form of life, with early protocells possibly emerging 3.5–4.1 billion years ago.

Riftia pachyptila, commonly known as the giant tube worm and less commonly known as the giant beardworm, is a marine invertebrate in the phylum Annelida related to tube worms commonly found in the intertidal and pelagic zones. R. pachyptila lives on the floor of the Pacific Ocean near hydrothermal vents. The vents provide a natural ambient temperature in their environment ranging from 2 to 30 °C, and this organism can tolerate extremely high hydrogen sulfide levels. These worms can reach a length of 3 m, and their tubular bodies have a diameter of 4 cm (1.6 in).
The purple sulfur bacteria (PSB) are part of a group of Pseudomonadota capable of photosynthesis, collectively referred to as purple bacteria. They are anaerobic or microaerophilic, and are often found in stratified water environments including hot springs, stagnant water bodies, as well as microbial mats in intertidal zones. Unlike plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, purple sulfur bacteria do not use water as their reducing agent, and therefore do not produce oxygen. Instead, they can use sulfur in the form of sulfide, or thiosulfate (as well, some species can use H2, Fe2+, or NO2−) as the electron donor in their photosynthetic pathways. The sulfur is oxidized to produce granules of elemental sulfur. This, in turn, may be oxidized to form sulfuric acid.

Purple bacteria or purple photosynthetic bacteria are Gram-negative proteobacteria that are phototrophic, capable of producing their own food via photosynthesis. They are pigmented with bacteriochlorophyll a or b, together with various carotenoids, which give them colours ranging between purple, red, brown, and orange. They may be divided into two groups – purple sulfur bacteria and purple non-sulfur bacteria. Purple bacteria are anoxygenic phototrophs widely spread in nature, but especially in aquatic environments, where there are anoxic conditions that favor the synthesis of their pigments.

Gammaproteobacteria is a class of bacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota. It contains about 250 genera, which makes it the most genus-rich taxon of the Prokaryotes. Several medically, ecologically, and scientifically important groups of bacteria belong to this class. All members of this class are Gram-negative. It is the most phylogenetically and physiologically diverse class of the Pseudomonadota.

Paulinella is a genus of at least eleven species including both freshwater and marine amoeboids. Like many members of euglyphids it is covered by rows of siliceous scales, and use filose pseudopods to crawl over the substrate of the benthic zone.

A soda lake or alkaline lake is a lake on the strongly alkaline side of neutrality, typically with a pH value between 9 and 12. They are characterized by high concentrations of carbonate salts, typically sodium carbonate, giving rise to their alkalinity. In addition, many soda lakes also contain high concentrations of sodium chloride and other dissolved salts, making them saline or hypersaline lakes as well. High pH and salinity often coincide, because of how soda lakes develop. The resulting hypersaline and highly alkalic soda lakes are considered some of the most extreme aquatic environments on Earth.
A mixotroph is an organism that uses a mix of different sources of energy and carbon, instead of having a single trophic mode, on the continuum from complete autotrophy to complete heterotrophy. It is estimated that mixotrophs comprise more than half of all microscopic plankton. There are two types of eukaryotic mixotrophs. There are those with their own chloroplasts - including those with endosymbionts providing the chloroplasts. And there are those that acquire them through kleptoplasty, or through symbiotic associations with prey, or through 'enslavement' of the prey's organelles.

Marine microorganisms are defined by their habitat as microorganisms living in a marine environment, that is, in the saltwater of a sea or ocean or the brackish water of a coastal estuary. A microorganism is any microscopic living organism or virus, which is invisibly small to the unaided human eye without magnification. Microorganisms are very diverse. They can be single-celled or multicellular and include bacteria, archaea, viruses, and most protozoa, as well as some fungi, algae, and animals, such as rotifers and copepods. Many macroscopic animals and plants have microscopic juvenile stages. Some microbiologists also classify viruses as microorganisms, but others consider these as non-living.
Soil microbiology is the study of microorganisms in soil, their functions, and how they affect soil properties. It is believed that between two and four billion years ago, the first ancient bacteria and microorganisms came about on Earth's oceans. These bacteria could fix nitrogen, in time multiplied, and as a result released oxygen into the atmosphere. This led to more advanced microorganisms, which are important because they affect soil structure and fertility. Soil microorganisms can be classified as bacteria, actinomycetes, fungi, algae and protozoa. Each of these groups has characteristics that define them and their functions in soil.
Rhodovulum sulfidophilum is a gram-negative purple nonsulfur bacteria. The cells are rod-shaped, and range in size from 0.6 to 0.9 μm wide and 0.9 to 2.0 μm long, and have a polar flagella. These cells reproduce asexually by binary fission. This bacterium can grow anaerobically when light is present, or aerobically (chemoheterotrophic) under dark conditions. It contains the photosynthetic pigments bacteriochlorophyll a and of carotenoids.
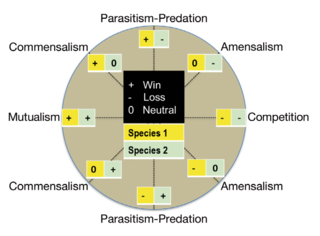
Microbial symbiosis in marine animals was not discovered until 1981. In the time following, symbiotic relationships between marine invertebrates and chemoautotrophic bacteria have been found in a variety of ecosystems, ranging from shallow coastal waters to deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Symbiosis is a way for marine organisms to find creative ways to survive in a very dynamic environment. They are different in relation to how dependent the organisms are on each other or how they are associated. It is also considered a selective force behind evolution in some scientific aspects. The symbiotic relationships of organisms has the ability to change behavior, morphology and metabolic pathways. With increased recognition and research, new terminology also arises, such as holobiont, which the relationship between a host and its symbionts as one grouping. Many scientists will look at the hologenome, which is the combined genetic information of the host and its symbionts. These terms are more commonly used to describe microbial symbionts.

All animals on Earth form associations with microorganisms, including protists, bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses. In the ocean, animal–microbial relationships were historically explored in single host–symbiont systems. However, new explorations into the diversity of marine microorganisms associating with diverse marine animal hosts is moving the field into studies that address interactions between the animal host and a more multi-member microbiome. The potential for microbiomes to influence the health, physiology, behavior, and ecology of marine animals could alter current understandings of how marine animals adapt to change, and especially the growing climate-related and anthropogenic-induced changes already impacting the ocean environment.

Marine prokaryotes are marine bacteria and marine archaea. They are defined by their habitat as prokaryotes that live in marine environments, that is, in the saltwater of seas or oceans or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. All cellular life forms can be divided into prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed within membranes, whereas prokaryotes are the organisms that do not have a nucleus enclosed within a membrane. The three-domain system of classifying life adds another division: the prokaryotes are divided into two domains of life, the microscopic bacteria and the microscopic archaea, while everything else, the eukaryotes, become the third domain.
Thiodictyon is a genus of gram-negative bacterium classified within purple sulfur bacteria (PSB).
Hydrogen sulfide chemosynthesis is a form of chemosynthesis which uses hydrogen sulfide. It is common in hydrothermal vent microbial communities Due to the lack of light in these environments this is predominant over photosynthesis
Blepharismidae is a family of unicellular ciliate protists found in fresh and salt water. Two genera are recognized: Blepharisma, which contains some model organisms, and Pseudoblepharisma













