
Botrytis cinerea is a necrotrophic fungus that affects many plant species, although its most notable hosts may be wine grapes. In viticulture, it is commonly known as "botrytis bunch rot"; in horticulture, it is usually called "grey mould" or "gray mold".
Blight refers to a specific symptom affecting plants in response to infection by a pathogenic organism.

Black sigatoka is a leaf-spot disease of banana plants caused by the ascomycete fungus Mycosphaerella fijiensis (Morelet), also known as black leaf streak. It was discovered in 1963 and named for its similarities with yellow Sigatoka, which is caused by Mycosphaerella musicola (Mulder), which was itself named after the Sigatoka Valley in Fiji. In the same valley an outbreak of this disease reached epidemic proportions from 1912 to 1923.

Fusarium wilt is a common vascular wilt fungal disease, exhibiting symptoms similar to Verticillium wilt. This disease has been investigated extensively since the early years of this century. The pathogen that causes Fusarium wilt is Fusarium oxysporum. The species is further divided into formae speciales based on host plant.

Phomopsis cane and leaf spot occurs wherever grapes are grown. Phomopsis cane and leaf spot is more severe in grape-growing regions characterized by a humid temperate climate through the growing season. Crop losses up to 30% have been reported to be caused by Phomopsis cane and leaf spot.

Pseudomonas cichorii is a Gram-negative soil bacterium that is pathogenic to plants. It has a wide host range, and can have an important economical impact on lettuce, celery and chrysanthemum crops. P. cichorii was first isolated on endives, from which it derives its name. It produces 6-aminopenicillanic acid. Based on 16S rRNA analysis, P. cichorii has been placed in the P. syringae group.
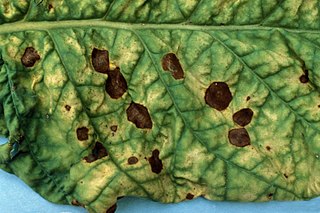
Alternaria alternata is a fungus causing leaf spots, rots, and blights on many plant parts, and other diseases. It is an opportunistic pathogen on over 380 host species of plant.

Pseudocercosporella capsellae is a plant pathogen infecting crucifers. P. capsellae is the causal pathogen of white leaf spot disease, which is an economically significant disease in global agriculture. P. capsellae has a significant affect on crop yields on agricultural products, such as canola seed and rapeseed. Researchers are working hard to find effective methods of controlling this plant pathogen, using cultural control, genetic resistance, and chemical control practices. Due to its rapidly changing genome, P. capsellae is a rapidly emerging plant pathogen that is beginning to spread globally and affect farmers around the world.
Alternaria japonica is a fungal plant pathogen. It is a cause of black spot disease in cruciferous plants. It is not a major source of crop loss, but is considered dangerous for plants during the seedling stage.

Sclerotinia sclerotiorum is a plant pathogenic fungus and can cause a disease called white mold if conditions are conducive. S. sclerotiorum can also be known as cottony rot, watery soft rot, stem rot, drop, crown rot and blossom blight. A key characteristic of this pathogen is its ability to produce black resting structures known as sclerotia and white fuzzy growths of mycelium on the plant it infects. These sclerotia give rise to a fruiting body in the spring that produces spores in a sac which is why fungi in this class are called sac fungi (Ascomycota). This pathogen can occur on many continents and has a wide host range of plants. When S. sclerotiorum is onset in the field by favorable environmental conditions, losses can be great and control measures should be considered.
Pseudopestalotiopsis theae is a plant pathogen affecting tea.

Corynespora cassiicola is a species of fungus well known as a plant pathogen. It is a sac fungus in the family Corynesporascaceae. It is the type species of the genus Corynespora.
Cercospora arachidicola is a fungal ascomycete plant pathogen that causes early leaf spot of peanut. Peanuts originated in South America and are cultivated globally in warm, temperate and tropical regions.
Pseudocercospora cannabina is a fungal plant pathogen infecting hemp. Cercospora cannabina was originally found on the leaves of Cannabis sativa in Uganda. Then in 1976, it was renamed as Pseudocercospora cannabina by mycologist Frederick Claude Deighton (1903-1992).

Pseudocercospora subsessilis is a fungal plant pathogen infecting chinaberry tree. It is widespread in tropical and subtropical areas on host species of the genera Azadirachta and Swietenia.

Alternaria solani is a fungal pathogen that produces a disease in tomato and potato plants called early blight. The pathogen produces distinctive "bullseye" patterned leaf spots and can also cause stem lesions and fruit rot on tomato and tuber blight on potato. Despite the name "early," foliar symptoms usually occur on older leaves. If uncontrolled, early blight can cause significant yield reductions. Primary methods of controlling this disease include preventing long periods of wetness on leaf surfaces and applying fungicides. Early blight can also be caused by Alternaria tomatophila, which is more virulent on stems and leaves of tomato plants than Alternaria solani.
Mycosphaerella musicola is a fungal plant pathogen, which is the causal agent of Yellow Sigatoka leaf spot disease on banana plants.

Boxwood blight is a widespread fungal disease affecting boxwoods, caused by Cylindrocladium buxicola. The disease causes widespread leaf loss and eventual death.
Septoria musiva, correct taxonomic name: Sphaerulina musiva, is an ascomycete fungus responsible of a leaf spot and canker disease on poplar trees. It is native on the eastern cottonwood poplar Populus deltoides, causing only a leaf spot symptom. On susceptible hybrid poplars, S. musiva causes necrotic lesions on the leaves which lead to premature defoliation, and cankers on the stem and branches which can reduce growth, predispose the tree to colonisation by secondary organisms, and cause stem breakage.
Epicoccum sorghinum is an ascomycete fungus with known plant pathogenicity to sugarcane and rice, causing ring spot disease and leaf spot disease. This fungus is primarily known for its production of tenuazonic acid, which leads to complications with growth and causes the symptoms of leaf spot disease. Tenuazonic acid not only affects plant growth, but has recently been proven to impact human health due to its prevalence in food and beverages. It is widely dispersed, affecting multiple hosts in different countries. Although not a serious threat, Epicoccum sorghinum has been known to influence the sorghum grain-mold complex in ways which reduce crop yields, seed viability, and kernel weight. As a result of continuous phylogenetic and morphological discoveries relevant to Epicoccum sorghinum, this fungus has undergone a number of name changes.











